The floor beam in Fig. 1-8 is used to support the 6-ft width of a lightweight plain concrete slab having a thickness of 4 in. The slab serves as a portion of the ceiling for the floor below, and therefore its bottom is coated with plaster. Furthermore, an 8-ft-high, 12-in.-thick lightweight solid concrete block wall is directly over the top flange of the beam. Determine the loading on the beam measured per foot of length of the beam. 12 in. 8 ft 4 in. 3 ft-3 ft7 Fig. 1-8
The floor beam in Fig. 1-8 is used to support the 6-ft width of a lightweight plain concrete slab having a thickness of 4 in. The slab serves as a portion of the ceiling for the floor below, and therefore its bottom is coated with plaster. Furthermore, an 8-ft-high, 12-in.-thick lightweight solid concrete block wall is directly over the top flange of the beam. Determine the loading on the beam measured per foot of length of the beam. 12 in. 8 ft 4 in. 3 ft-3 ft7 Fig. 1-8
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
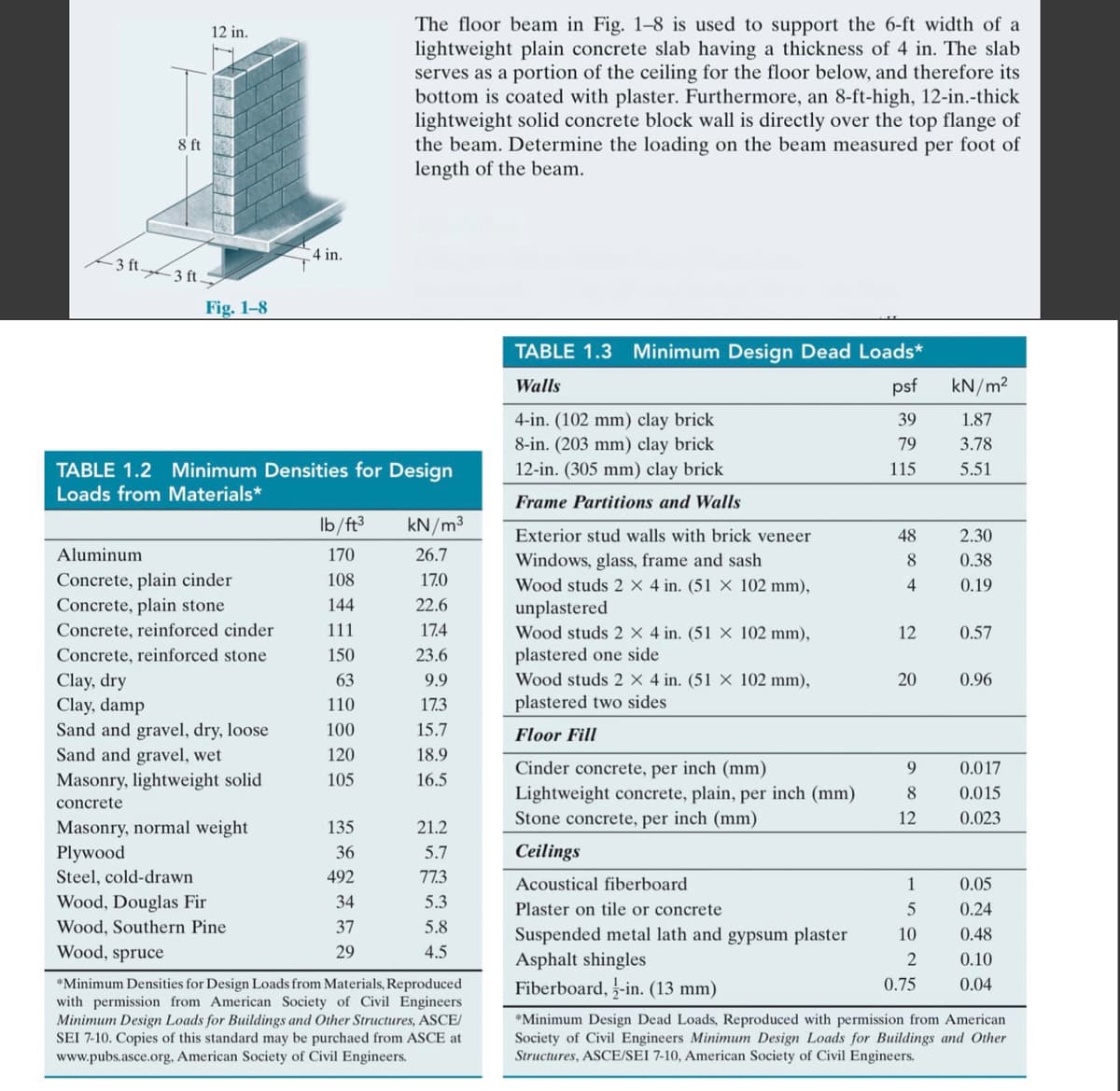
Transcribed Image Text:The floor beam in Fig. 1-8 is used to support the 6-ft width of a
lightweight plain concrete slab having a thickness of 4 in. The slab
serves as a portion of the ceiling for the floor below, and therefore its
bottom is coated with plaster. Furthermore, an 8-ft-high, 12-in.-thick
lightweight solid concrete block wall is directly over the top flange of
the beam. Determine the loading on the beam measured per foot of
length of the beam.
12 in.
8 ft
4 in.
3 ft
3 ft.
Fig. 1-8
TABLE 1.3 Minimum Design Dead Loads*
Walls
psf
kN/m2
4-in. (102 mm) clay brick
8-in. (203 mm) clay brick
12-in. (305 mm) clay brick
39
1.87
79
3.78
TABLE 1.2 Minimum Densities for Design
Loads from Materials*
115
5.51
Frame Partitions and Walls
Ib/ft3
kN/m3
Exterior stud walls with brick veneer
48
2.30
Aluminum
170
26.7
Windows, glass, frame and sash
Wood studs 2 X 4 in. (51 × 102 mm),
unplastered
Wood studs 2 X 4 in. (51 X 102 mm),
plastered one side
0.38
Concrete, plain cinder
Concrete, plain stone
108
17.0
0.19
144
22.6
Concrete, reinforced cinder
111
17.4
12
0.57
Concrete, reinforced stone
150
23.6
Wood studs 2 × 4 in. (51 × 102 mm),
Clay, dry
Clay, damp
Sand and gravel, dry, loose
Sand and gravel, wet
63
9.9
20
0.96
110
17.3
plastered two sides
100
15.7
Floor Fill
120
18.9
0.017
Cinder concrete, per inch (mm)
Lightweight concrete, plain, per inch (mm)
Stone concrete, per inch (mm)
9
Masonry, lightweight solid
105
16.5
8
0.015
concrete
12
0.023
Masonry, normal weight
Plywood
135
21.2
36
5.7
Ceilings
Steel, cold-drawn
492
77.3
Acoustical fiberboard
1
0.05
Wood, Douglas Fir
34
5.3
Plaster on tile or concrete
0.24
Wood, Southern Pine
37
5.8
Suspended metal lath and gypsum plaster
Asphalt shingles
Fiberboard, -in. (13 mm)
10
0.48
Wood, spruce
29
4.5
0.10
0.04
*Minimum Densities for Design Loads from Materials, Reproduced
with permission from American Society of Civil Engineers
Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures, ASCE/
SEI 7-10. Copies of this standard may be purchaed from ASCE at
www.pubs.asce.org, American Society of Civil Engineers.
0.75
*Minimum Design Dead Loads, Reproduced with permission from American
Society of Civil Engineers Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other
Structures, ASCE/SEI 7-10, American Society of Civil Engineers.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning