Problem Set question: A particle moves according to the position function s (t) = et sin (6t). %3D Enclose arguments of functions in parentheses. For example, sin (2t). (a) Find the velocity function.
Problem Set question: A particle moves according to the position function s (t) = et sin (6t). %3D Enclose arguments of functions in parentheses. For example, sin (2t). (a) Find the velocity function.
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter2: Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 30P: In this problem you are asked to find a function that models in real life situation and then use the...
Related questions
Question
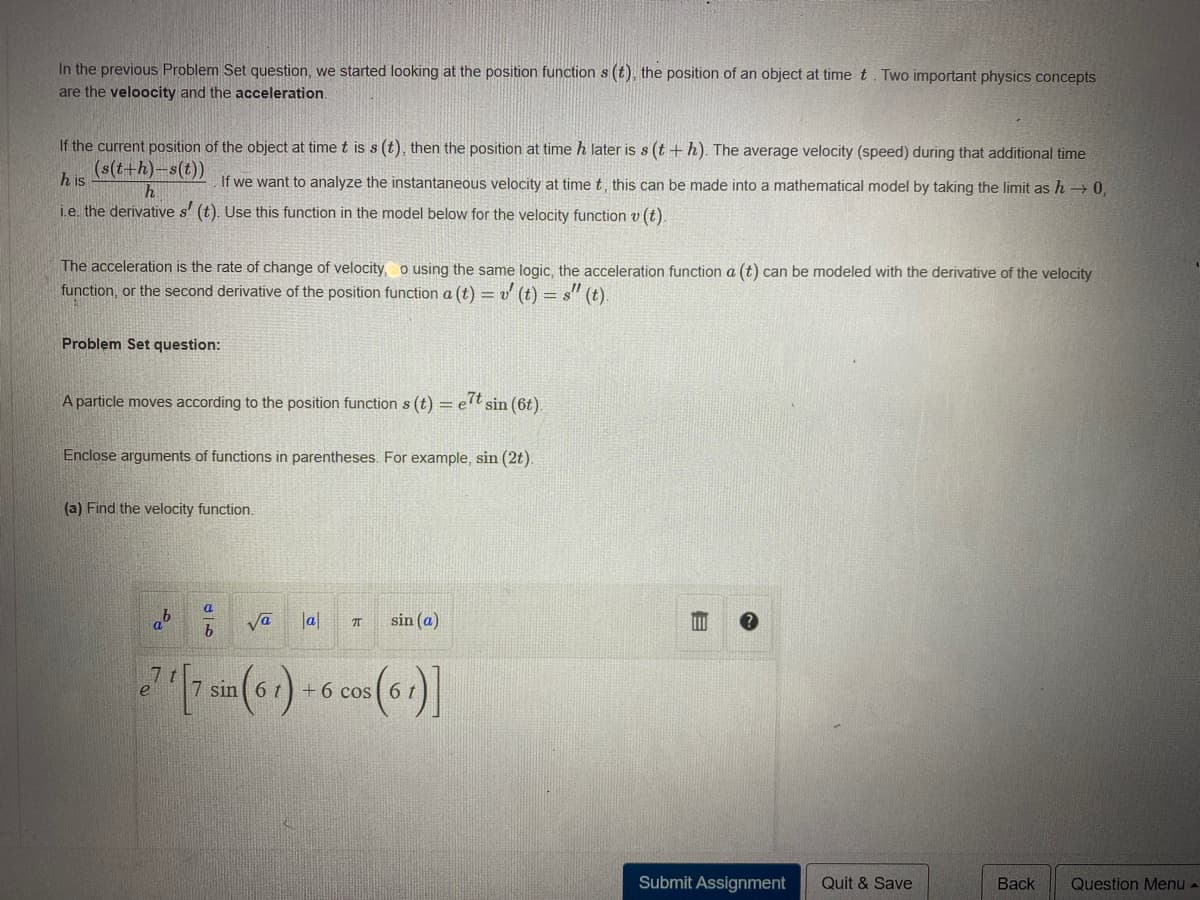
Transcribed Image Text:In the previous Problem Set question, we started looking at the position function s (t), the position of an object at time t. Two important physics concepts
are the veloocity and the acceleration.
If the current position of the object at time t is s (t), then the position at time h later is s (t +h). The average velocity (speed) during that additional time
(s(t+h)-s(t))
h is
If we want to analyze the instantaneous velocity at time t, this can be made into a mathematical model by taking the limit as h → 0,
h
i.e. the derivative s' (t). Use this function in the model below for the velocity function v (t).
The acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, o using the same logic, the acceleration function a (t) can be modeled with the derivative of the velocity
function, or the second derivative of the position function a (t) = v (t) = s" (t)
Problem Set question:
A particle moves according to the position function s (t) = e" sin
Enclose arguments of functions in parentheses. For example, sin (2t)
(a) Find the velocity function.
a
Va
Ja|
sin (a)
7 sin ( 6 t
+6 cos 6
Submit Assignment
Quit & Save
Вack
Question Menu -
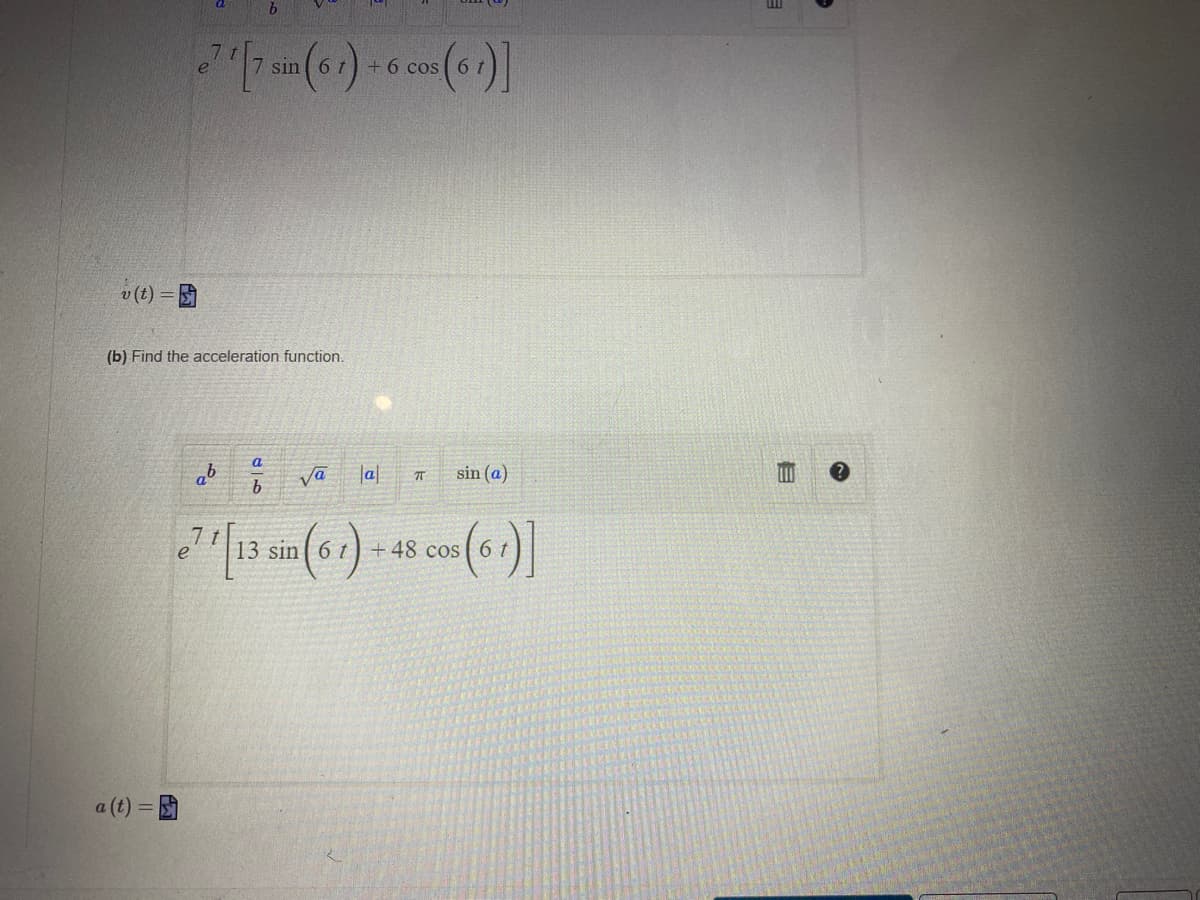
Transcribed Image Text:7 sın
6 t
+ 6 cos ( 6
v (t) =
(b) Find the acceleration function.
la|
sin (a)
b
7 t
e
13 sin 6 t) +48 cos 6 t
a (t) =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning