The management of Zigby Manufacturing prepared the following balance sheet for March 31. ZIGBY MANUFACTURING Balance Sheet March 31 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Raw materials inventory. Finished goods inventory Equipment Less: Accumulated depreciation $ 2,160,000 540,000 $144,000 Liabilities 1,239,840 354,600 1,171,944 1,620,000 Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Loan payable Long-term note payable Equity Common stock Retained earnings $ 723,600 12,000 1,800,000 1,206,000 788,784 $ 2,535,600 1,994,784 $4,530,384 Total assets $4,530,384 Total liabilities and equity To prepare a master budget for April, May, and June, management gathers the following information. a. Sales for March total 73,800 units. Budgeted sales in units follow: April, 73,800; May, 70,200; June, 72,000; and July, 73,800. The product's selling price is $24.00 per unit and its total product cost is $19.85 per unit. b. Raw materials inventory consists solely of direct materials that cost $20 per pound. Company policy calls for a given month's ending materials inventory to equal 50% of the next month's direct materials requirements. The March 31 raw materials inventory is 17,730 pounds. The budgeted June 30 ending raw materials inventory is 14,400 pounds. Each finished unit requires 0.50 pound of direct materials. c. Company policy calls for a given month's ending finished goods inventory to equal 80% of the next month's budgeted unit sales. The March 31 finished goods inventory is 59,040 units. d. Each finished unit requires 0.50 hour of direct labor at a rate of $15 per hour. e. The predetermined variable overhead rate is $2.70 per direct labor hour. Depreciation of $72,000 per month is the only fixed factory overhead item. f. Sales commissions of 8% of sales are paid in the month of the sales. The sales manager's monthly salary is $10,800. g. Monthly general and administrative expenses include $43,200 for administrative salaries and 0.9% monthly interest on the long- term note payable. h. The company budgets 30% of sales to be for cash and the remaining 70% on credit. Credit sales are collected in full in the month following the sale (no credit sales are collected in the month of sale). i. All raw materials purchases are on credit, and accounts payable are solely tied to raw materials purchases. Raw materials purchases are fully paid in the next month (none are paid in the month of purchase). j. The minimum ending cash balance for all months is $144,000. If necessary, the company borrows enough cash using a loan to reach the minimum. Loans require an interest payment of 1% at each month-end (before any repayment). If the month-end preliminary cash balance exceeds the minimum, the excess will be used to repay any loans. Factory overhead budget. Note: Round variable overhead rate values to 2 decimal places. ZIGBY MANUFACTURING Factory Overhead Budget April Direct labor hours needed. Variable overhead rate per direct labor hour Budgeted variable overhead k. Dividends of $36,000 are budgeted to be declared and paid in May. I. No cash payments for income taxes are budgeted in the second calendar quarter. Income tax will be assessed at 35% in the Budgeted fixed overhead udgotod t aid in the thire rd calendar May June Totall
The management of Zigby Manufacturing prepared the following balance sheet for March 31. ZIGBY MANUFACTURING Balance Sheet March 31 Assets Cash Accounts receivable Raw materials inventory. Finished goods inventory Equipment Less: Accumulated depreciation $ 2,160,000 540,000 $144,000 Liabilities 1,239,840 354,600 1,171,944 1,620,000 Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Loan payable Long-term note payable Equity Common stock Retained earnings $ 723,600 12,000 1,800,000 1,206,000 788,784 $ 2,535,600 1,994,784 $4,530,384 Total assets $4,530,384 Total liabilities and equity To prepare a master budget for April, May, and June, management gathers the following information. a. Sales for March total 73,800 units. Budgeted sales in units follow: April, 73,800; May, 70,200; June, 72,000; and July, 73,800. The product's selling price is $24.00 per unit and its total product cost is $19.85 per unit. b. Raw materials inventory consists solely of direct materials that cost $20 per pound. Company policy calls for a given month's ending materials inventory to equal 50% of the next month's direct materials requirements. The March 31 raw materials inventory is 17,730 pounds. The budgeted June 30 ending raw materials inventory is 14,400 pounds. Each finished unit requires 0.50 pound of direct materials. c. Company policy calls for a given month's ending finished goods inventory to equal 80% of the next month's budgeted unit sales. The March 31 finished goods inventory is 59,040 units. d. Each finished unit requires 0.50 hour of direct labor at a rate of $15 per hour. e. The predetermined variable overhead rate is $2.70 per direct labor hour. Depreciation of $72,000 per month is the only fixed factory overhead item. f. Sales commissions of 8% of sales are paid in the month of the sales. The sales manager's monthly salary is $10,800. g. Monthly general and administrative expenses include $43,200 for administrative salaries and 0.9% monthly interest on the long- term note payable. h. The company budgets 30% of sales to be for cash and the remaining 70% on credit. Credit sales are collected in full in the month following the sale (no credit sales are collected in the month of sale). i. All raw materials purchases are on credit, and accounts payable are solely tied to raw materials purchases. Raw materials purchases are fully paid in the next month (none are paid in the month of purchase). j. The minimum ending cash balance for all months is $144,000. If necessary, the company borrows enough cash using a loan to reach the minimum. Loans require an interest payment of 1% at each month-end (before any repayment). If the month-end preliminary cash balance exceeds the minimum, the excess will be used to repay any loans. Factory overhead budget. Note: Round variable overhead rate values to 2 decimal places. ZIGBY MANUFACTURING Factory Overhead Budget April Direct labor hours needed. Variable overhead rate per direct labor hour Budgeted variable overhead k. Dividends of $36,000 are budgeted to be declared and paid in May. I. No cash payments for income taxes are budgeted in the second calendar quarter. Income tax will be assessed at 35% in the Budgeted fixed overhead udgotod t aid in the thire rd calendar May June Totall
Century 21 Accounting General Journal
11th Edition
ISBN:9781337680059
Author:Gilbertson
Publisher:Gilbertson
Chapter20: Accounting For Inventory
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3AP
Related questions
Question
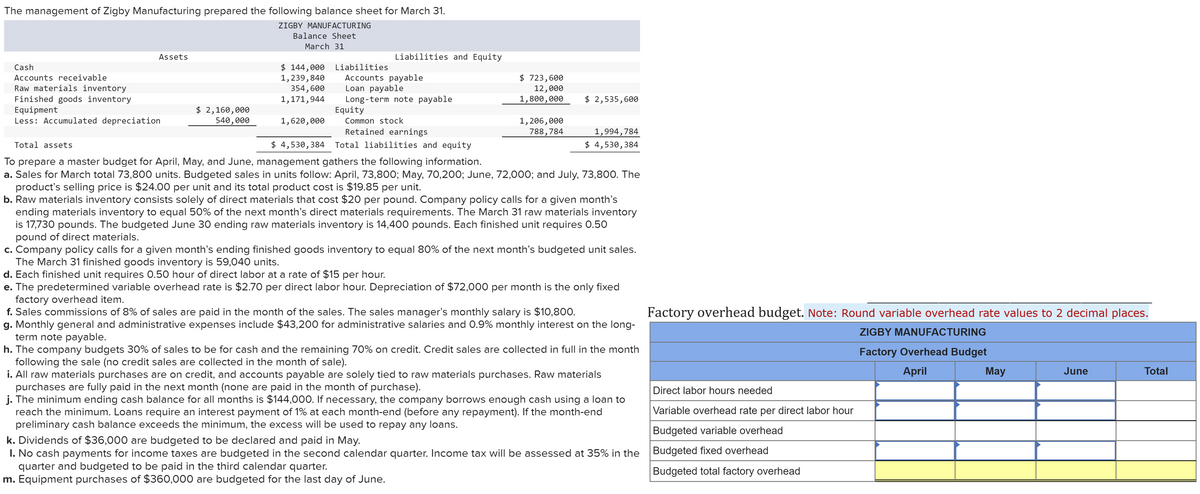
Transcribed Image Text:The management of Zigby Manufacturing prepared the following balance sheet for March 31.
ZIGBY MANUFACTURING
Balance Sheet
March 31
Assets
Cash
Accounts receivable
Raw materials inventory
Finished goods inventory
Equipment
Less: Accumulated depreciation
$ 2,160,000
540,000
$ 144,000 Liabilities
1,239,840
354,600
1,171,944
1,620,000
Liabilities and Equity
Accounts payable
Loan payable
Long-term note payable
Equity
Common stock
Retained earnings
$ 723,600
12,000
1,800,000
1,206,000
788,784
$ 2,535,600
1,994,784
$ 4,530,384
Total assets
$4,530,384 Total liabilities and equity
To prepare a master budget for April, May, and June, management gathers the following information.
a. Sales for March total 73,800 units. Budgeted sales in units follow: April, 73,800; May, 70,200; June, 72,000; and July, 73,800. The
product's selling price is $24.00 per unit and its total product cost is $19.85 per unit.
b. Raw materials inventory consists solely of direct materials that cost $20 per pound. Company policy calls for a given month's
ending materials inventory to equal 50% of the next month's direct materials requirements. The March 31 raw materials inventory
is 17,730 pounds. The budgeted June 30 ending raw materials inventory is 14,400 pounds. Each finished unit requires 0.50
pound of direct materials.
c. Company policy calls for a given month's ending finished goods inventory to equal 80% of the next month's budgeted unit sales.
The March 31 finished goods inventory is 59,040 units.
d. Each finished unit requires 0.50 hour of direct labor at a rate of $15 per hour.
e. The predetermined variable overhead rate is $2.70 per direct labor hour. Depreciation of $72,000 per month is the only fixed
factory overhead item.
f. Sales commissions of 8% of sales are paid in the month of the sales. The sales manager's monthly salary is $10,800.
g. Monthly general and administrative expenses include $43,200 for administrative salaries and 0.9% monthly interest on the long-
term note payable.
h. The company budgets 30% of sales to be for cash and the remaining 70% on credit. Credit sales are collected in full in the month
following the sale (no credit sales are collected in the month of sale).
i. All raw materials purchases are on credit, and accounts payable are solely tied to raw materials purchases. Raw materials
purchases are fully paid in the next month (none are paid in the month of purchase).
j. The minimum ending cash balance for all months is $144,000. If necessary, the company borrows enough cash using a loan to
reach the minimum. Loans require an interest payment of 1% at each month-end (before any repayment). If the month-end
preliminary cash balance exceeds the minimum, the excess will be used to repay any loans.
k. Dividends of $36,000 are budgeted to be declared and paid in May.
I. No cash payments for income taxes are budgeted in the second calendar quarter. Income tax will be assessed at 35% in the
quarter and budgeted to be paid in the third calendar quarter.
m. Equipment purchases of $360,000 are budgeted for the last day of June.
Factory overhead budget. Note: Round variable overhead rate values to 2 decimal places.
ZIGBY MANUFACTURING
Factory Overhead Budget
April
Direct labor hours needed
Variable overhead rate per direct labor hour
Budgeted variable overhead
Budgeted fixed overhead
Budgeted total factory overhead
May
June
Total
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning