Second-Order Control System Models One standard second-order control system model is Ко 2 3 Y(s) R(s) where п K steady-state gain the damping ratio the undamped natural ( 0) frequency , the damped natural frequency о, 1 o 125, the damped resonant frequency If the damping ratio is less than unity, the system is said to be underdamped; if is equal to unity, it is said to be critically damped, and if Ç is greater than unity, the system is said to be overdamped First-Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients yay Solution, y a constant that satisfies the initial conditions 0, where a is a real constant: Ce a where C First-Order Linear Nonhomogeneous Differential Equations 1 < 0l dy x(t) = + y = Kr(t) |B t> of dt y(0) KA t is the time constant K is the gain The solution is KA (KB KA)1 - exp t or y(t) = In КА КВ t КВ
Second-Order Control System Models One standard second-order control system model is Ко 2 3 Y(s) R(s) where п K steady-state gain the damping ratio the undamped natural ( 0) frequency , the damped natural frequency о, 1 o 125, the damped resonant frequency If the damping ratio is less than unity, the system is said to be underdamped; if is equal to unity, it is said to be critically damped, and if Ç is greater than unity, the system is said to be overdamped First-Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients yay Solution, y a constant that satisfies the initial conditions 0, where a is a real constant: Ce a where C First-Order Linear Nonhomogeneous Differential Equations 1 < 0l dy x(t) = + y = Kr(t) |B t> of dt y(0) KA t is the time constant K is the gain The solution is KA (KB KA)1 - exp t or y(t) = In КА КВ t КВ
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter9: Counting And Probability
Section9.2: Probability
Problem 53E
Related questions
Question
100%
Hi,
Given the question:
Find the general solution for dy/dx = x + x*y2
Can it be solved by the method of undetermined coefficients shown in the attached image?
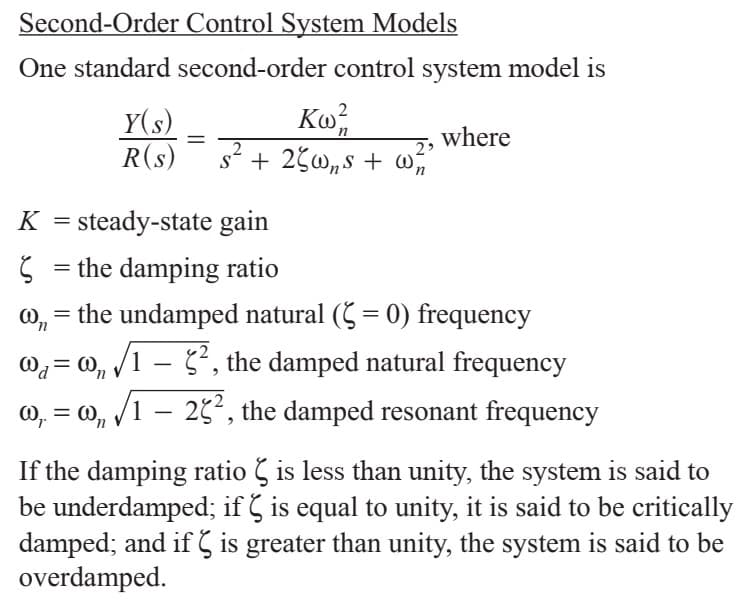
Transcribed Image Text:Second-Order Control System Models
One standard second-order control system model is
Ко
2 3
Y(s)
R(s)
where
п
K steady-state gain
the damping ratio
the undamped natural ( 0) frequency
, the damped natural frequency
о,
1
o
125, the damped resonant frequency
If the damping ratio is less than unity, the system is said to
be underdamped; if is equal to unity, it is said to be critically
damped, and if Ç is greater than unity, the system is said to be
overdamped
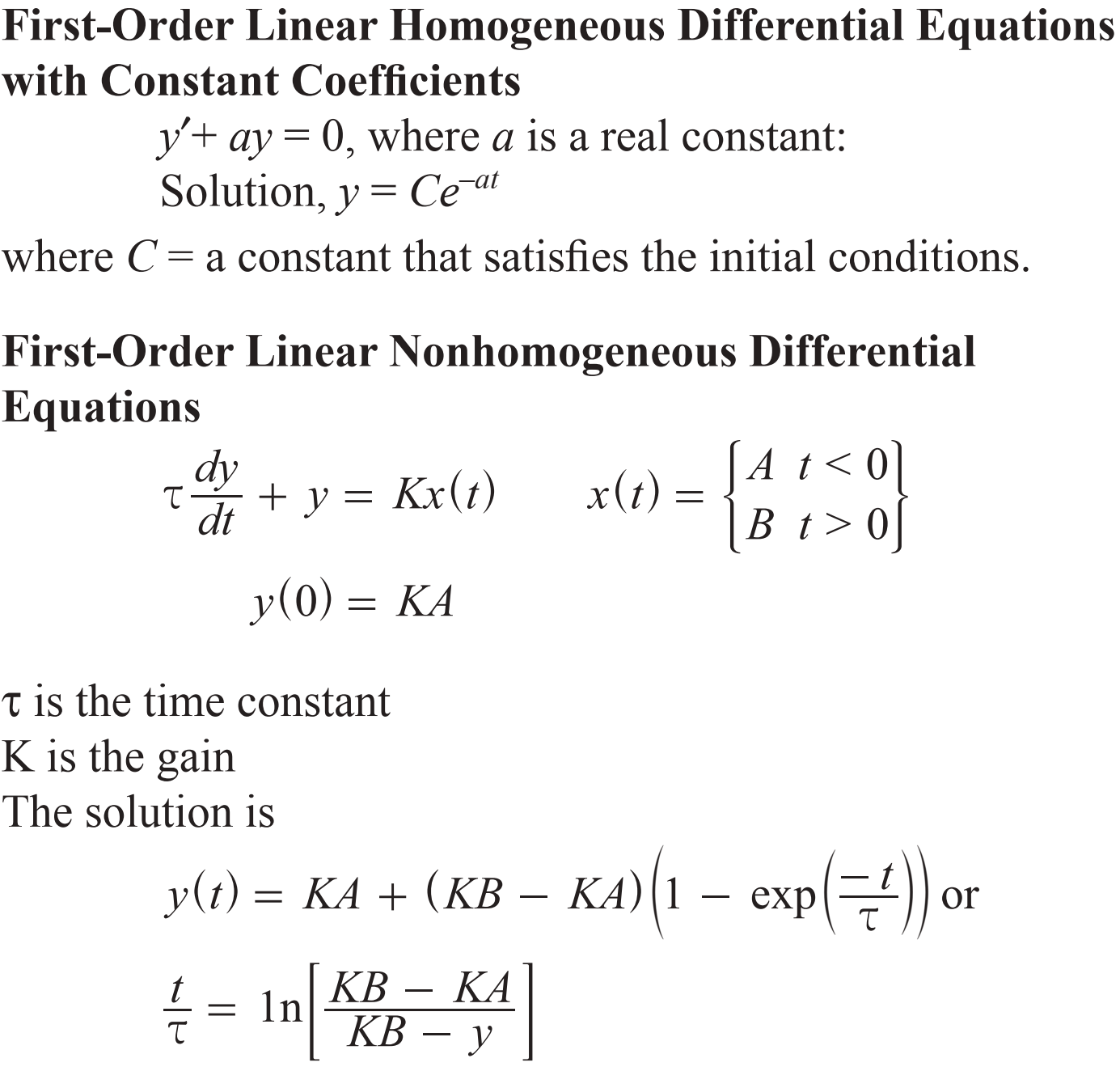
Transcribed Image Text:First-Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations
with Constant Coefficients
yay
Solution, y
a constant that satisfies the initial conditions
0, where a is a real constant:
Ce a
where C
First-Order Linear Nonhomogeneous Differential
Equations
1 < 0l
dy
x(t) =
+ y = Kr(t)
|B t> of
dt
y(0) KA
t is the time constant
K is the gain
The solution is
KA (KB KA)1 - exp
t
or
y(t) =
In
КА
КВ
t
КВ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage