QUESTION 1 Izdham sell watches at RM10 each and his variable costs (ie plastics and metal) is RM3 for each watch. To sell this watch, the fixed cost (i.e flat fee of rent, salary) is RM100. If you sell 12 watches in 1 month, how much will you earn / lose? (a) Calculate the Gross Profit / Loss (b) Calculate the Net Profit / Loss (c) Calculate the Break Even Point in units.
QUESTION 1 Izdham sell watches at RM10 each and his variable costs (ie plastics and metal) is RM3 for each watch. To sell this watch, the fixed cost (i.e flat fee of rent, salary) is RM100. If you sell 12 watches in 1 month, how much will you earn / lose? (a) Calculate the Gross Profit / Loss (b) Calculate the Net Profit / Loss (c) Calculate the Break Even Point in units.
Chapter4A: Nopat Breakeven: Revenues Needed To Cover Total Operating Costs
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1EP
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 1
Izdham sell watches at RM10 each and his variable costs (ie plastics and metal) is
RM3 for each watch. To sell this watch, the fixed cost (i.e flat fee of rent, salary) is
RM100. If you sell 12 watches in 1 month, how much will you eam / lose?
(a) Calculate the Gross Profit / Loss
(b) Calculate the Net Profit / Loss
(c) Calculate the Break Even Point in units.
QUESTION 2
Ahmad is selling shoes in IOI Malls. If the selling price (SP) per shoes is RM20 per
unit and total quantity sold were 500,000 units. The fixed cost (FC) involved were
RM40,000 with a variable cost (VC) of RM10 per unit.
a) Calculate the Total Revenue (Gross Profit).
b) Calculate the Total Cost.
c) Calculate the Net Profit.
d) Calculate the Contribution Margin.
e) Calculate the Break Even Point (in quantity).
f) Calculate the Break Even Point (in Ringgit).
g) Calculate the Target Quantity (unit) if the target desired profit is RM100,000.
Note:
TR=PxQ; GP= TR-TC; TC=FC+VC; VC=UVCXQ; CM=P-UVC;
BEP(U)=FC/CM; BEP(RM)=BEP(Q)xSP(per unit); TQ(per
unit)=FC+PD/SP(per unit)-VC(per unit)
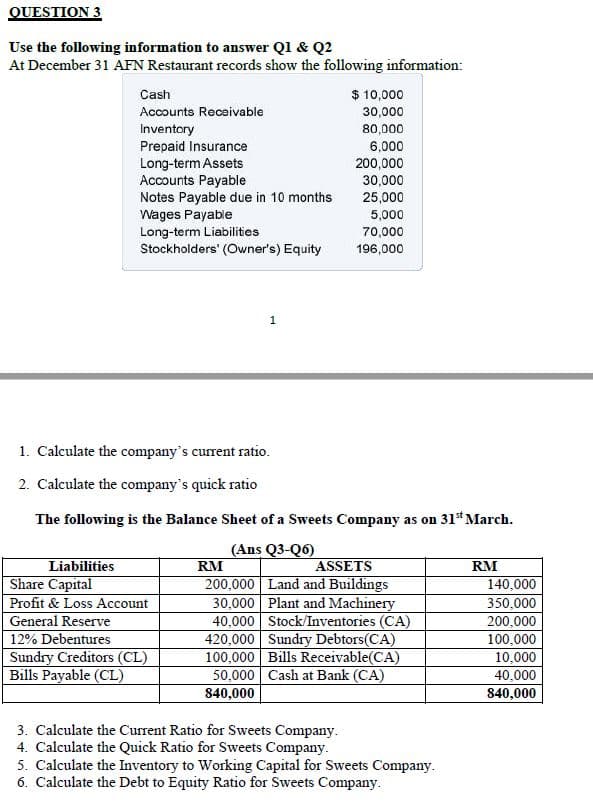
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 3
Use the following information to answer Ql & Q2
At December 31 AFN Restaurant records show the following information:
$ 10,000
Cash
Accounts Receivable
30,000
80,000
Inventory
Prepaid Insurance
Long-term Assets
Accounts Payable
Notes Payable due in 10 months
Wages Payable
Long-term Liabilities
Stockholders' (Owner's) Equity
6,000
200,000
30,000
25,000
5,000
70,000
196,000
1
1. Calculate the company's current ratio.
2. Calculate the company's quick ratio
The following is the Balance Sheet of a Sweets Company as on 31* March.
(Ans Q3-Q6)
RM
Liabilities
ASSETS
RM
Share Capital
200,000 Land and Buildings
30,000 Plant and Machinery
40,000 Stock/Inventories (CA)
420,000 Sundry Debtors(CA)
100,000 Bills Receivable(CA)
50,000 Cash at Bank (CA)
840,000
140,000
Profit & Loss Account
350,000
General Reserve
12% Debentures
Sundry Creditors (CL)
Bills Payable (CL)
200,000
100,000
10,000
40,000
840,000
3. Calculate the Current Ratio for Sweets Company.
4. Calculate the Quick Ratio for Sweets Company.
5. Calculate the Inventory to Working Capital for Sweets Company.
6. Calculate the Debt to Equity Ratio for Sweets Company.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Includes step-by-step video
Learn your way
Includes step-by-step video
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College


Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College