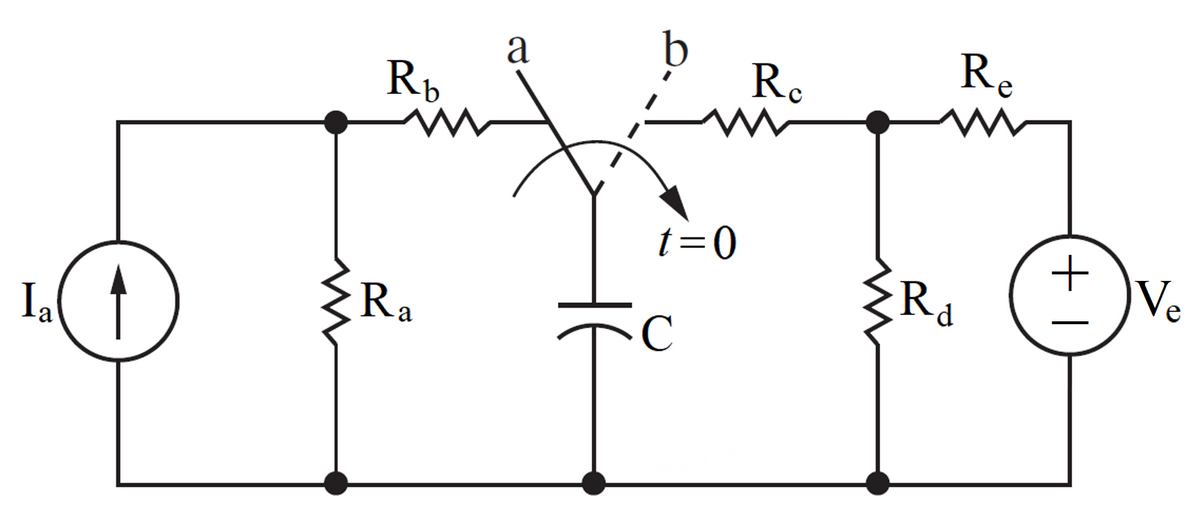
The switch has been in position a for a long time when it is moved to position b at time t = 0. The values for the circuit are as follows: Ia = 0.250A, Ra = 44.0Ω, Rb = 37.0Ω, Rc = 24.0Ω, Rd = 20.0Ω, Re = 30.0Ω, Ve = 45.0V, C = 40.0μF. Recall that for a capacitor, i=C·dv/dt. (Hint: source transformations might help as well.) When the switch has been in position a for a long time, solve for the voltage across Rb, and the voltage across the capacitor. Solve for the voltage across the capacitor immediately after the switch is moved to position b at t = 0, and explain why. After the switch is moved to position b, solve for the time constant of the circuit. Solve for the voltage across the capacitor v(t) as a function of time, when t ≥ 0.
The switch has been in position a for a long time when it is moved to position b at time t = 0. The values for the circuit are as follows: Ia = 0.250A, Ra = 44.0Ω, Rb = 37.0Ω, Rc = 24.0Ω, Rd = 20.0Ω, Re = 30.0Ω, Ve = 45.0V, C = 40.0μF. Recall that for a capacitor, i=C·dv/dt. (Hint: source transformations might help as well.) When the switch has been in position a for a long time, solve for the voltage across Rb, and the voltage across the capacitor. Solve for the voltage across the capacitor immediately after the switch is moved to position b at t = 0, and explain why. After the switch is moved to position b, solve for the time constant of the circuit. Solve for the voltage across the capacitor v(t) as a function of time, when t ≥ 0.
Chapter28: Overcurrent Protection–fuses And Circuit Breakers
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21R: Overcurrent devices must be accessible. (True) (False). (Circle the correct response.)
Related questions
Question
The switch has been in position a for a long time when it is moved to position b at time t = 0. The values for the circuit are as follows:
Ia = 0.250A, Ra = 44.0Ω, Rb = 37.0Ω, Rc = 24.0Ω, Rd = 20.0Ω, Re = 30.0Ω, Ve = 45.0V, C = 40.0μF.
Recall that for a capacitor, i=C·dv/dt. (Hint: source transformations might help as well.)
- When the switch has been in position a for a long time, solve for the voltage across Rb, and the voltage across the capacitor.
- Solve for the voltage across the capacitor immediately after the switch is moved to position b at t = 0, and explain why.
- After the switch is moved to position b, solve for the time constant of the circuit.
- Solve for the voltage across the capacitor v(t) as a function of time, when t ≥ 0.
Transcribed Image Text:Ia( ↑
R₁
Ra
a
t=0
C
Re
{Rd
Re
+ I
Ve
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 13 images

Recommended textbooks for you

EBK ELECTRICAL WIRING RESIDENTIAL
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337516549
Author:
Simmons
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

EBK ELECTRICAL WIRING RESIDENTIAL
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337516549
Author:
Simmons
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT