The following graph shows the value of a stock's dividends over time. The stock's current dividend is $1.00 per share, and dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 4.50% per year . The intrinsic value of a stock should equal the sum of the present value (PV) of all of the dividends that a stock is supposed to pay in the future, but many people find it difficult to imagine adding up an infinite number of dividends Calculate the present value (PV) of the dividend paid today (Do) and the discounted value of the dividends expected to be paid 10 and 20 years from now (D1g and D2g). Assume that the stock's required return (r) is 5.40 % Note: Carry and round the calculations to four decimal places. Time Period Dividend's Expected Expected Dividend's Future Value Present Value Now End of Year 10 End of Year 20 End of Year 50 Using the blue curve (circle symbols), plot the future value of each of the expected future dividends for years 10, 20, and 50. The resulting curve will illustrate how the FV of a particular dividend payment will increase depending on how far from today the dividend is expected to be received Note: Round each of the discounted values of the of dividends to the nearest tenth decimal place before plotting it on the graph. You can mouse over the points in the graph to see their coordinates. DIVIDENDS I$ 10.00 Expected Dividends 8.00 FV of Dividends 6.00 4,00 2,00 PV of Dividends 0.00 10 30 50 60 YEARS 40 20
The following graph shows the value of a stock's dividends over time. The stock's current dividend is $1.00 per share, and dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 4.50% per year . The intrinsic value of a stock should equal the sum of the present value (PV) of all of the dividends that a stock is supposed to pay in the future, but many people find it difficult to imagine adding up an infinite number of dividends Calculate the present value (PV) of the dividend paid today (Do) and the discounted value of the dividends expected to be paid 10 and 20 years from now (D1g and D2g). Assume that the stock's required return (r) is 5.40 % Note: Carry and round the calculations to four decimal places. Time Period Dividend's Expected Expected Dividend's Future Value Present Value Now End of Year 10 End of Year 20 End of Year 50 Using the blue curve (circle symbols), plot the future value of each of the expected future dividends for years 10, 20, and 50. The resulting curve will illustrate how the FV of a particular dividend payment will increase depending on how far from today the dividend is expected to be received Note: Round each of the discounted values of the of dividends to the nearest tenth decimal place before plotting it on the graph. You can mouse over the points in the graph to see their coordinates. DIVIDENDS I$ 10.00 Expected Dividends 8.00 FV of Dividends 6.00 4,00 2,00 PV of Dividends 0.00 10 30 50 60 YEARS 40 20
Chapter7: Common Stock: Characteristics, Valuation, And Issuance
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
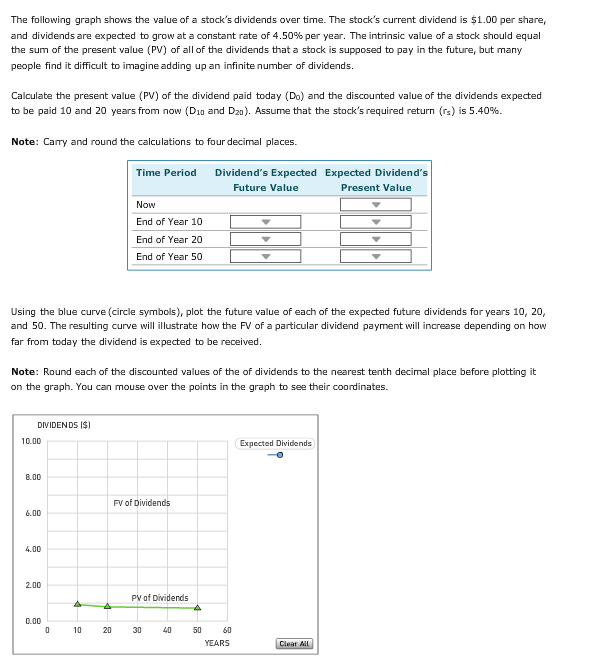
Transcribed Image Text:The following graph shows the value of a stock's dividends over time. The stock's current dividend is $1.00 per share,
and dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 4.50% per year . The intrinsic value of a stock should equal
the sum of the present value (PV) of all of the dividends that a stock is supposed to pay in the future, but many
people find it difficult to imagine adding up an infinite number of dividends
Calculate the present value (PV) of the dividend paid today (Do) and the discounted value of the dividends expected
to be paid 10 and 20 years from now (D1g and D2g). Assume that the stock's required return (r) is 5.40 %
Note: Carry and round the calculations to four decimal places.
Time Period
Dividend's Expected Expected Dividend's
Future Value
Present Value
Now
End of Year 10
End of Year 20
End of Year 50
Using the blue curve (circle symbols), plot the future value of each of the expected future dividends for years 10, 20,
and 50. The resulting curve will illustrate how the FV of a particular dividend payment will increase depending on how
far from today the dividend is expected to be received
Note: Round each of the discounted values of the of dividends to the nearest tenth decimal place before plotting it
on the graph. You can mouse over the points in the graph to see their coordinates.
DIVIDENDS I$
10.00
Expected Dividends
8.00
FV of Dividends
6.00
4,00
2,00
PV of Dividends
0.00
10
30
50
60
YEARS
40
20
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

