The estimated times and immediate predecessors for the activities in a project at Howard Umrah's retinal scanning company are given in the following table. Assume that the activity times are independent. Immediate Predecessor(s) Time (weeks) Time (weeks) Immediate Predecessor(s) Activity Activity 10 10 11 16 10 11 11 A 4 в This exercise contains only parts a, b, c, d, and e. a) Based on the activity time estimates, the expected times and variance for each of the activities are (round your response to two decimal places): Expected Time Activity A Variance b) The expected completion time of the critical path = weeks (round your response to two decimal places). The expected completion time of the path other than the critical path weeks (round your response to two decimal places). = c) The variance of the critical path = weeks (round your response to two decimal places). The variance of the path other than the critical path = weeks (round your response to two decimal places). d) If the time to complete the activities on the critical path is normally distributed, then the probability that the critical path will be finished in 22 weeks or less = (enter as a probability and round your response to two decimal places). e) If the time to complete the activities on the non critical path is normally distributed, then the probability that the non critical path will be finished in 22 weeks or less = (enter as a probability and round your response to two decimal places).
The estimated times and immediate predecessors for the activities in a project at Howard Umrah's retinal scanning company are given in the following table. Assume that the activity times are independent. Immediate Predecessor(s) Time (weeks) Time (weeks) Immediate Predecessor(s) Activity Activity 10 10 11 16 10 11 11 A 4 в This exercise contains only parts a, b, c, d, and e. a) Based on the activity time estimates, the expected times and variance for each of the activities are (round your response to two decimal places): Expected Time Activity A Variance b) The expected completion time of the critical path = weeks (round your response to two decimal places). The expected completion time of the path other than the critical path weeks (round your response to two decimal places). = c) The variance of the critical path = weeks (round your response to two decimal places). The variance of the path other than the critical path = weeks (round your response to two decimal places). d) If the time to complete the activities on the critical path is normally distributed, then the probability that the critical path will be finished in 22 weeks or less = (enter as a probability and round your response to two decimal places). e) If the time to complete the activities on the non critical path is normally distributed, then the probability that the non critical path will be finished in 22 weeks or less = (enter as a probability and round your response to two decimal places).
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter2: Introduction To Spreadsheet Modeling
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20P: Julie James is opening a lemonade stand. She believes the fixed cost per week of running the stand...
Related questions
Question
100%
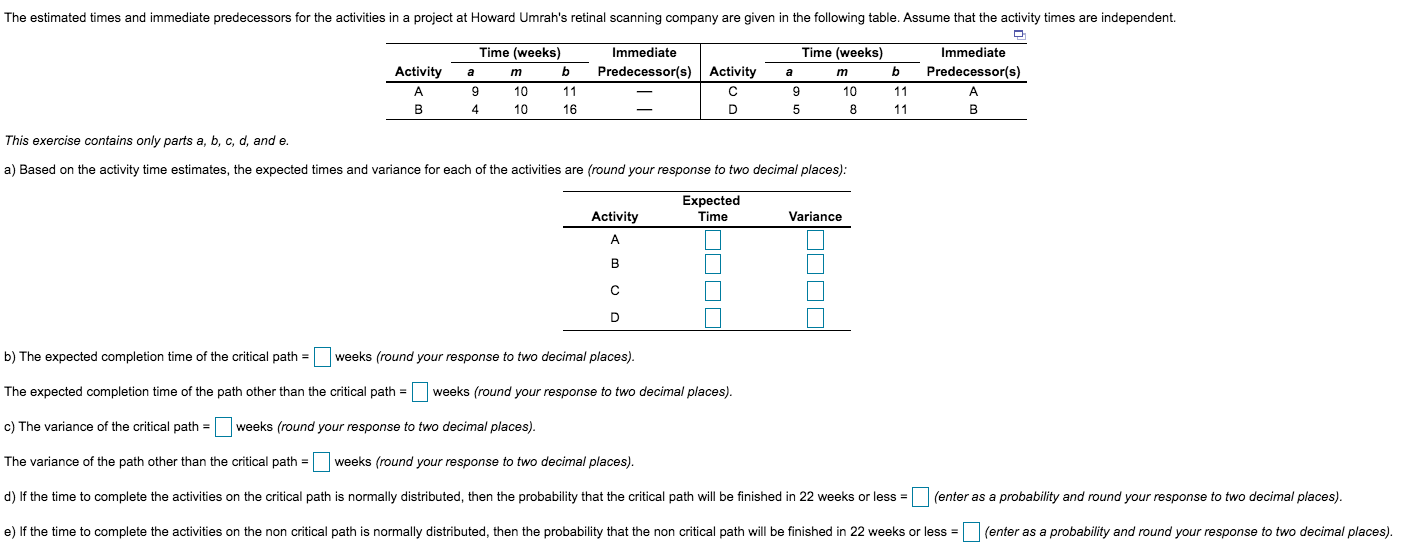
Transcribed Image Text:The estimated times and immediate predecessors for the activities in a project at Howard Umrah's retinal scanning company are given in the following table. Assume that the activity times are independent.
Immediate
Predecessor(s)
Time (weeks)
Time (weeks)
Immediate
Predecessor(s)
Activity
Activity
10
10
11
16
10
11
11
A
4
в
This exercise contains only parts a, b, c, d, and e.
a) Based on the activity time estimates, the expected times and variance for each of the activities are (round your response to two decimal places):
Expected
Time
Activity
A
Variance
b) The expected completion time of the critical path =
weeks (round your response to two decimal places).
The expected completion time of the path other than the critical path
weeks (round your response to two decimal places).
=
c) The
variance of the critical path =
weeks (round your response to two decimal places).
The variance of the path other than the critical path =
weeks (round your response to two decimal places).
d) If the time to complete the activities on the critical path is normally distributed, then the probability that the critical path will be finished in 22 weeks or less =
(enter as a probability and round your response to two decimal places).
e) If the time to complete the activities on the non critical path is normally distributed, then the probability that the non critical path will be finished in 22 weeks or less =
(enter as a probability and round your response to two decimal places).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259667473
Author:
William J Stevenson
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781259666100
Author:
F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781285869681
Author:
Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi…
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781478623069
Author:
Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:
Waveland Press, Inc.