Sexual Reproduction and Genetic Variation Genetic variation describes the genetic differences in DNA segments of organisms within a population. Genetic variation is important because it enables some individuals to have traits that are favorable in a changing environment. Sexual reproduction is a method that introduces genetic variation. A human being is a diploid organism whose somatic cells contain 46 chromosomes found in 23 homologous pairs. Sexual reproduction requires that sex cells, or gametes, reduce their number of chromosomes in order for fertilization to occur. In humans, meiosis is the process that forms the gametes required for reproduction. The diagram shows the process of meiosis. Cytokinesis Interphase G' Telophase 11 Anaphase II Interphase Prophase Metaphase Metaphase Prophase Crossing over chromatids of homologous chromosomes. Telophase Anaphase I 7 Genetic variation can be introduced during the process of meiosis in different ways as shown in the table. The exchange of genetic material between non-sister As the chromosome pairs line up during prophase I, some material from the chromatids switch to the exact same position on the other chromosomes. This exchange can happen multiple times on the same pair of chromosomes. The diagram shows crossing over and the resulting gametes. CA 0₂ M-1111 Homologous Pair Crossing over Which BEST describes how crossing over increases genetic diversity? C D O O A Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it prevents genetic mutations from occurring within the genes. B B D. Gametes Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it ensures that offspring receive the dominant alleles for traits. Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it results in new combinations of genes on each chromosome. Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it creates an uneven amount of genetic material on the chromatids.
Sexual Reproduction and Genetic Variation Genetic variation describes the genetic differences in DNA segments of organisms within a population. Genetic variation is important because it enables some individuals to have traits that are favorable in a changing environment. Sexual reproduction is a method that introduces genetic variation. A human being is a diploid organism whose somatic cells contain 46 chromosomes found in 23 homologous pairs. Sexual reproduction requires that sex cells, or gametes, reduce their number of chromosomes in order for fertilization to occur. In humans, meiosis is the process that forms the gametes required for reproduction. The diagram shows the process of meiosis. Cytokinesis Interphase G' Telophase 11 Anaphase II Interphase Prophase Metaphase Metaphase Prophase Crossing over chromatids of homologous chromosomes. Telophase Anaphase I 7 Genetic variation can be introduced during the process of meiosis in different ways as shown in the table. The exchange of genetic material between non-sister As the chromosome pairs line up during prophase I, some material from the chromatids switch to the exact same position on the other chromosomes. This exchange can happen multiple times on the same pair of chromosomes. The diagram shows crossing over and the resulting gametes. CA 0₂ M-1111 Homologous Pair Crossing over Which BEST describes how crossing over increases genetic diversity? C D O O A Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it prevents genetic mutations from occurring within the genes. B B D. Gametes Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it ensures that offspring receive the dominant alleles for traits. Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it results in new combinations of genes on each chromosome. Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it creates an uneven amount of genetic material on the chromatids.
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Chapter11: Meiosis: The Cellular Basis Of Sexual Reproduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1ITD
Related questions
Question
100%
12
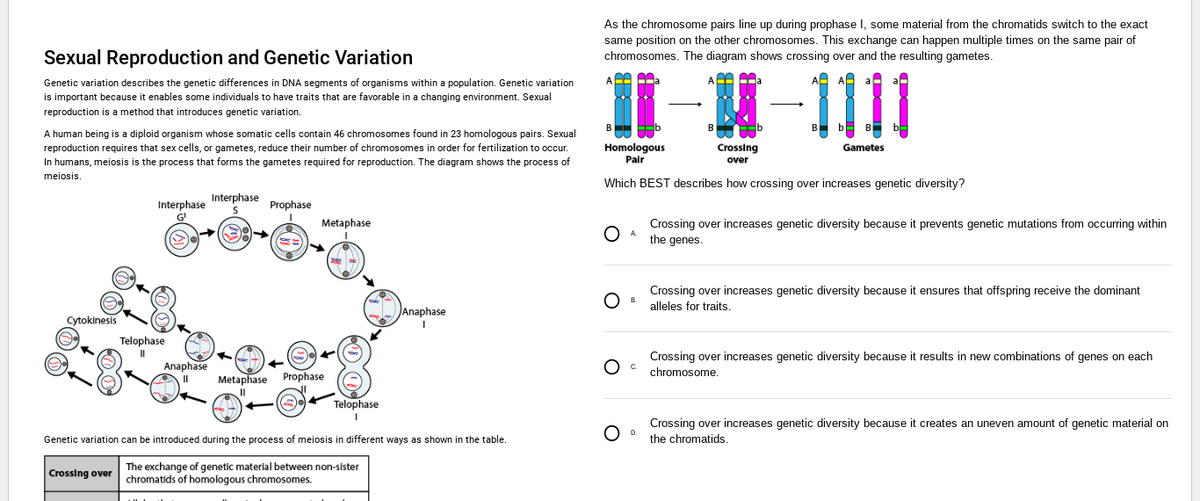
Transcribed Image Text:Sexual Reproduction and Genetic Variation
Genetic variation describes the genetic differences in DNA segments of organisms within a population. Genetic variation
is important because it enables some individuals to have traits that are favorable in a changing environment. Sexual
reproduction is a method that introduces genetic variation.
A human being is a diploid organism whose somatic cells contain 46 chromosomes found in 23 homologous pairs. Sexual
reproduction requires that sex cells, or gametes, reduce their number of chromosomes in order for fertilization to occur.
In humans, meiosis is the process that forms the gametes required for reproduction. The diagram shows the process of
meiosis.
Cytokinesis
Interphase
G¹
Crossing over
Telophase
II
Anaphase
||
Interphase
S
Prophase
Metaphase
24
Metaphase Prophase
Telophase
Anaphase
I
Genetic variation can be introduced during the process of meiosis in different ways as shown in the table.
The exchange of genetic material between non-sister
chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
As the chromosome pairs line up during prophase I, some material from the chromatids switch to the exact
same position on the other chromosomes. This exchange can happen multiple times on the same pair of
chromosomes. The diagram shows crossing over and the resulting gametes.
11
Homologous
Pair
O
O
A.
Which BEST describes how crossing over increases genetic diversity?
B.
C
·|-||||
Bb B
O
O D
B
Crossing
over
Gametes
Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it prevents genetic mutations from occurring within
the genes.
Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it ensures that offspring receive the dominant
alleles for traits.
Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it results in new combinations of genes on each
chromosome.
Crossing over increases genetic diversity because it creates an uneven amount of genetic material on
the chromatids.
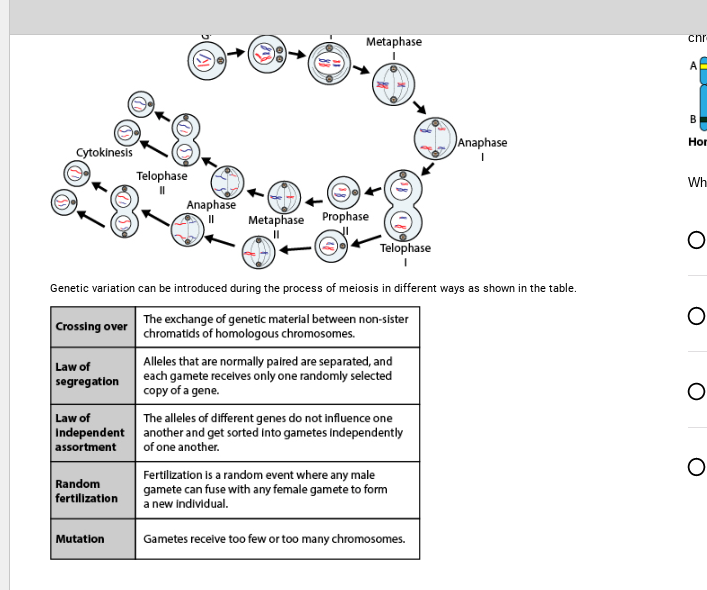
Transcribed Image Text:Cytokinesis
Crossing over
Law of
segregation
Law of
Independent
assortment
Random
fertilization
Telophase
Mutation
A
Anaphase
II
(818)
Genetic variation can be introduced during the process of meiosis in different ways as shown in the table.
The exchange of genetic material between non-sister
chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
Metaphase
Metaphase Prophase
Telophase
Alleles that are normally paired are separated, and
each gamete receives only one randomly selected
copy of a gene.
The alleles of different genes do not influence one
another and get sorted Into gametes Independently
of one another.
Anaphase
I
Fertilization is a random event where any male
gamete can fuse with any female gamete to form
a new individual.
Gametes receive too few or too many chromosomes.
cnr
A
CI
B
Hor
Wh
O
O
O
O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning