Right- and left-hand derivatives Let f (x) = |x|. (a) Calculate the right-hand derivatives of f(x) at x = 0. (b) Calculate the left-hand derivative of f (x) at x = 0. (c) Does f (x) have a derivative at x = 0? (d) Illustrate the conclusions in (a), (b), and (c) 4.7. from a graph.
Right- and left-hand derivatives Let f (x) = |x|. (a) Calculate the right-hand derivatives of f(x) at x = 0. (b) Calculate the left-hand derivative of f (x) at x = 0. (c) Does f (x) have a derivative at x = 0? (d) Illustrate the conclusions in (a), (b), and (c) 4.7. from a graph.
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Chapter5: A Survey Of Other Common Functions
Section5.4: Combining And Decomposing Functions
Problem 14E: Decay of Litter Litter such as leaves falls to the forest floor, where the action of insects and...
Related questions
Concept explainers
Equations and Inequations
Equations and inequalities describe the relationship between two mathematical expressions.
Linear Functions
A linear function can just be a constant, or it can be the constant multiplied with the variable like x or y. If the variables are of the form, x2, x1/2 or y2 it is not linear. The exponent over the variables should always be 1.
Question
4.7)My professor says I have to explain the steps in the solved problems in the picture. Not just copy eveything down from the text.
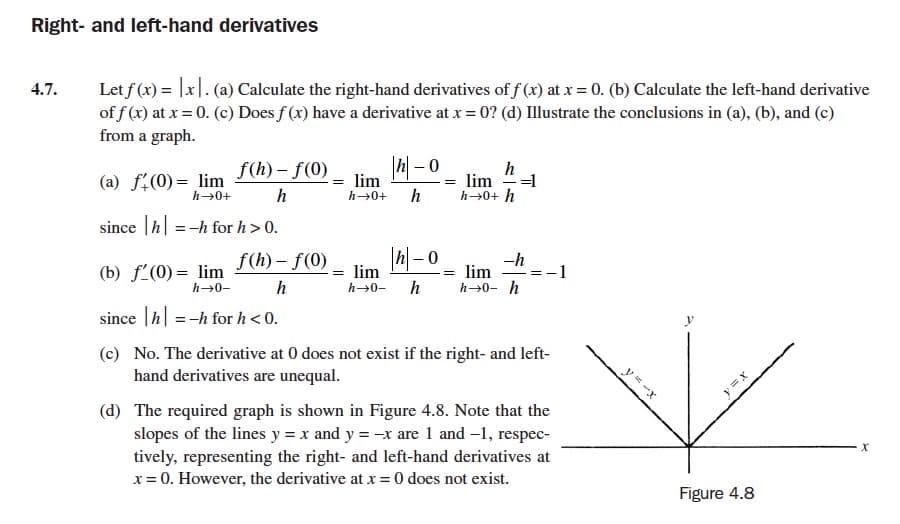
Transcribed Image Text:Right- and left-hand derivatives
Let f (x) = |x|. (a) Calculate the right-hand derivatives of f (x) at x = 0. (b) Calculate the left-hand derivative
of f (x) at x = 0. (c) Does f (x) have a derivative at x = 0? (d) Illustrate the conclusions in (a), (b), and (c)
from a graph.
4.7.
h
=1
lim
h→0+ h
f(h) – f(0)
(a) f:(0)= lim
h→0+
= lim
h
%3|
h
h→0+
since |h| =-h for h> 0.
f(h) – f(0)
|h-0
lim
-h
(b) f'(0) = lim
h→0-
= lim
1
h
h→0- h h→0- h
since |h| =-h for h < 0.
(c) No. The derivative at 0 does not exist if the right- and left-
hand derivatives are unequal.
(d) The required graph is shown in Figure 4.8. Note that the
slopes of the lines y = x and y = -x are 1 and -1, respec-
tively, representing the right- and left-hand derivatives at
x = 0. However, the derivative at x = 0 does not exist.
Figure 4.8
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage