The form of the argument is: vx (P(x) → (Q(x) v R(x))) -R(John) John is a particular element P(John) .: 3x Q(x) Select the definitions for predicates P, Q, and R. P(x): Pick Q(x): Pick
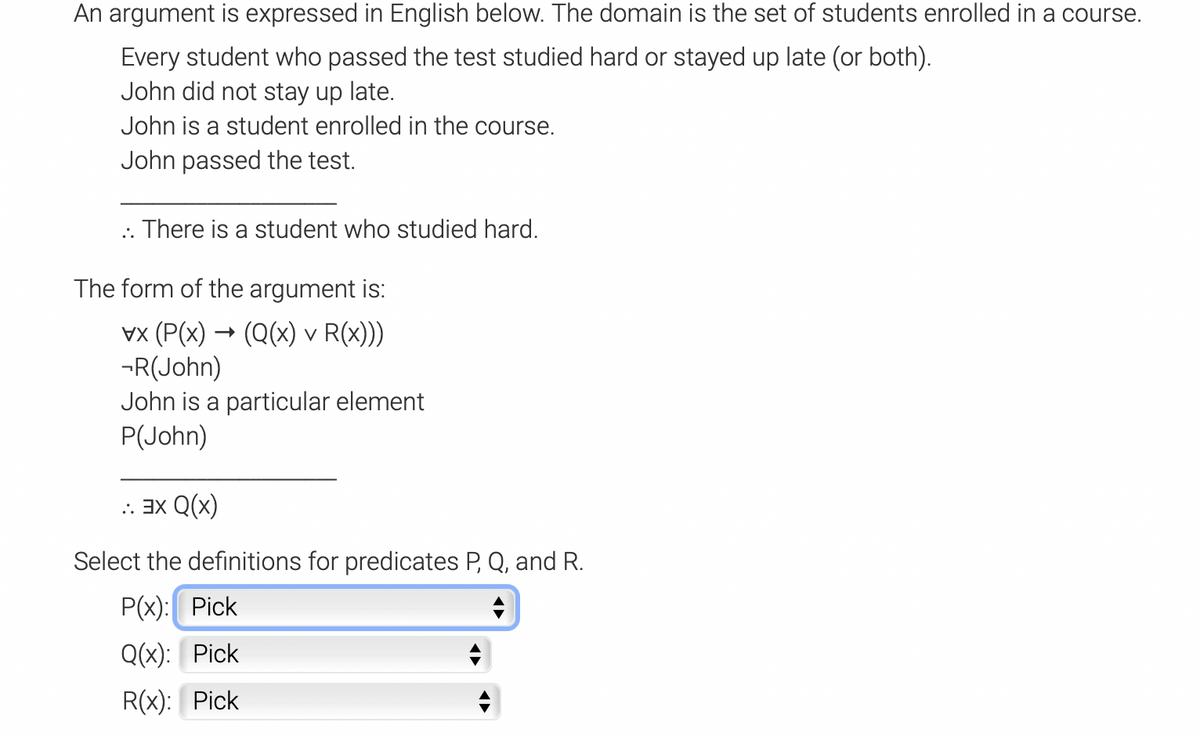
In this question, the concept of argument is applied.
Argument in Premises
Every argument having true premises and a wrong conclusion is, by definition, invalid. When the premises are true, invalidity is not any assurance of a real conclusion. In an invalid argument, true premises can result in either a real or false conclusion. providing all of the premises are true can a sound argument have an accurate conclusion. As a result, a sound argument can have a false conclusion if a minimum of one in every one of the premises is inaccurate. There cannot be all true premises and a false conclusion in a very valid argument. As a result, a legitimate argument cannot have all true premises if it's a false conclusion. As a result, a minimum of one in every one of the premises must be erroneous.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps




