Q3// let X and Y have the joint probability distribution function as : . (x, y) (1,1) (1,2) (1,3) (2,1) (2,2) (2,3) p(x,y) 2/15 4/15 3/15 1/15 1/15 4/15 and p(x, y) is equal to zero elsewhere.
Q3// let X and Y have the joint probability distribution function as : . (x, y) (1,1) (1,2) (1,3) (2,1) (2,2) (2,3) p(x,y) 2/15 4/15 3/15 1/15 1/15 4/15 and p(x, y) is equal to zero elsewhere.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 22E
Related questions
Question
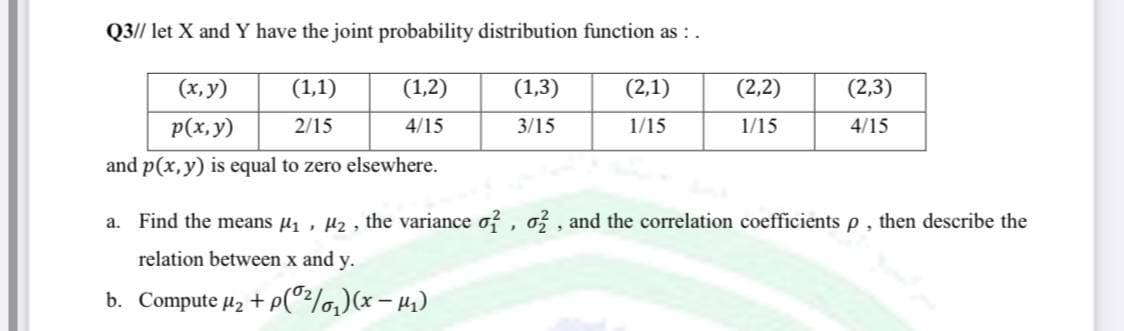
Transcribed Image Text:Q3// let X and Y have the joint probability distribution function as :.
(x, y)
(1,1)
(1,2)
(1,3)
(2,1)
(2,2)
(2,3)
p(x,y)
2/15
4/15
3/15
1/15
1/15
4/15
and p(x, y) is equal to zero elsewhere.
a. Find the means u , µz, the variance o?, o , and the correlation coefficients p , then describe the
relation between x and y.
b. Compute µ2 + p(°?/o,)(x – 41)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage