rb+c f (x)dx : f (x – c)dxr. a a+c Explain this result geometrically.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter3: Functions And Graphs
Section3.6: Quadratic Functions
Problem 58E
Related questions
Question
![DEFINITION 7.1. A partition of [a, b] is a finite set
P = {x0, x₁,x2,..., En}
such that a = xo, b = xn, and x0 < x1 < x2 < ... < Xn•
REMARK 7.2. Given a partition {x0, x1, x2, ..., xn} of [a, b] and a bounded function f : [a, b] → R,
consider a subinterval [xi-1, x₂]. Denote
• mi := inf{ƒ(x) : ƒ € [xi_1, xi]}
f
• M₁ = sup{f(x): f = [xi-1, xi]}
€
:=](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fdb708fa5-116d-42c3-bb62-31dd00678e29%2Fe7c4929a-2c94-41a5-923b-7a7d02bd015e%2Friw2w7_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:DEFINITION 7.1. A partition of [a, b] is a finite set
P = {x0, x₁,x2,..., En}
such that a = xo, b = xn, and x0 < x1 < x2 < ... < Xn•
REMARK 7.2. Given a partition {x0, x1, x2, ..., xn} of [a, b] and a bounded function f : [a, b] → R,
consider a subinterval [xi-1, x₂]. Denote
• mi := inf{ƒ(x) : ƒ € [xi_1, xi]}
f
• M₁ = sup{f(x): f = [xi-1, xi]}
€
:=
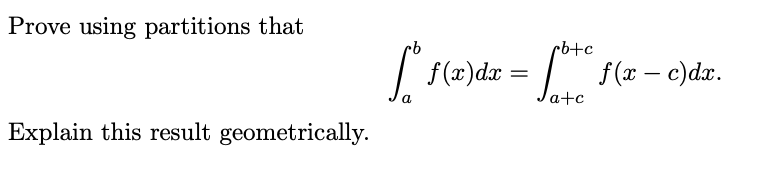
Transcribed Image Text:Prove using partitions that
Explain this result geometrically.
cb+c
f* f (x)dx = ft+ f(x − c)dx.
-
a
a+c
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage