The Hermite polynomials Hn(x) are special functions that are extremely im- portant in quantum mechanics. The Hn(x) may be defined by: P(x, h) = exp(2rh – h²) = H,(x)h". n=0 Show that 2x + 2h 0. %3D and hence H" («) — 2 Н, (х) + 2nH, (2) — 0.
The Hermite polynomials Hn(x) are special functions that are extremely im- portant in quantum mechanics. The Hn(x) may be defined by: P(x, h) = exp(2rh – h²) = H,(x)h". n=0 Show that 2x + 2h 0. %3D and hence H" («) — 2 Н, (х) + 2nH, (2) — 0.
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter4: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section4.6: Applications And The Perron-frobenius Theorem
Problem 70EQ
Related questions
Question
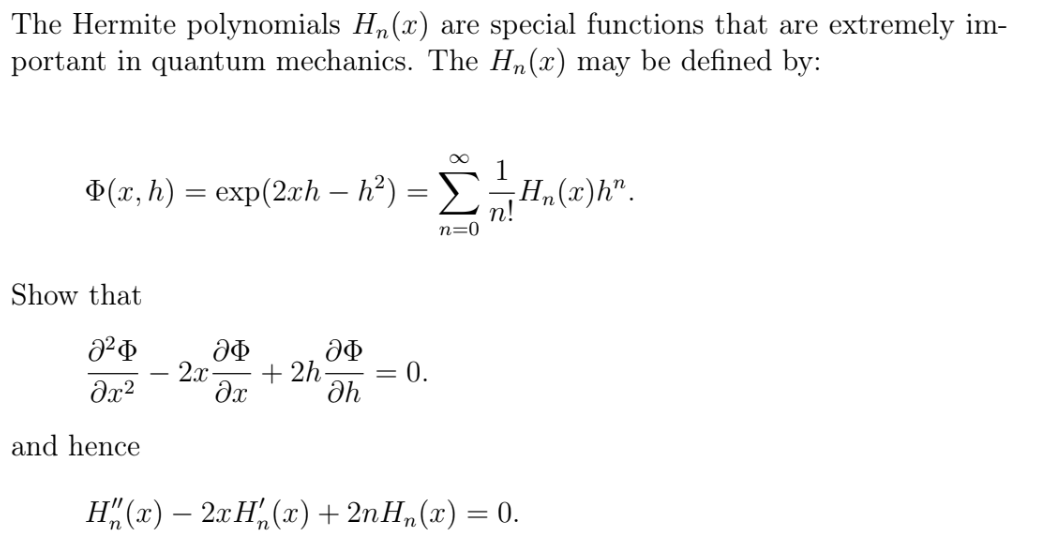
Transcribed Image Text:The Hermite polynomials Hn(x) are special functions that are extremely im-
portant in quantum mechanics. The Hn(x) may be defined by:
P(x, h) = exp(2rh – h²) =
H,(x)h".
n=0
Show that
2x
+ 2h
0.
%3D
and hence
H" («) — 2 Н, (х) + 2nH, (2) — 0.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning