Q1: A/ Explain the concrete failures and which type is the common for concrete in Iraq? B/ Define A.C.V and list Aggregate shape? C/What is the effect of chloride in aggregate?
Q1: A/ Explain the concrete failures and which type is the common for concrete in Iraq? B/ Define A.C.V and list Aggregate shape? C/What is the effect of chloride in aggregate?
Fundamentals Of Construction Estimating
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337399395
Author:Pratt, David J.
Publisher:Pratt, David J.
Chapter11: Pricing Concrete Work
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4RQ
Related questions
Question
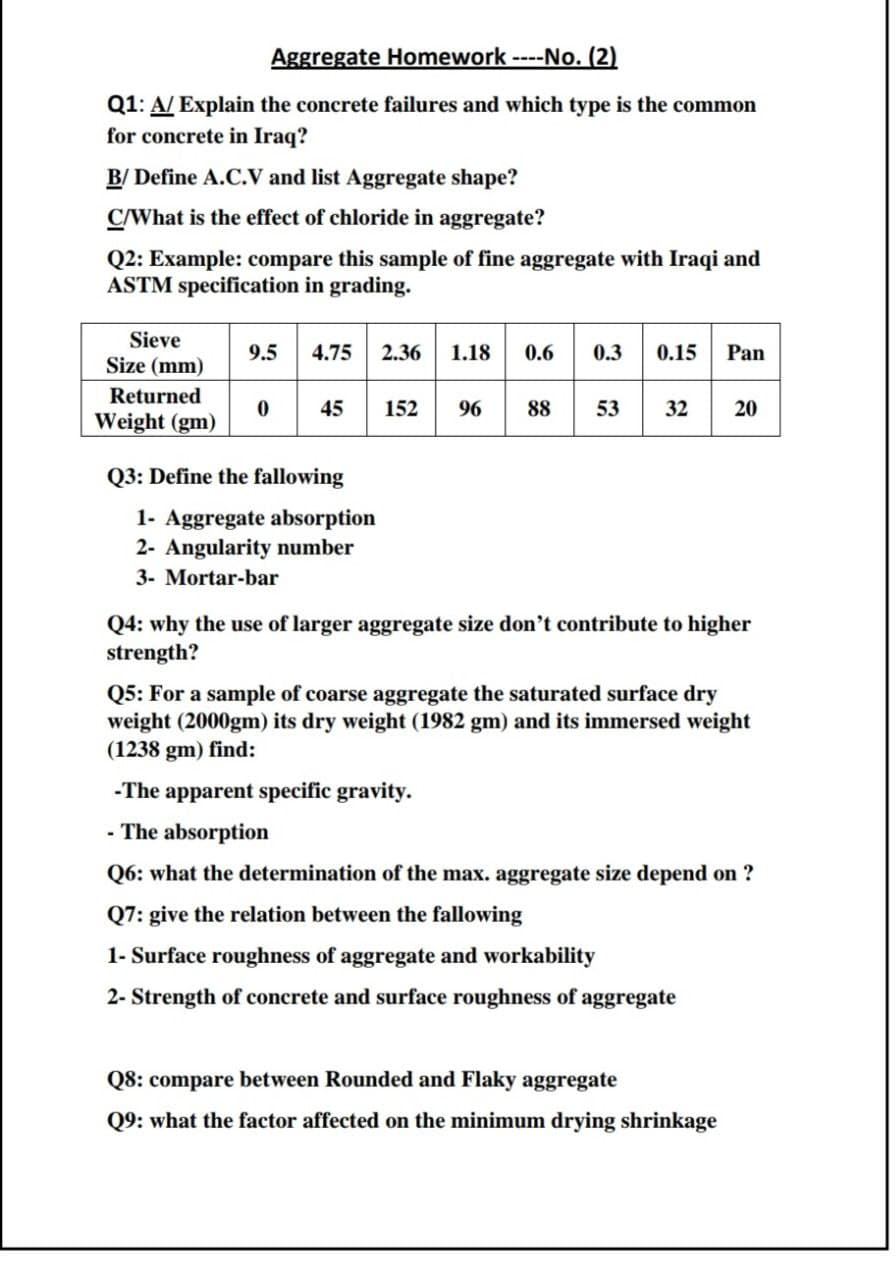
Transcribed Image Text:Aggregate Homework --No. (2)
Q1: A/ Explain the concrete failures and which type is the common
for concrete in Iraq?
B/ Define A.C.V and list Aggregate shape?
C/What is the effect of chloride in aggregate?
Q2: Example: compare this sample of fine aggregate with Iraqi and
ASTM specification in grading.
Sieve
9.5
4.75
2.36
1.18
0.6
0.3 0.15
Pan
Size (mm)
Returned
45
152
96
88
53
32
20
Weight (gm)
Q3: Define the fallowing
1- Aggregate absorption
2- Angularity number
3- Mortar-bar
Q4: why the use of larger aggregate size don't contribute to higher
strength?
Q5: For a sample of coarse aggregate the saturated surface dry
weight (2000gm) its dry weight (1982 gm) and its immersed weight
(1238 gm) find:
-The apparent specific gravity.
- The absorption
Q6: what the determination of the max. aggregate size depend on ?
Q7: give the relation between the fallowing
1- Surface roughness of aggregate and workability
2- Strength of concrete and surface roughness of aggregate
Q8: compare between Rounded and Flaky aggregate
Q9: what the factor affected on the minimum drying shrinkage
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Fundamentals Of Construction Estimating
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337399395
Author:
Pratt, David J.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Fundamentals Of Construction Estimating
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337399395
Author:
Pratt, David J.
Publisher:
Cengage,