Purchase Price Sale Price Activity Units (per unit) (per unit) Beginning inventory Purchase 1, Jan. 18 Sale 1 Sale 2 Purchase 2, Mar. 10 Sale 3 Sale 4 Purchase 3, Sept. 30 Sale 5 110 $7.10 575 7.20 380 $12.00 225 12.00 680 7.50 270 12.00 290 12.50 230 7.70 240 12.50
Purchase Price Sale Price Activity Units (per unit) (per unit) Beginning inventory Purchase 1, Jan. 18 Sale 1 Sale 2 Purchase 2, Mar. 10 Sale 3 Sale 4 Purchase 3, Sept. 30 Sale 5 110 $7.10 575 7.20 380 $12.00 225 12.00 680 7.50 270 12.00 290 12.50 230 7.70 240 12.50
Corporate Financial Accounting
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305653535
Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Chapter6: Inventories
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.2BE: Perpetual inventory using FIFO Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Item Zeta9 are as...
Related questions
Question
Practice Pack
| Crandall Distributors uses a perpetual inventory system and has the following data available for inventory, purchases, and sales for a recent year: Required: 1. Compute the cost of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold using the specific identification method. Assume the ending inventory is made up of 40 units from beginning inventory, 30 units from Purchase 1, 80 units from Purchase 2, and 40 units from Purchase 3. 2. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the FIFO inventory costing method. 3. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the LIFO inventory costing method. 4. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the average cost inventory costing method. (Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.) 5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compare the ending inventory and cost of goods sold computed under all four methods. What can you conclude about the effects of the inventory costing methods on the balance sheet and the income statement? |
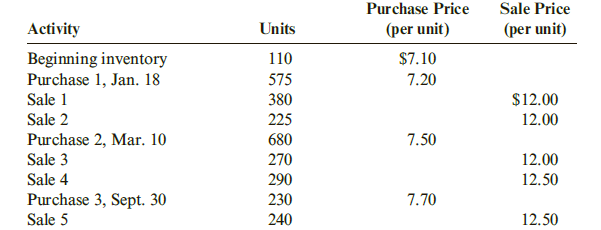
Transcribed Image Text:Purchase Price
Sale Price
Activity
Units
(per unit)
(per unit)
Beginning inventory
Purchase 1, Jan. 18
Sale 1
Sale 2
Purchase 2, Mar. 10
Sale 3
Sale 4
Purchase 3, Sept. 30
Sale 5
110
$7.10
575
7.20
380
$12.00
225
12.00
680
7.50
270
12.00
290
12.50
230
7.70
240
12.50
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Includes step-by-step video
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Learn your way
Includes step-by-step video
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Corporate Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305653535
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Corporate Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305653535
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305961883
Author:
Carl Warren
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning