The next two questions refer to the following situation: Two masses travel at the same speed, and they collide at the origin. After the collision, the two masses are stuck together. The mass, M₁, of the object traveling in the positive x-direction is 1 kg. After the collision the combined masses travel at 30° with respect to the x-axis, as shown. 2. The kinetic energy after the collision is + 0=30° Equal to the kinetic energy before the collision. OSmaller than the kinetic energy before the collision. Larger than the kinetic energy before the collision.
The next two questions refer to the following situation: Two masses travel at the same speed, and they collide at the origin. After the collision, the two masses are stuck together. The mass, M₁, of the object traveling in the positive x-direction is 1 kg. After the collision the combined masses travel at 30° with respect to the x-axis, as shown. 2. The kinetic energy after the collision is + 0=30° Equal to the kinetic energy before the collision. OSmaller than the kinetic energy before the collision. Larger than the kinetic energy before the collision.
Related questions
Question
Please explain with steps
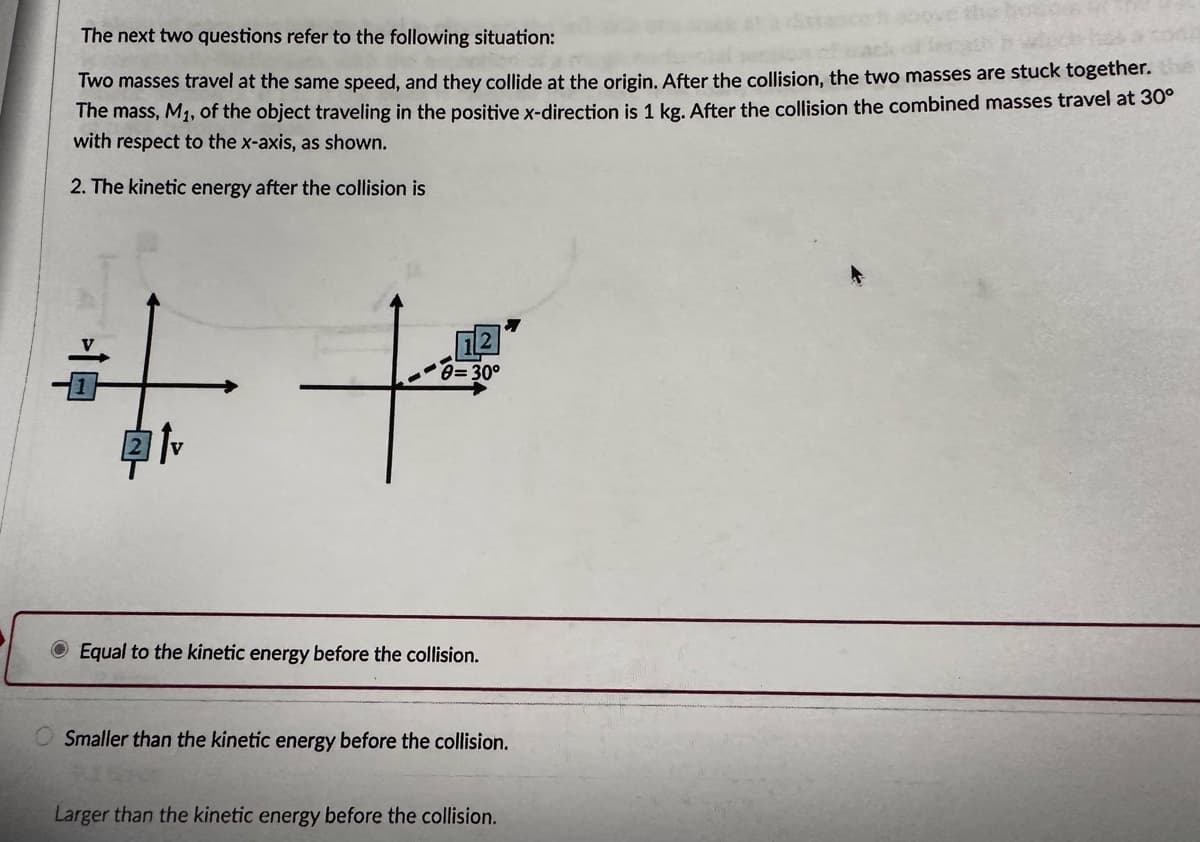
Transcribed Image Text:The next two questions refer to the following situation:
Two masses travel at the same speed, and they collide at the origin. After the collision, the two masses are stuck together.
The mass, M₁, of the object traveling in the positive x-direction is 1 kg. After the collision the combined masses travel at 30°
with respect to the x-axis, as shown.
2. The kinetic energy after the collision is
++
0=30°
Equal to the kinetic energy before the collision.
OSmaller than the kinetic energy before the collision.
Larger than the kinetic energy before the collision.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
