The starting length of a shaft is 25.00 mm. This shaft is to be inserted into a hole in an expansion fit assembly operation. To be readily inserted, the shaft must be reduced in length by cooling. Determine the temperature to which the shaft must be reduced from room temperature (20° C) in order to reduce its length to 24.98 mm. Refer to the Table below.
The starting length of a shaft is 25.00 mm. This shaft is to be inserted into a hole in an expansion fit assembly operation. To be readily inserted, the shaft must be reduced in length by cooling. Determine the temperature to which the shaft must be reduced from room temperature (20° C) in order to reduce its length to 24.98 mm. Refer to the Table below.
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter1: Basic Modes Of Heat Transfer
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.68P
Related questions
Question
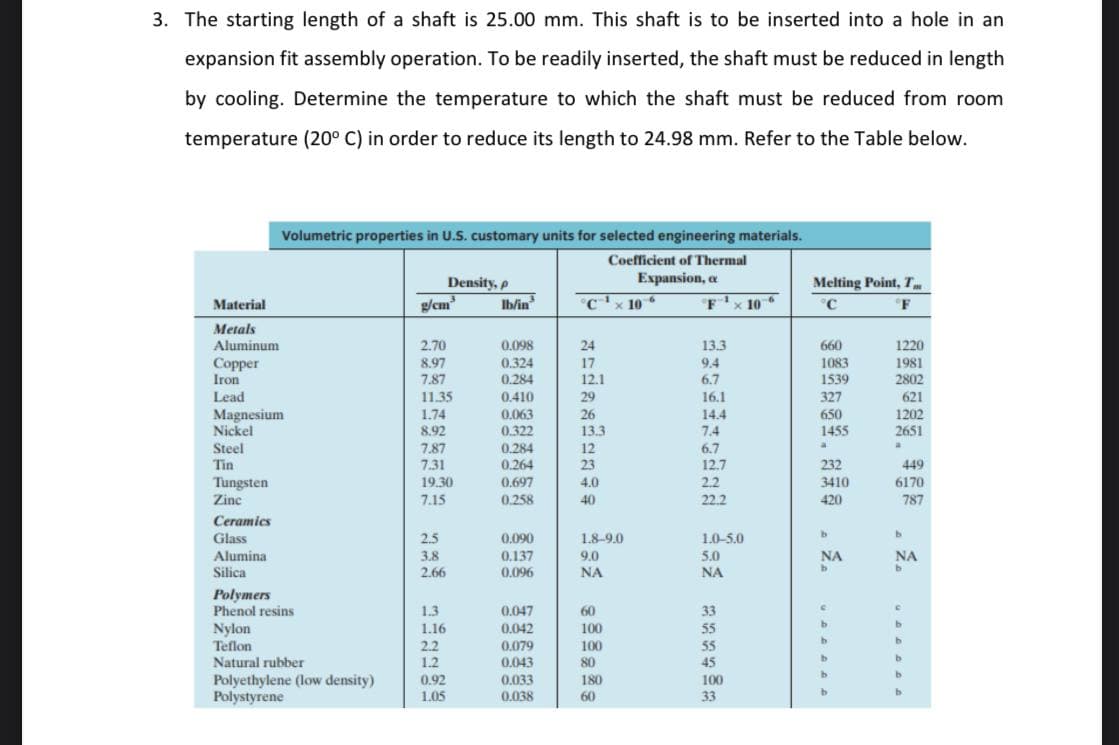
Transcribed Image Text:3. The starting length of a shaft is 25.00 mm. This shaft is to be inserted into a hole in an
expansion fit assembly operation. To be readily inserted, the shaft must be reduced in length
by cooling. Determine the temperature to which the shaft must be reduced from room
temperature (20° C) in order to reduce its length to 24.98 mm. Refer to the Table below.
Volumetric properties in U.S. customary units for selected engineering materials.
Coefficient of Thermal
Density, p
Expansion, a
Melting Point, T
Material
g/cm
Ib/in
c'x 10
x 10
°C
'F
Metals
Aluminum
2.70
0.098
24
13.3
660
1220
Copper
Iron
0.324
0.284
0.410
8.97
17
9.4
1083
1981
2802
7.87
12.1
6.7
1539
Lead
11.35
29
16.1
327
621
Magnesium
Nickel
1.74
0.063
0.322
0.284
26
14.4
7.4
650
1202
8.92
13.3
1455
2651
7.87
7.31
19.30
7.15
Steel
Tin
12
23
6.7
0.264
12.7
232
449
Tungsten
Zinc
0.697
4.0
2.2
3410
6170
0.258
40
22.2
420
787
Ceramics
b.
Glass
2.5
0,090
1.8-9.0
1.0-5.0
Alumina
3.8
0.137
9.0
5.0
NA
NA
b.
Silica
2.66
0,096
NA
NA
Polymers
Phenol resins
Nylon
Teflon
Natural rubber
1.3
0.047
60
33
b
1.16
0.042
100
55
2.2
0.079
100
55
1.2
0.043
80
45
Polyethylene (low density)
Polystyrene
0.033
0.038
0.92
180
100
1.05
60
33
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning