Prove that the ratio of methane to ethylene in a purge stream must exceed that same ratio in the ethylene feed for the purge stream to work in removing methane from our ethylene-to-ethyl alcohol process.
Prove that the ratio of methane to ethylene in a purge stream must exceed that same ratio in the ethylene feed for the purge stream to work in removing methane from our ethylene-to-ethyl alcohol process.
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
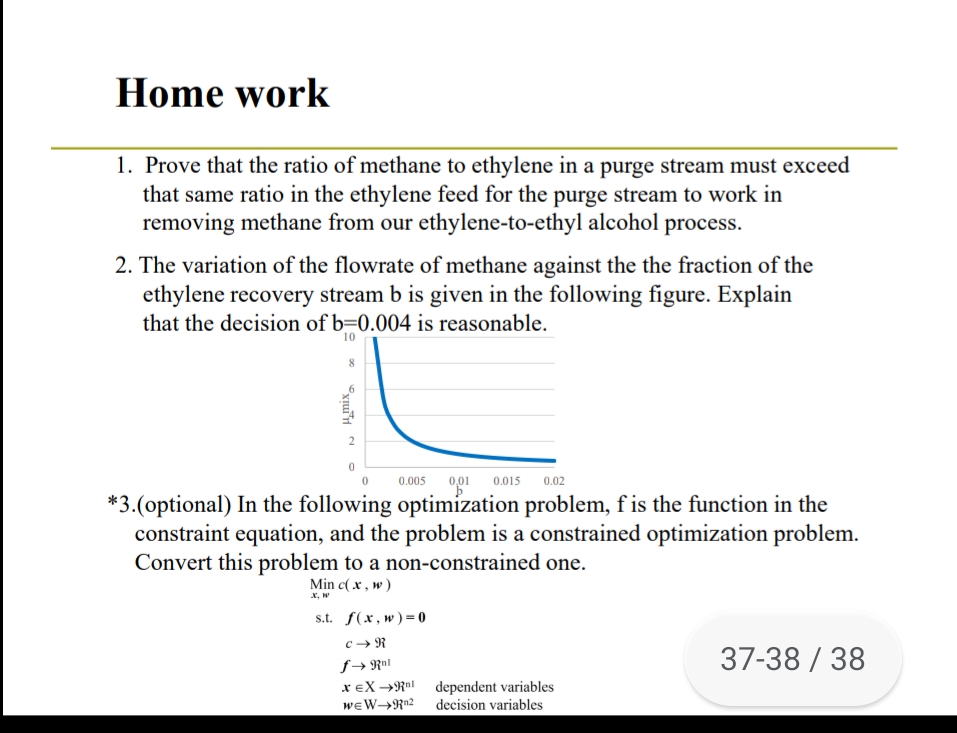
Transcribed Image Text:Home work
1. Prove that the ratio of methane to ethylene in a purge stream must exceed
that same ratio in the ethylene feed for the purge stream to work in
removing methane from our ethylene-to-ethyl alcohol process.
2. The variation of the flowrate of methane against the the fraction of the
ethylene recovery stream b is given in the following figure. Explain
that the decision of b=0.004 is reasonable.
10
8.
01
0.005
0.015
0.02
*3.(optional) In the following optimization problem, f is the function in the
constraint equation, and the problem is a constrained optimization problem.
Convert this problem to a non-constrained one.
Min c(x , w )
X, W
s.t. f(x,w)=0
c → R
37-38 / 38
f→ Ral
x eX →R"! dependent variables
wɛW→R®2
decision variables
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The