The linear approximation L(x) of a differentiable function f(x) near the point x = a is L(x) = f'(a) + f (a)(x – a).
The linear approximation L(x) of a differentiable function f(x) near the point x = a is L(x) = f'(a) + f (a)(x – a).
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
ChapterA: Appendix
SectionA.2: Geometric Constructions
Problem 10P: A soda can has a volume of 25 cubic inches. Let x denote its radius and h its height, both in...
Related questions
Question
true or false and why
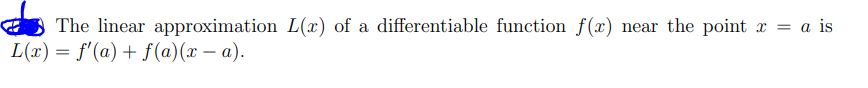
Transcribed Image Text:The linear approximation L(x) of a differentiable function f(x) near the point x = a is
L(x) = f'(a) + f (a)(x – a).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning