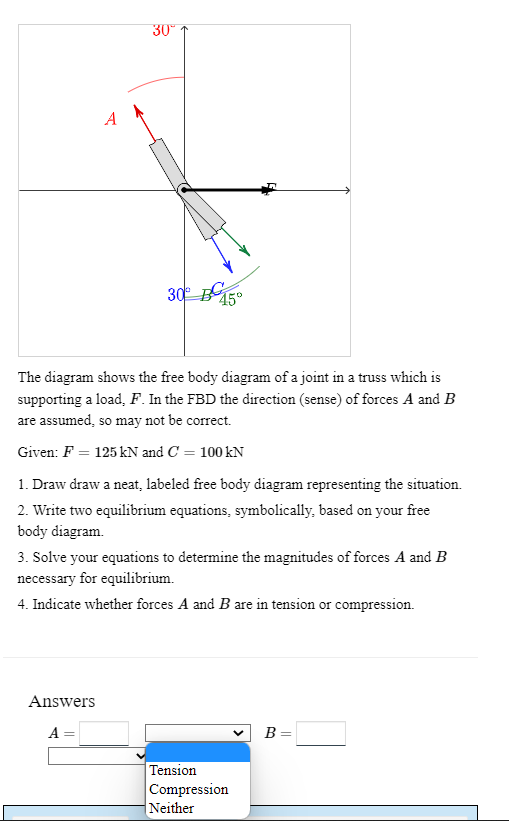
The diagram shows the free body diagram of a joint in a truss which is supporting a load, F. In the FBD the direction (sense) of forces A and B are assumed, so may not be correct. Given: F = 125 kN and C= 100 kN 1. Draw draw a neat, labeled free body diagram representing the situation. 2. Write two equilibrium equations, symbolically, based on your free body diagram. 3. Solve your equations to determine the magnitudes of forces A and B necessary for equilibrium. 4. Indicate whether forces A and B are in tension or compression.
The diagram shows the free body diagram of a joint in a truss which is supporting a load, F. In the FBD the direction (sense) of forces A and B are assumed, so may not be correct. Given: F = 125 kN and C= 100 kN 1. Draw draw a neat, labeled free body diagram representing the situation. 2. Write two equilibrium equations, symbolically, based on your free body diagram. 3. Solve your equations to determine the magnitudes of forces A and B necessary for equilibrium. 4. Indicate whether forces A and B are in tension or compression.
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter10: Virtual Work And Potential Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10.62P: The bar ABC is supported by three identical, ideal springs. Note that the springs are always...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:A
30⁰
30⁰
Answers
A
45°
The diagram shows the free body diagram of a joint in a truss which is
supporting a load, F. In the FBD the direction (sense) of forces A and B
are assumed, so may not be correct.
Given: F = 125 kN and C = 100 kN
1. Draw draw a neat, labeled free body diagram representing the situation.
2. Write two equilibrium equations, symbolically, based on your free
body diagram.
3. Solve your equations to determine the magnitudes of forces A and B
necessary for equilibrium.
4. Indicate whether forces A and B are in tension or compression.
Tension
Compression
Neither
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L