The inner product in V is defined according to the formula (u, v) 1V₂ - U₂v₁ +2u₂v₂. Let u (4, 1) and v = (2,3). i. Show that u and v form an orthogonal basis in the inner product space Use this basis to find an orthonormal basis by normalizing each vector. ii. Use the inner product defined in part b) to express the vector (1,1). as a linear combination of the orthonormal basis vectors obtained in part i. W: =
The inner product in V is defined according to the formula (u, v) 1V₂ - U₂v₁ +2u₂v₂. Let u (4, 1) and v = (2,3). i. Show that u and v form an orthogonal basis in the inner product space Use this basis to find an orthonormal basis by normalizing each vector. ii. Use the inner product defined in part b) to express the vector (1,1). as a linear combination of the orthonormal basis vectors obtained in part i. W: =
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter5: Orthogonality
Section5.1: Orthogonality In Rn
Problem 34EQ
Related questions
Question
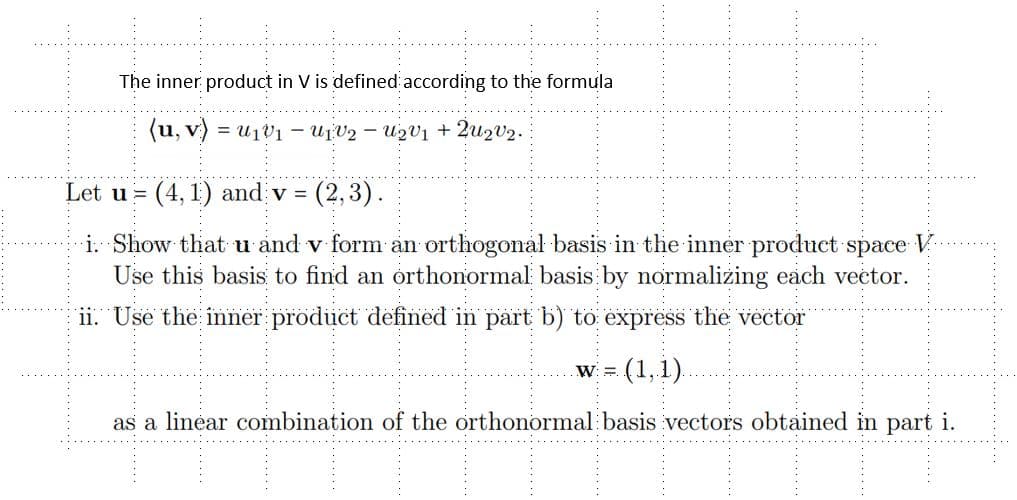
Transcribed Image Text:The inner product in V is defined according to the formula
(u, v)
1V2 - U₂v₁ + 2U₂V₂.
Let u (4,1) and v = (2,3).
i. Show that u and v form an orthogonal basis in the inner product space
Use this basis to find an orthonormal basis by normalizing each vector.
11. Use the inner product defined in part b) to express the vector
(1,1).
as a linear combination of the orthonormal basis vectors obtained in part i.
W: =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage