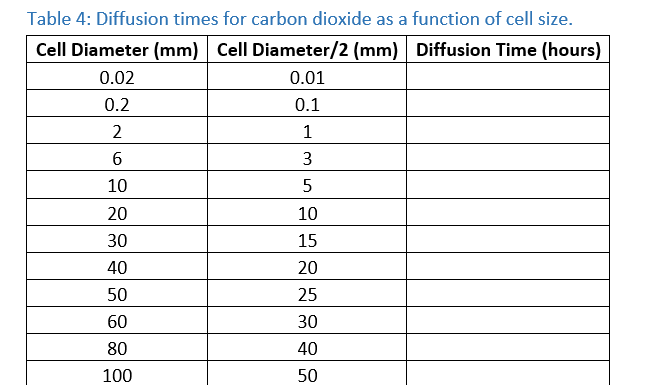
Table 4: Diffusion times for carbon dioxide as a function of cell size. Cell Diameter (mm) Cell Diameter/2 (mm) Diffusion Time (hours) 0.02 0.01 0.2 0.1 2 1 3 10 20 10 30 15 40 20 50 25 60 30 80 40 100 50
The surface area to volume ratio affects the ability of the cell to exchange nutrients and waste products with the outside environment. Many factors affect the movement of molecules across the cell membrane, including membrane thickness, temperature, pressure, concentration gradient, molecular mass, distance travelled, solvent properties and surface area of the cell. In general, according to Einstein’s approximation equation (Equation 1), diffusion time is inversely proportional to the to the diffusion coefficient (D), where t is time and x is distance travelled. The diffusion coefficient is unique to each type of molecule and is determined experimentally.
Waste products such as carbon dioxide (CO2) pose a unique problem to cells as their accumulation may be lethal. Exchange with the external environment is dependent upon the distance the waste must travel; for a round cell this will be up to half the cell diameter.
- Using the diffusion coefficient (D) for carbon dioxide (1.97 × 10-5 cm2/sec), calculate the diffusion time in hours for carbon dioxide for each of the cells listed in Table 4 (remember to use ½ cell diameter in the equation). Use the Diffusion Time Calculator (https://www.physiologyweb.com/calculators/diffusion_time_calculator.html).
2. Plot a line graph of cell diameter (x-axis) against diffusion time for carbon dioxide (y-axis). This graph should be formatted as it would appear in a scientific report.
3. What does the graph indicate about diffusion times for large cells? Small cells? Cell survival? Explain using direct reference to the results.

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images








