pute u + v and u - 2v. 目 …日 olay the following vectors using arrows --2v, u + v, u- v, and u- 2v. Notice a parallelogram whose other vertices are
pute u + v and u - 2v. 目 …日 olay the following vectors using arrows --2v, u + v, u- v, and u- 2v. Notice a parallelogram whose other vertices are
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.3: Spanning Sets And Linear Independence
Problem 21EQ
Related questions
Concept explainers
Equations and Inequations
Equations and inequalities describe the relationship between two mathematical expressions.
Linear Functions
A linear function can just be a constant, or it can be the constant multiplied with the variable like x or y. If the variables are of the form, x2, x1/2 or y2 it is not linear. The exponent over the variables should always be 1.
Question
100%
solution for ex : 2,4,6
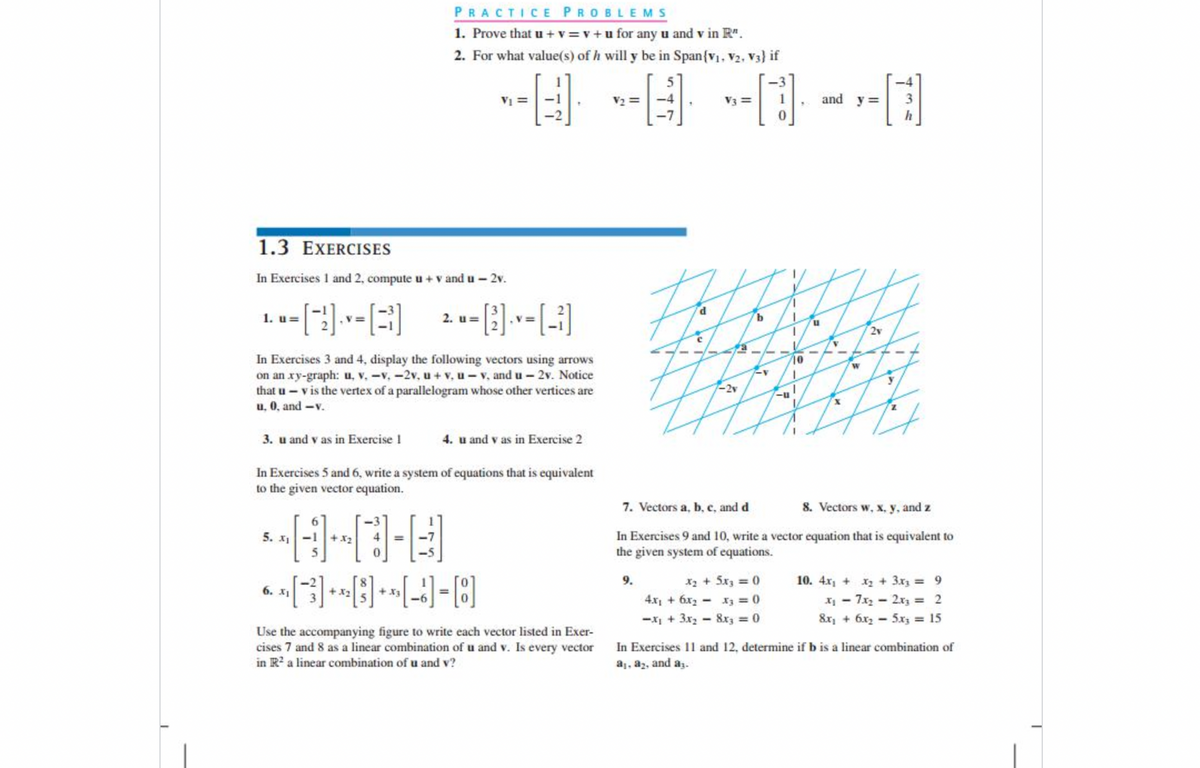
Transcribed Image Text:PRACTICE PROBLEMS
1. Prove that u + v =v + u for any u and v in R".
2. For what value(s) of h will y be in Span{v. V2. V3) if
-3
VI
V2 =
V3 =
and y =
1.3 EXERCISES
In Exercises 1 and 2, compute u + v and u - 2v.
1. u=
2. u=
2v
In Exercises 3 and 4, display the following vectors using arrows
on an xy-graph: u, v. -v,-2v, u+ v, u- v, and u - 2v. Notice
that u - v is the vertex of a parallelogram whose other vertices are
u, 0, and -v.
-2v
3. u and v as in Exercise I
4. u and v as in Exercise 2
In Exercises 5 and 6, write a system of equations that is equivalent
to the given vector equation.
7. Vectors a, b, c, and d
8. Vectors w, x, y. and z
In Exercises 9 and 10, write a vector equation that is equivalent to
the given system of equations.
5. x1
-1
+ x2
X2 + 5x3 = 0
4.x + 6x2 - x3 = 0
9.
10. 4x, + x2 + 3xrz = 9
6. x1
+x2
+ x3
I - 7x - 2x3 = 2
&x, + 6x2 - 5x3 = 15
-x + 3x2 - 8x3 = 0
Use the accompanying figure to write each vector listed in Exer-
cises 7 and 8 as a linear combination of u and v. Is every vector
in R? a linear combination of u and v?
In Exercises 11 and 12, determine if b is a linear combination of
a, az, and a;.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage