Problem 5 Trace the following program. This tracing include all the variable values. |/ Using the unary scope resolution operator #include using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::ios; #include using std::setprecision; using std::setiosflags; using std::setw; const double PI = int main() 3.14159265358979; const float PI = static_cast< float >(::PI); cout << setprecision(20) Local float value of PI = " << PI << "\nGlobal double value of PI = " << ::PI << end%3; << cout << setw(28) << "Local float value of PI =" << setiosflags (ios::fixed | 1os::showpoint) << setprecision(10) << PI <« endl; system("pause"); return 0; // setiosflags(ios:fixed) : never use scientific notation // setiosflags( 1os:showpoint ) : controls if the trailing zeros and decimal point will be output (default is no) // setprecision( digits): if fixed or scientific format is selected, controls the number of digits after thc decimal place, otherwise controls the total number of significant digits // setw( width) gives a minimum width for the next output operation
Problem 5 Trace the following program. This tracing include all the variable values. |/ Using the unary scope resolution operator #include using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::ios; #include using std::setprecision; using std::setiosflags; using std::setw; const double PI = int main() 3.14159265358979; const float PI = static_cast< float >(::PI); cout << setprecision(20) Local float value of PI = " << PI << "\nGlobal double value of PI = " << ::PI << end%3; << cout << setw(28) << "Local float value of PI =" << setiosflags (ios::fixed | 1os::showpoint) << setprecision(10) << PI <« endl; system("pause"); return 0; // setiosflags(ios:fixed) : never use scientific notation // setiosflags( 1os:showpoint ) : controls if the trailing zeros and decimal point will be output (default is no) // setprecision( digits): if fixed or scientific format is selected, controls the number of digits after thc decimal place, otherwise controls the total number of significant digits // setw( width) gives a minimum width for the next output operation
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Chapter1: Computer Networks And The Internet
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem R1RQ: What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end...
Related questions
Question
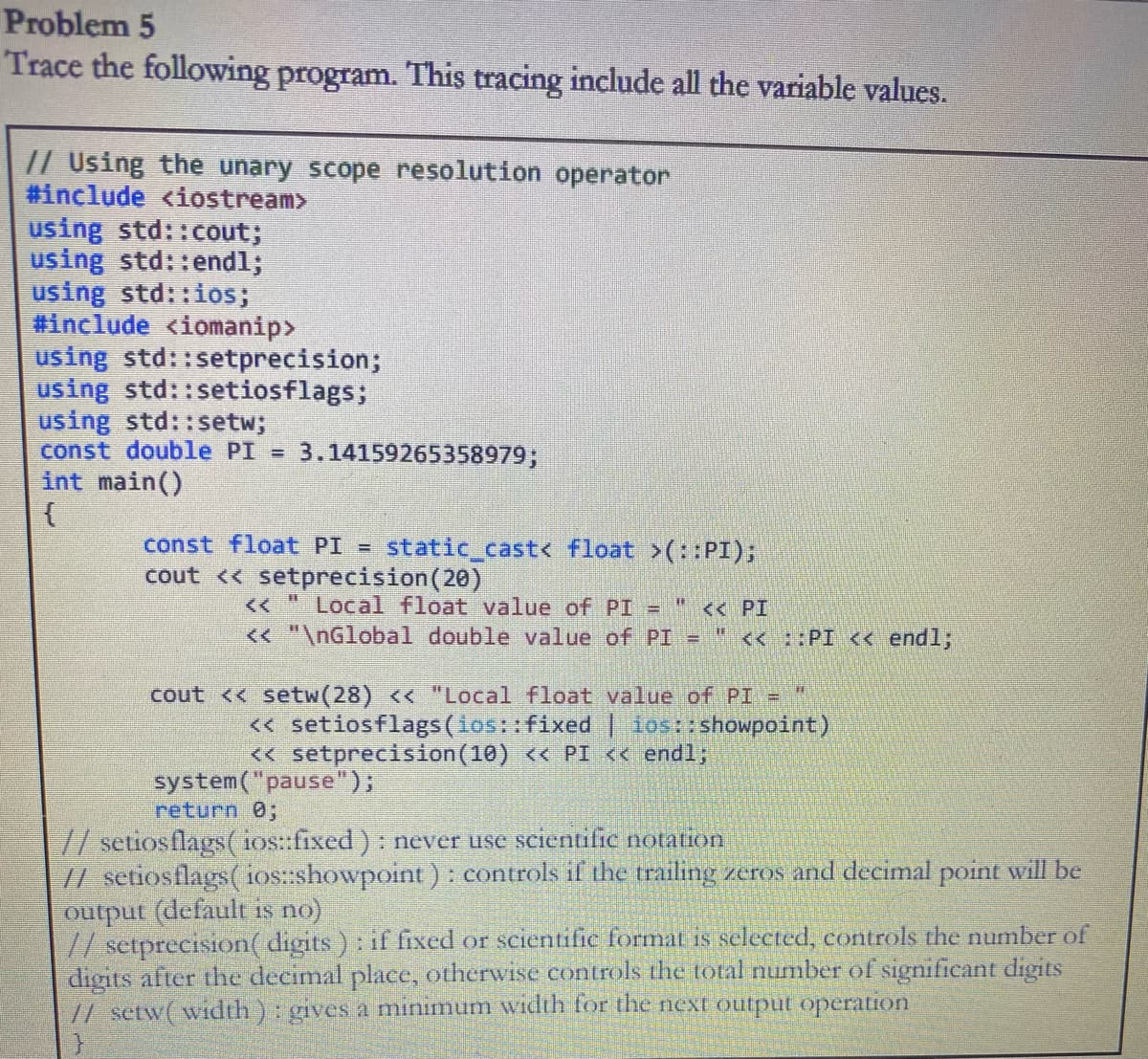
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 5
Trace the following program. This tracing include all the variable values.
// Using the unary scope resolution operator
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::ios;
#include <iomanip>
using std::setprecision;
using std::setiosflags;
using std::setw;
const double PI =
int main()
3.14159265358979;
const float PI =
static cast< float >(::PI);
cout << setprecision(20)
<< "Local float value of PI = " << PI
<< "\nGlobal double value of PI ="<<:PI << endl;
cout << setw(28) << "Local float value of PI = "
« setiosflags(1os::fixed| lostshowpoint)
<< setprecision(10) << PI << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
/ setiosflags( ios:fixed) : never use scientific notation
// setiosflags( 1os:showpoint ) : controls if the trailing zeros and decimal point will be
output (default is no)
// setprecision( digits) : if fixed or scientific format is selected, controls the number of
digits after the decimal place, otherwise controls the total number of significant digits
// setw( width) gives a minimum width for the next output operation
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093422
Author:
Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133750423
Author:
VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:
Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781119368830
Author:
FITZGERALD
Publisher:
WILEY