QUESTION 5 Consider the function f(2)= 1 2³(2-3) (5.1) Use a known Maclaurin series to find the Laurent series expansion of f(z) in the following regions: (5.1.1) 0<2<3 (5.1.2) 3<|2|<∞ (5.2) Classify the singularity z = 0. Find the residue of f at z = 0. (5.3) Find the residues of the f at all singular points without using the Laurent series. (5.4) Hence, evaluate the contour integral e f(2)dz, where C is the circle |z − 2| = 3.
QUESTION 5 Consider the function f(2)= 1 2³(2-3) (5.1) Use a known Maclaurin series to find the Laurent series expansion of f(z) in the following regions: (5.1.1) 0<2<3 (5.1.2) 3<|2|<∞ (5.2) Classify the singularity z = 0. Find the residue of f at z = 0. (5.3) Find the residues of the f at all singular points without using the Laurent series. (5.4) Hence, evaluate the contour integral e f(2)dz, where C is the circle |z − 2| = 3.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.2: Arithmetic Sequences
Problem 68E
Related questions
Question
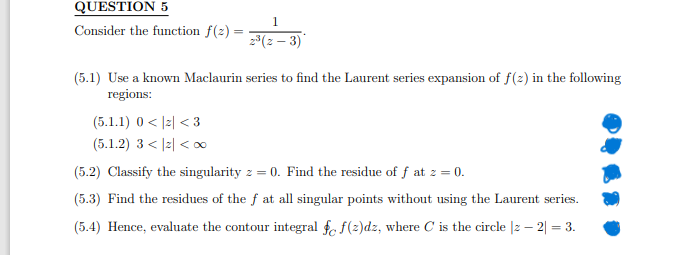
Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 5
Consider the function f(2)=
1
2³(2-3)*
(5.1) Use a known Maclaurin series to find the Laurent series expansion of f(z) in the following
regions:
(5.1.1) 0<2<3
(5.1.2) 3<|2|<∞0
(5.2) Classify the singularity z = 0. Find the residue of f at z = 0.
(5.3) Find the residues of the f at all singular points without using the Laurent series.
(5.4) Hence, evaluate the contour integral fc f(z)dz, where C is the circle |2 - 2| = 3.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage