Problem 2 Figures on page 3 show the partial framing plan and elevations of a three story steel structure. The floor dead load is 60 psf and the floor live load is 80 psf. The roof dead load is 20 psf and the roof live load is 10 psf. Assume that the stair load is the same as the floor load. Using the LRFD load combinations, find the: Ultimate loading for the beams B-1 through B-9, located on the second level. Ultimate loading for the beams RB-1 through RB-9, located on the roof. Ultimate loading for the girders G-3 through G-5, located on the second level. Ultimate loading for the girders RG-3 through RG-5, located on the roof. Ultimate loading for the columns G-1 through G-3, H-1, and H-2 between the first and second levels. Compare the loading in columns G-3, H-1, and H-2 by adding up the loads transferred to them from the beams and the girders they sunnort and the tributary areas. (a) (b) (d) (e)
Problem 2 Figures on page 3 show the partial framing plan and elevations of a three story steel structure. The floor dead load is 60 psf and the floor live load is 80 psf. The roof dead load is 20 psf and the roof live load is 10 psf. Assume that the stair load is the same as the floor load. Using the LRFD load combinations, find the: Ultimate loading for the beams B-1 through B-9, located on the second level. Ultimate loading for the beams RB-1 through RB-9, located on the roof. Ultimate loading for the girders G-3 through G-5, located on the second level. Ultimate loading for the girders RG-3 through RG-5, located on the roof. Ultimate loading for the columns G-1 through G-3, H-1, and H-2 between the first and second levels. Compare the loading in columns G-3, H-1, and H-2 by adding up the loads transferred to them from the beams and the girders they sunnort and the tributary areas. (a) (b) (d) (e)
Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course List)
7th Edition
ISBN:9781285165738
Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. Madsen
Publisher:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. Madsen
Chapter31: Determining Beam Sizes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 31.3P: If the soil-bearing pressure is 1500 psf and the concrete has a strength of 2500 psi, what size pier...
Related questions
Question
100%

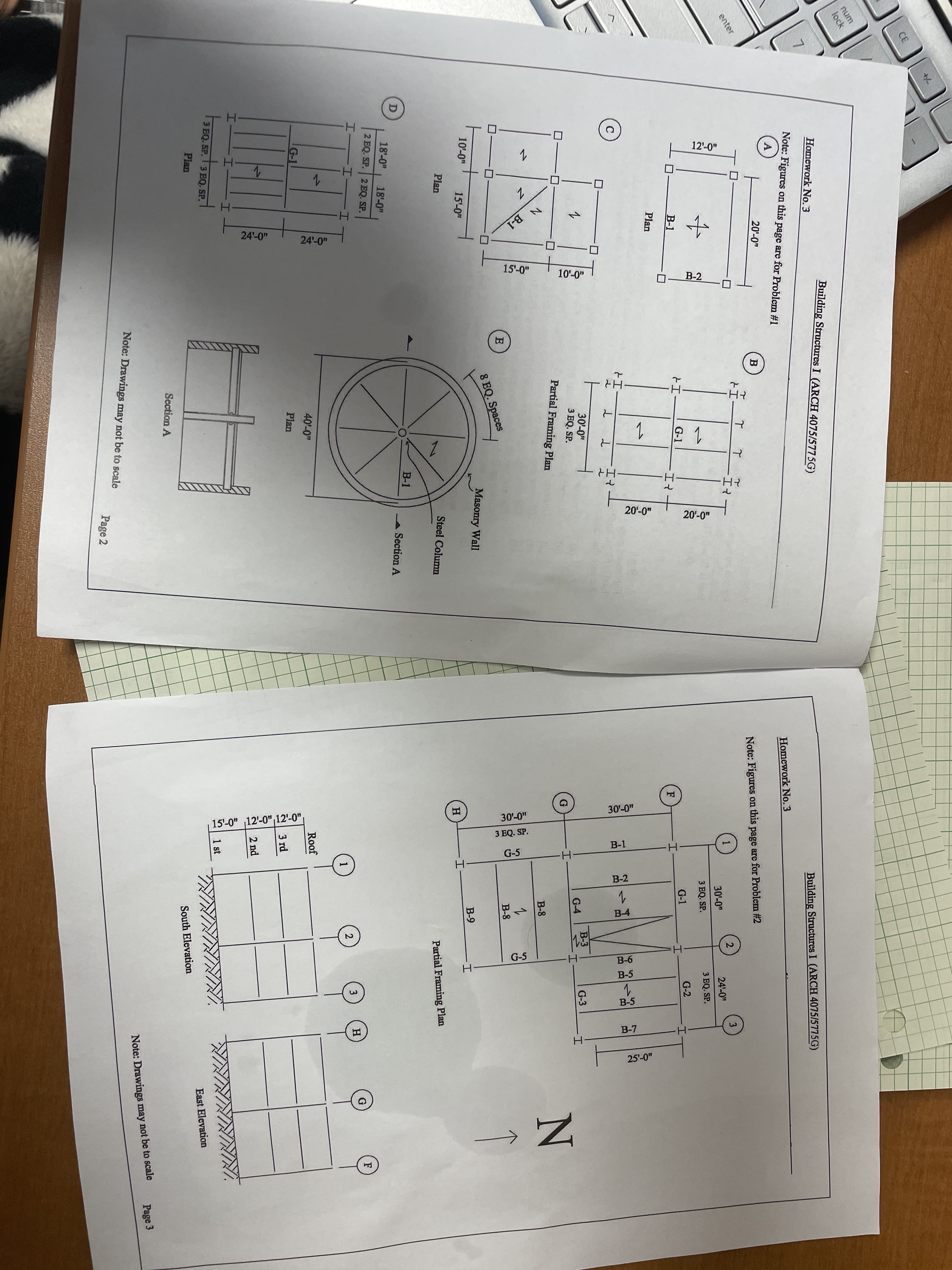
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 1
Figures on page 2 show the floor framing plans of steel buildings, which are made with 3.5" thick concrete
slabs. The mechanical and electrical systems weigh 5 psf, the steelworks weigh 7.5 psf, and the floor live
load is 50 psf. The unit weight of concrete is 150 pcf. For cases A through E:
Find the ultimate loading on only the beams or girders marked in the drawings
using the LRFD load combination.
(a)
Find the maximum moments and shears for these members.
Problem 2
Figures on page 3 show the partial framing plan and elevations of a three story steel structure. The floor dead
load is 60 psf and the floor live load is 80 psf. The roof dead load is 20 psf and the roof live load is 10 psf.
Assume that the stair load is the same as the floor load. Using the LRFD load combinations, find the:
Ultimate loading for the beams B-1 through B-9, located on the second level.
(8)
Ultimate loading for the beams RB-1 through RB-9, located on the roof.
(a)
Ultimate loading for the girders G-3 through G-5, located on the second level.
()
Ultimate loading for the girders RG-3 through RG-5, located on the roof.
Ultimate loading for the columns G-1 through G-3, H-1, and H-2 between the
(e)
first and second levels. Compare the loading in columns G-3, H-1, and H-2 by
adding up the loads transferred to them from the beams and the girders they
support, and the tributary areas.
Maximum shear and moments for the beams B-2, B-4, G-3, and G-4, on the
second level. (The loading has already been found in part a, and c from
above.)
Pag
Transcribed Image Text:CE
num
lock
Building Structures I (ARCH 4075/5775G)
Homework No. 3
7
Note: Figures on this page are for Problem #1
Building Structures I (ARCH 4075/5775G)
A
Homework No.3
20'-0"
B
enter
Note: Figures on this page are for Problem #2
3.
30'-0"
24'-0"
3 EQ. SP.
3 EQ. SP.
В-1
G-1
G-1
G-2
Plan
F
C
30'-0"
3 EQ. SP.
Partial Framing Plan
B-3
G-4
G-3
I-
B-8
E
B-8
8 EQ. Spaces
10'-0"
Masonry Wall
15-0"
B-9
Plan
Steel Column
Partial Framing Plan
B-1
18'-0"
Section A
18'-0"
2 EQ. SP. 2 EQ. SP.
I.
2
3
H
1
40'-0"
G-1
Roof
Plan
3 rd
HI
2 nd
3 EQ. SP. I 3 EQ. SP.
Plan
1 st
Section A
East Elevation
South Elevation
Note: Drawings may not be to scale
Page 3
Note: Drawings may not be to scale
Page 2
12'-0"
N B-1
24'-0"
24-0"
15'-0"
10'-0"
B-2
-H-
| 15'-0" 12'-0",12'-0",
3 EQ. SP.
B-1
G-5
B-2
B-4
G-5
B-6
B-5
B-5
B-7
25'-0"
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781285165738
Author:
Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. Madsen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781285165738
Author:
Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. Madsen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning