Suppose that y = f(x) is differentiable at x = a and that g(x) = m(x - a) +c is a linear function in which m and c are constants. If the error E(x) = f(x)– g(x) were small enough near x = a, it might be considered to use g as a linear approximation of f instead of the linearization L(x) = f(a) + f'(x – a). Show that if accompanying conditions were imposed on g then g(x) = f(a) +f'(a)(x– a). Thus, the linearization L(x) gives the only linear approximation whose error is both zero at x= a and negligible in comparison with x - a.
Suppose that y = f(x) is differentiable at x = a and that g(x) = m(x - a) +c is a linear function in which m and c are constants. If the error E(x) = f(x)– g(x) were small enough near x = a, it might be considered to use g as a linear approximation of f instead of the linearization L(x) = f(a) + f'(x – a). Show that if accompanying conditions were imposed on g then g(x) = f(a) +f'(a)(x– a). Thus, the linearization L(x) gives the only linear approximation whose error is both zero at x= a and negligible in comparison with x - a.
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter4: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section4.6: Applications And The Perron-frobenius Theorem
Problem 69EQ: Let x=x(t) be a twice-differentiable function and consider the second order differential equation...
Related questions
Question
100%
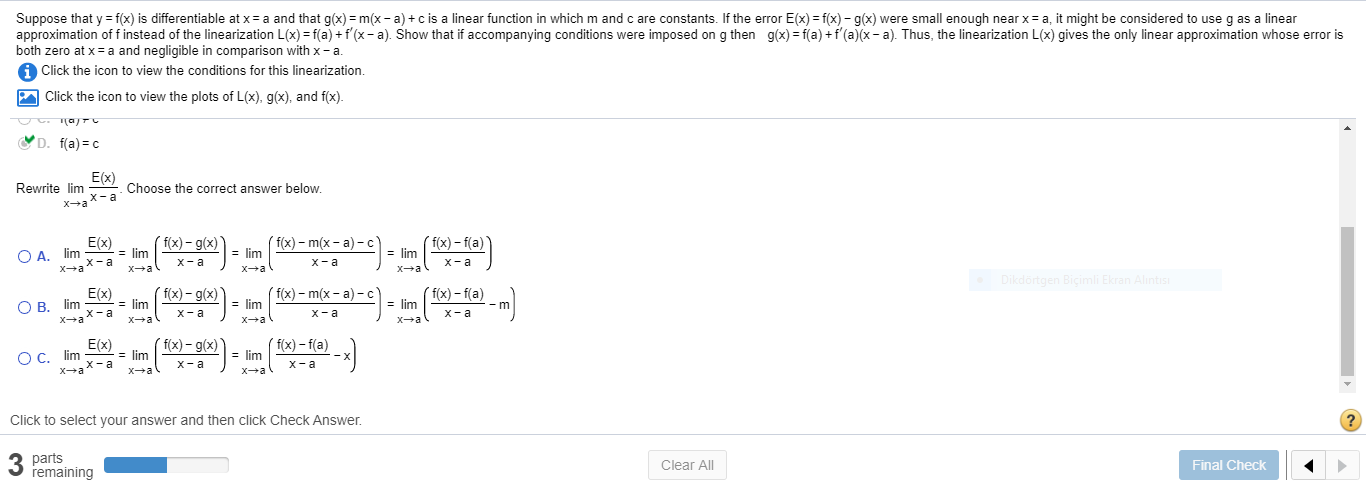
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that y = f(x) is differentiable at x = a and that g(x) = m(x - a) +c is a linear function in which m and c are constants. If the error E(x) = f(x)– g(x) were small enough near x = a, it might be considered to use g as a linear
approximation of f instead of the linearization L(x) = f(a) + f'(x – a). Show that if accompanying conditions were imposed on g then g(x) = f(a) +f'(a)(x– a). Thus, the linearization L(x) gives the only linear approximation whose error is
both zero at x= a and negligible in comparison with x - a.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning