The rate of proliferation (that is, reproduction) for the cells in a tumor varies depending on the size of the tumor. The Gompertz growth model is sometimes used to model this growth. According to the Gompertz model the total number of divisions occurring in 1 hour, R, depends on the number of cells, N, through the formula given below. R(N) = N In The positive constants, d and A, both depend on the type of tumor, whether it is being treated or not, and so on. (a) Assume that d-A=1. Use a table or a graph to show that lim-R(N) = 0. Complete the table of values to show that lim-R(N)=0. (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed.) N 0.1 0.01 0.001 R(N) O
The rate of proliferation (that is, reproduction) for the cells in a tumor varies depending on the size of the tumor. The Gompertz growth model is sometimes used to model this growth. According to the Gompertz model the total number of divisions occurring in 1 hour, R, depends on the number of cells, N, through the formula given below. R(N) = N In The positive constants, d and A, both depend on the type of tumor, whether it is being treated or not, and so on. (a) Assume that d-A=1. Use a table or a graph to show that lim-R(N) = 0. Complete the table of values to show that lim-R(N)=0. (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed.) N 0.1 0.01 0.001 R(N) O
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.7: Applications
Problem 13EQ
Related questions
Question
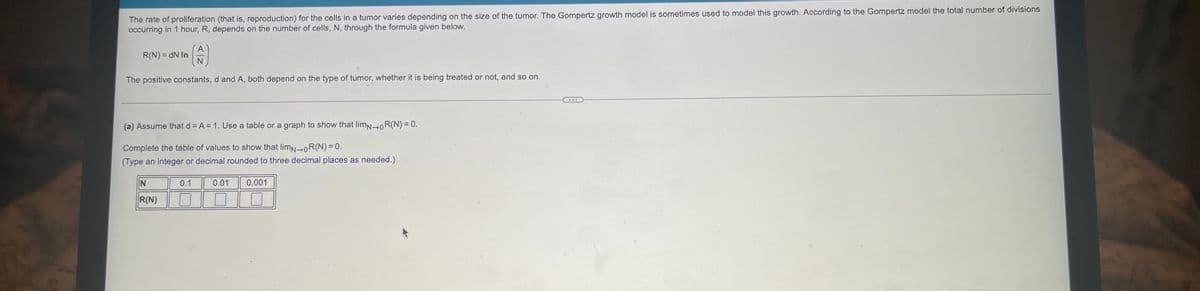
Transcribed Image Text:The rate of proliferation (that is, reproduction) for the cells in a tumor varies depending on the size of the tumor. The Gompertz growth model is sometimes used to model this growth. According to the Gompertz model the total number of divisions
occurring in 1 hour, R, depends on the number of cells, N, through the formula given below.
R(N) = dN In
(A)
N
The positive constants, d and A, both depend on the type of tumor, whether it is being treated or not, and so on.
(a) Assume that d= A= 1. Use a table or a graph to show that limN-OR(N) = 0.
Complete the table of values to show that limN-OR(N) = 0.
(Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed.)
N
0.1
0.01 0.001
R(N)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage