The sliding glass door rolls on the two small lower wheels A and B. Under normal conditions the upper wheels do not touch their horizontal guide. (a) Compute the force P required to slide the door at a steady speed if wheel A becomes "frozen" and does not turn in its bearing. (b) Rework the problem if wheel B becomes frozen instead of wheel A. The coefficient of kinetic friction between a frozen wheel and the supporting surface is 0.33, and the center of mass of the 118-lb door is at its geometric center. Neglect the small diameter of the wheels. Answer: A (a) P = i (b) P- i 28" B 6" P lb lb 38" 38"
The sliding glass door rolls on the two small lower wheels A and B. Under normal conditions the upper wheels do not touch their horizontal guide. (a) Compute the force P required to slide the door at a steady speed if wheel A becomes "frozen" and does not turn in its bearing. (b) Rework the problem if wheel B becomes frozen instead of wheel A. The coefficient of kinetic friction between a frozen wheel and the supporting surface is 0.33, and the center of mass of the 118-lb door is at its geometric center. Neglect the small diameter of the wheels. Answer: A (a) P = i (b) P- i 28" B 6" P lb lb 38" 38"
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter7: Dry Friction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.72P
Related questions
Question
b.5
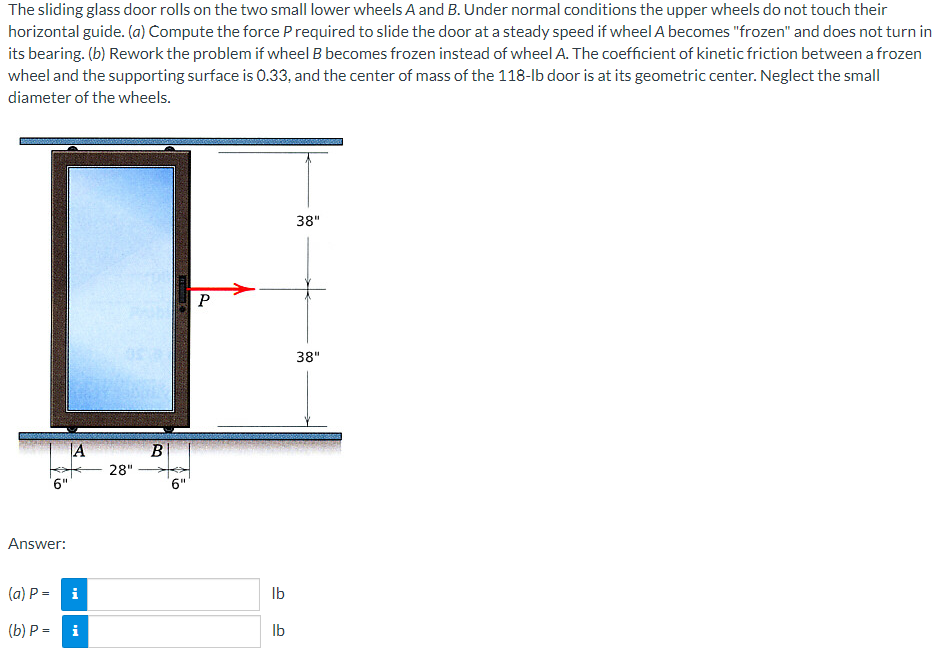
Transcribed Image Text:The sliding glass door rolls on the two small lower wheels A and B. Under normal conditions the upper wheels do not touch their
horizontal guide. (a) Compute the force P required to slide the door at a steady speed if wheel A becomes "frozen" and does not turn in
its bearing. (b) Rework the problem if wheel B becomes frozen instead of wheel A. The coefficient of kinetic friction between a frozen
wheel and the supporting surface is 0.33, and the center of mass of the 118-lb door is at its geometric center. Neglect the small
diameter of the wheels.
Answer:
(a) P =
(b) P =
A
i
i
28"
B
6"
P
lb
lb
38"
38"
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L