T c) When the muscles connected to the crystalline lens relax, the focal length is 9.0000 cm. With this focal length, how close must an object be to form sharply focused images on the retina? (Note: this distance is called the near point of vision.) d) As people age, the crystalline lens hardens (a condition called presbyopia or "old-age" eyes) and can only vary in focal length from 12 to 15.60 cm. Calculate range of vision (the new near point and far point) for this older eye.
T c) When the muscles connected to the crystalline lens relax, the focal length is 9.0000 cm. With this focal length, how close must an object be to form sharply focused images on the retina? (Note: this distance is called the near point of vision.) d) As people age, the crystalline lens hardens (a condition called presbyopia or "old-age" eyes) and can only vary in focal length from 12 to 15.60 cm. Calculate range of vision (the new near point and far point) for this older eye.
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Chapter36: Sensory Systems
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21RQ: Why is it easier to see images at night using peripheral, rather than the central, vision? Cones are...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:11:21 AM Fri Jun 4
* 77% 4
YYY
c) When the muscles connected to the crystalline lens relax, the focal length is 9.0000 cm. With this focal
length, how close must an object be to form sharply focused images on the retina? (Note: this distance is
called the near point of vision.)
d) As people age, the crystalline lens hardens (a condition called presbyopia or "old-age" eyes) and can
only vary in focal length from 12 to 15.60 cm. Calculate range of vision (the new near point and far point)
for this older eye.
e) Based on part d) why might an older person hold the newspaper at arm's length to read it?
f) The iris of the eye serves two different purposes. First, the iris controls the total amount of light entering
the eye so a person can see in varying light levels. Secondly, the iris blocks light from hitting the extreme
edges of the crystalline lens. Why might an eye want to block the light hitting the extreme edges of a
lens? What is the name for the effect when light does hit the edges of a lens? Can you understand why
a person's vision is blurred when they get their eyes dilated at the doctor?
g) A person's eyes also dilate when they get drunk. What effect does this have on vision (not to mention
judgment)?
h) What is the pupil of the eye?
i) Explain why the crystalline lens of the eye gets a virtual object from the cornea.
>
D
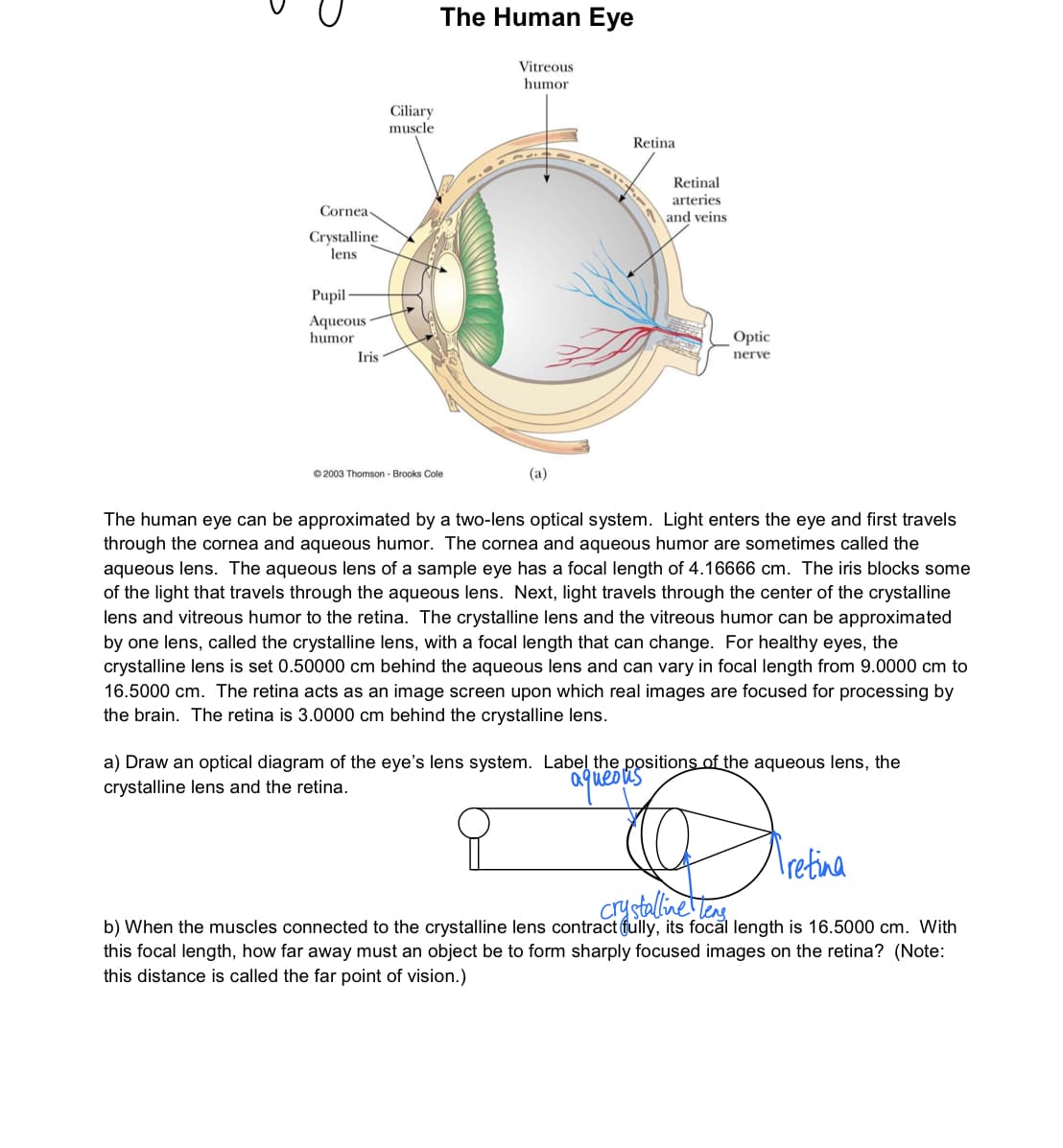
Transcribed Image Text:The Human Eye
Vitreous
humor
Ciliary
muscle
Retina
Retinal
arteries
and veins
Cornea
Crystalline
lens
Pupil -
Aqueous
humor
Optic
Iris
nerve
© 2003 Thomson - Brooks Cole
(a)
The human eye can be approximated by a two-lens optical system. Light enters the eye and first travels
through the cornea and aqueous humor. The cornea and aqueous humor are sometimes called the
aqueous lens. The aqueous lens of a sample eye has a focal length of 4.16666 cm. The iris blocks some
of the light that travels through the aqueous lens. Next, light travels through the center of the crystalline
lens and vitreous humor to the retina. The crystalline lens and the vitreous humor can be approximated
by one lens, called the crystalline lens, with a focal length that can change. For healthy eyes, the
crystalline lens is set 0.50000 cm behind the aqueous lens and can vary in focal length from 9.0000 cm to
16.5000 cm. The retina acts as an image screen upon which real images are focused for processing by
the brain. The retina is 3.0000 cm behind the crystalline lens.
a) Draw an optical diagram of the eye's lens system. Label the positions of the aqueous lens, the
crystalline lens and the retina.
Iretina
crystaline teng
b) When the muscles connected to the crystalline lens contract fully, its focăl length is 16.5000 cm. With
this focal length, how far away must an object be to form sharply focused images on the retina? (Note:
this distance is called the far point of vision.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A …
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781337711067
Author:
Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168130
Author:
Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A …
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:
9781337711067
Author:
Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning