Problem 2 Let (,,P) be a probability space. (1) For measurable events A,B,CE A with P(C) >0 and P(BnC) > 0, show that P(AnBnC)=P(A | BOC) P(B | C)P(C). (2) Let A be a measurable event and let B₁,...,B, EA as well as C₁,...,Cm E A be partitions of the sample space 2, i.e. B, nB, = Ø for i #j; CnCe = for k‡ l; and Show that n m Q=UB₁=UC₁. j=1
Problem 2 Let (,,P) be a probability space. (1) For measurable events A,B,CE A with P(C) >0 and P(BnC) > 0, show that P(AnBnC)=P(A | BOC) P(B | C)P(C). (2) Let A be a measurable event and let B₁,...,B, EA as well as C₁,...,Cm E A be partitions of the sample space 2, i.e. B, nB, = Ø for i #j; CnCe = for k‡ l; and Show that n m Q=UB₁=UC₁. j=1
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 29E
Related questions
Question
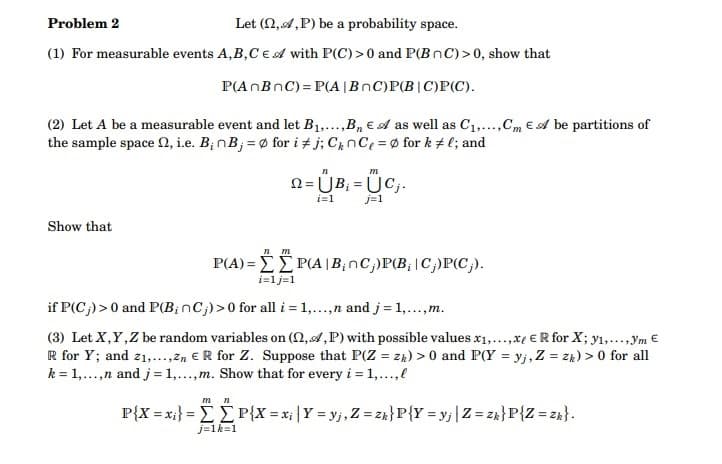
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 2
Let (,,P) be a probability space.
(1) For measurable events A,B,CE A with P(C) >0 and P(BnC)>0, show that
P(AnBnC)=P(A | BnC)P(B|C)P(C).
(2) Let A be a measurable event and let B₁,...,B₁ € A as well as C₁,...,Cm E A be partitions of
the sample space , i.e. B; nB;= for i #j; CnCe = fork #l; and
Show that
n m
P(A)=P(A|B₂nC;)P(B, C;)P(C;).
m n
n
m
Q=ÜB₁ =ÜC₁.
i=1
j=1
i=1j=1
if P(C;) >0 and P(B; nC;) >0 for all i = 1,...,n and j = 1,..., m.
(3) Let X, Y, Z be random variables on (n,A,P) with possible values x₁,...,xe ER for X; y₁,...,ym €
R for Y; and 2₁,...,Zn ER for Z. Suppose that P(Z = zh) >0 and P(Y = yj, Z = zk) > 0 for all
k = 1,...,n and j = 1,...,m. Show that for every i = 1,...,.
j=1k=1
P{X = xi} = [[P{X=xi | Y=yj, Z = zh} P {Y=yj | Z = zk} P {Z = zk}.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning