The distance d(v, w) between two vertices v and w in an undirected graph is defined as the minimal length of any path connecting these two vertices. If v and w are not connected, then d(v, w) = ∞. Now, define the diameter of the graph G = (V, E) as diam(G) = max d(v,w). v,wɛV And define the radius of the graph as rad(G) = min max d(v, w) . veV weV Prove that rad(G) < diam(G) < 2rad(G).
The distance d(v, w) between two vertices v and w in an undirected graph is defined as the minimal length of any path connecting these two vertices. If v and w are not connected, then d(v, w) = ∞. Now, define the diameter of the graph G = (V, E) as diam(G) = max d(v,w). v,wɛV And define the radius of the graph as rad(G) = min max d(v, w) . veV weV Prove that rad(G) < diam(G) < 2rad(G).
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter9: Systems Of Equations And Inequalities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12T
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Question
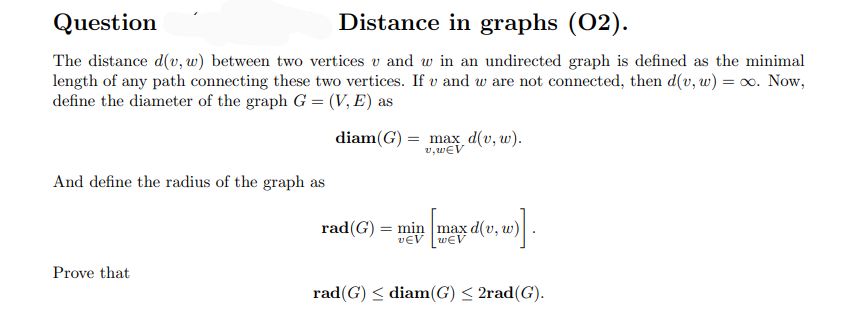
Distance in graphs (02).
The distance d(v, w) between two vertices v and w in an undirected graph is defined as the minimal
length of any path connecting these two vertices. If v and w are not connected, then d(v, w) = o. Now,
define the diameter of the graph G = (V, E) as
diam(G) = max d(v, w).
v, wEV
And define the radius of the graph as
rad(G) = min max d(v, w)
vEV wEV
Prove that
rad(G) < diam(G) < 2rad(G).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning