Prove that the given proposition is logically equivalent to False. Apply appropriate laws of equivalences for proving. Provide handwritten solution following the table format provided. Upload a clear copy of the image, file should only be an image type or pdf. 1. (p → q)A -g) Ap= False Resulting propositions Applied Law of Equivalence You can refer to this example: Prove that -(p v-p Aql) = -p A-g Resulting propositions Applied Law of Equivalence by the De Morgan's law -p A--p) v-g) by the De Morgan's low by the double negation law -p A(p v-a) (-p Ap) vl-pA-a) by the distributive law by the negation law, becouse p Ap = F FV(-p1-a) by the commutative law by the identity law -p A-9 Use the following tables as references for the equivalences. TABLE 6 Logical Equivalences. Equivalence Name PAT=P Identity laws TABLE 8 Logical TABLE 7 Logical Equivalences
Prove that the given proposition is logically equivalent to False. Apply appropriate laws of equivalences for proving. Provide handwritten solution following the table format provided. Upload a clear copy of the image, file should only be an image type or pdf. 1. (p → q)A -g) Ap= False Resulting propositions Applied Law of Equivalence You can refer to this example: Prove that -(p v-p Aql) = -p A-g Resulting propositions Applied Law of Equivalence by the De Morgan's law -p A--p) v-g) by the De Morgan's low by the double negation law -p A(p v-a) (-p Ap) vl-pA-a) by the distributive law by the negation law, becouse p Ap = F FV(-p1-a) by the commutative law by the identity law -p A-9 Use the following tables as references for the equivalences. TABLE 6 Logical Equivalences. Equivalence Name PAT=P Identity laws TABLE 8 Logical TABLE 7 Logical Equivalences
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
ChapterP: Preliminary Concepts
SectionP.CT: Test
Problem 10CT: Statement P and Q are true while R is a false statement. Classify as true or false:...
Related questions
Question
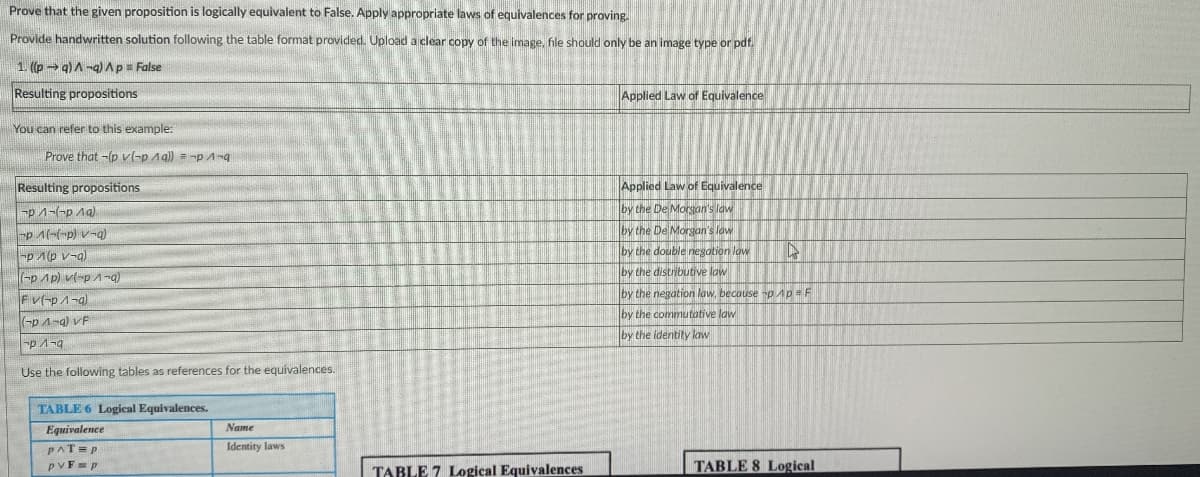
Transcribed Image Text:Prove that the given proposition is logically equivalent to False. Apply appropriate laws of equivalences for proving.
Provide handwritten solution following the table format provided. Upload a clear copy of the image, file should only be an image type or pdf.
1. ((p 9)A-q) Ap = False
Resulting propositions
Applied Law of Equivalence
You can refer to this example:
Prove that -(p v(-p 1g)) = -p A-q
Resulting propositions
Applied Law of Equivalence
by the De Morgan's law
by the De Morgan's law
by the double niegation law
-p 1-(-p Ag)
-p A(-(-p) v-q)
-p A(p v-g)
(-pAp) vl-p -a)
by the distributive law
by the negation law, because -pAp = F
Fv(-p1-g)
by the commutative law
(-p A-a) vF
-p 1-9
by the identity law
Use the following tables as references for the equivalences.
TABLE 6 Logical Equivalences.
Equivalence
PAT= P
Name
Identity laws
PVF= p
TABLE 7 Logical Equivalences
TABLE 8 Logical

Transcribed Image Text:PV (q Ar) = (Pv q)A (p vr)
Distributive laws
PA(q vr) = (p ^ q) v (par)
(p r) A(q- r) = (p v q) -r
-(pAq) =-p v n
-(p v q) =-pA
(p q) V (pr) = p (q vr)
(p r) V (qr) = (p Aq)→r
De Morgan's laws
PV (pAq) = p
Absorption laws
PA(pvq) = P
PV-p=T
Negation laws
PA-p=F
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,