The desired percentage of SiO₂ in a certain type of aluminous cement is 5.5. To test whether the true average percentage is 5.5 for a particular production facility, 16 independently obtained samples are analyzed. Suppose that the percentage of SiO₂ in a sample is normally distributed with = 0.32 and that x 5.24. (Use a = 0.05.) (a) Does this indicate conclusively that the true average percentage differs from 5.5? State the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses. OH: 5.5 H₂H< 5.5 OHH-5.5 H: #25.5 O Ho: H-5.5 H₂₁: = 5.5 O Ho: -5.5 H:> 5.5 Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) P-value= State the conclusion in the problem context. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage. O Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage. O Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage. (b) If the true average percentage is = 5.6 and a level a = 0.01 test based on n 16 is used, what is the probability of detecting this departure from Ho? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) (c) What value of n is required to satisfy a 0.01 and B(5.6) 0.01? (Round your answer up to the next whole number.) n samples
The desired percentage of SiO₂ in a certain type of aluminous cement is 5.5. To test whether the true average percentage is 5.5 for a particular production facility, 16 independently obtained samples are analyzed. Suppose that the percentage of SiO₂ in a sample is normally distributed with = 0.32 and that x 5.24. (Use a = 0.05.) (a) Does this indicate conclusively that the true average percentage differs from 5.5? State the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses. OH: 5.5 H₂H< 5.5 OHH-5.5 H: #25.5 O Ho: H-5.5 H₂₁: = 5.5 O Ho: -5.5 H:> 5.5 Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) P-value= State the conclusion in the problem context. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage. O Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage. O Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage. (b) If the true average percentage is = 5.6 and a level a = 0.01 test based on n 16 is used, what is the probability of detecting this departure from Ho? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) (c) What value of n is required to satisfy a 0.01 and B(5.6) 0.01? (Round your answer up to the next whole number.) n samples
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:Sheldon Ross
Chapter1: Combinatorial Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P: a. How many different 7-place license plates are possible if the first 2 places are for letters and...
Related questions
Question
PLEASE ANSWER B,C,D
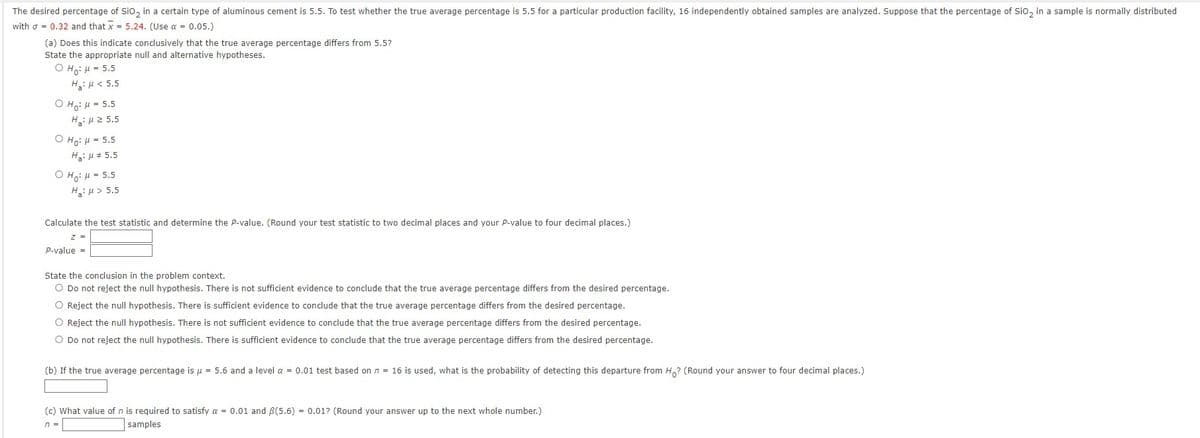
Transcribed Image Text:The desired percentage of SiO₂ in a certain type of aluminous cement is 5.5. To test whether the true average percentage is 5.5 for a particular production facility, 16 independently obtained samples are analyzed. Suppose that the percentage of SiO₂ in a sample is normally distributed
with = 0.32 and that x = 5.24. (Use a = 0.05.)
(a) Does this indicate conclusively that the true average percentage differs from 5.5?
State the appropriate null and alternative hypotheses.
OHO: H = 5.5
Hg: μ < 5.5
OH: μ = 5.5
Hg: μ 2 5.5
O Ho: H = 5.5
Ha:
5.5
OH: 5.5
H₂:μ> 5.5
Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.)
Z =
P-value=
State the conclusion in the problem context.
O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage.
O Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage.
O Reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage.
O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average percentage differs from the desired percentage.
(b) If the true average percentage is μ = 5.6 and a level a = 0.01 test based on n = 16 is used, what is the probability of detecting this departure from Ho? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(c) What value of n is required to satisfy a = 0.01 and 3(5.6) = 0.01? (Round your answer up to the next whole number.)
n =
samples
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON


A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON
