Chapter9: Sequences, Probability And Counting Theory
Section9.5: Counting Principles
Problem 38SE: Suppose a set A has 2,048 subsets. How many distinct objects are contained in A?
Related questions
Question
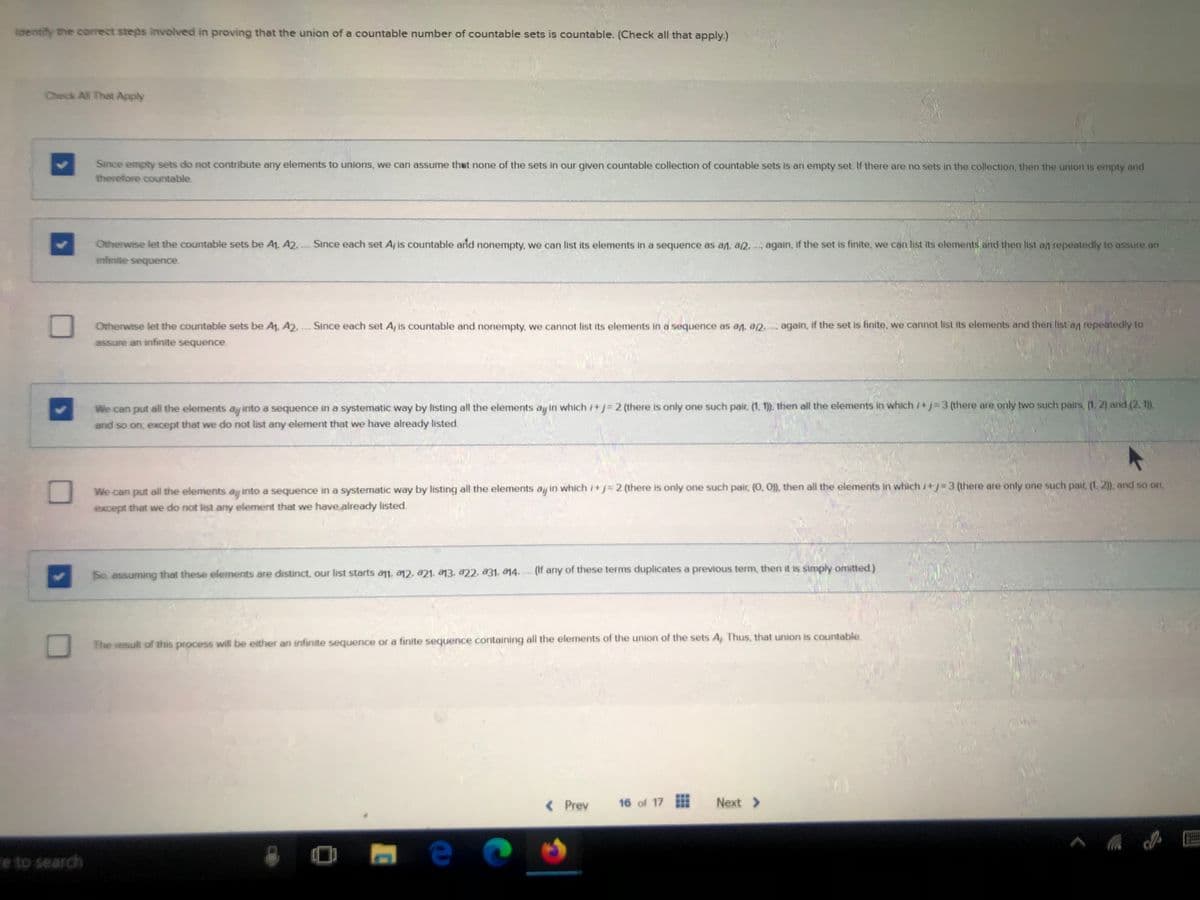
Transcribed Image Text:Identify the correct steps involved in proving that the union of a countable number of countable sets is countable. (Check all that apply.)
Check All That Apply
☐
Since empty sets do not contribute any elements to unions, we can assume that none of the sets in our given countable collection of countable sets is an empty set. If there are no sets in the collection, then the union is empty and
therefore countable.
Otherwise let the countable sets be A1, A2... Since each set A, is countable and nonempty, we can list its elements in a sequence as aд. a..... again, if the set is finite, we can list its elements and then list an repeatedly to assure an
infinite sequence.
Otherwise let the countable sets be A1, A2... Since each set A, is countable and nonempty, we cannot list its elements in a sequence as aд. .
assure an infinite sequence
again, if the set is finite, we cannot list its elements and then list aд repeatedly to
We can put all the elements ay into a sequence in a systematic way by listing all the elements ay in which 1+1=2 (there is only one such pair, (1, 1)), then all the elements in which /+/-3 (there are only two such pairs, (1, 2) and (2, 1)).
and so on, except that we do not list any element that we have already listed.
We can put all the elements ay into a sequence in a systematic way by listing all the elements ay in which 1+1=2 (there is only one such pair, (0, 0)), then all the elements in which /+/-3 (there are only one such pair, (1, 2)), and so on.
except that we do not list any element that we have already listed.
So assuming that these elements are distinct, our list starts a11. 12. 21. 13. 22. a31. a14. (If any of these terms duplicates a previous term, then it is simply omitted.)
The result of this process will be either an infinite sequence or a finite sequence containing all the elements of the union of the sets A Thus, that union is countable
< Prev
16 of 17
Next >
e to search
нес
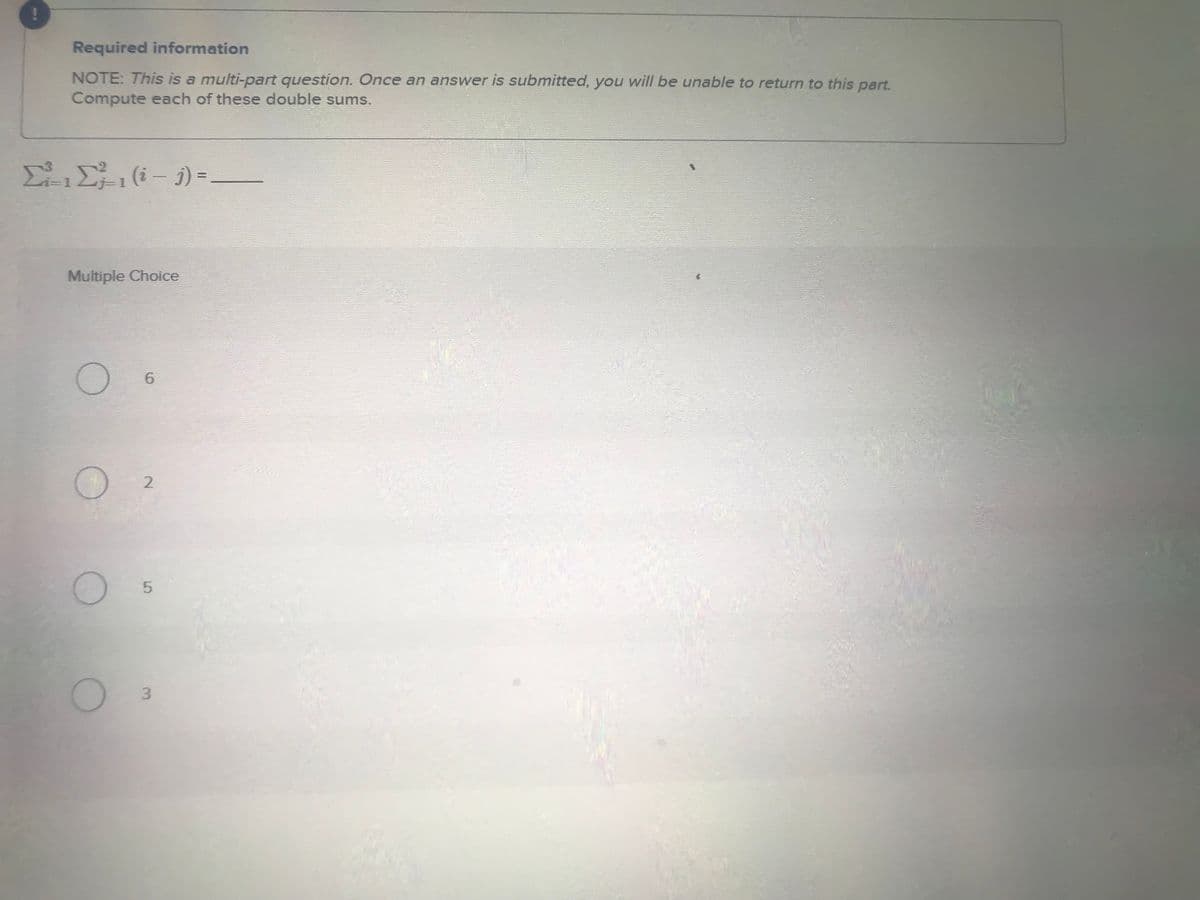
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part.
Compute each of these double sums.
Σ(i-1)=-
Multiple Choice
6
2
5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

