The system shown below consists of two disks, each with a mass of 1.00 kg, and a Hooke's Law spring with k= 50.0 N/m. See figure. In the initial figure, the speeds are known, and the spring is stretched 20.0 cm. In the final figure, the speeds are unknown, and the spring is compressed an unknown amount. Find vi, v2, and the final compression in the spring. You may assume that the system moves on a frictionless, horizontal plane, that system momentum is conserved, and that energy is conserved.
The system shown below consists of two disks, each with a mass of 1.00 kg, and a Hooke's Law spring with k= 50.0 N/m. See figure. In the initial figure, the speeds are known, and the spring is stretched 20.0 cm. In the final figure, the speeds are unknown, and the spring is compressed an unknown amount. Find vi, v2, and the final compression in the spring. You may assume that the system moves on a frictionless, horizontal plane, that system momentum is conserved, and that energy is conserved.
Related questions
Question
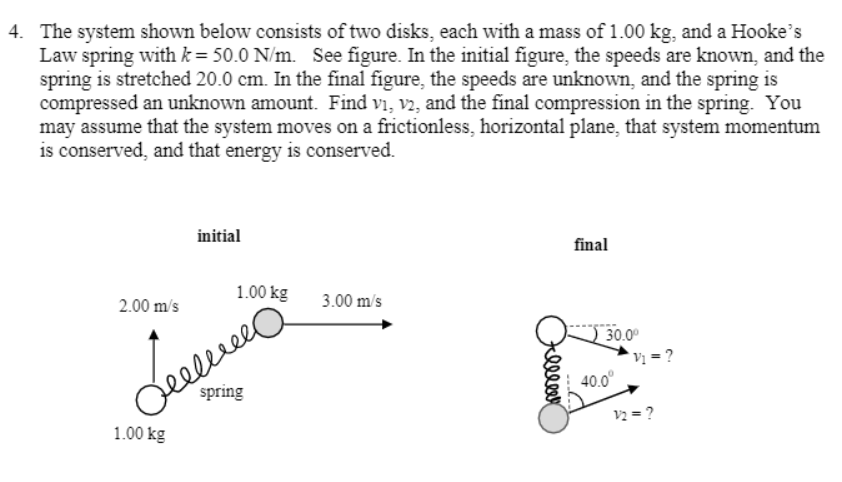
Transcribed Image Text:4. The system shown below consists of two disks, each with a mass of 1.00 kg, and a Hooke's
Law spring with k = 50.0 N/m. See figure. In the initial figure, the speeds are known, and the
spring is stretched 20.0 cm. In the final figure, the speeds are unknown, and the spring is
compressed an unknown amount. Find vi, v2, and the final compression in the spring. You
may assume that the system moves on a frictionless, horizontal plane, that system momentum
is conserved, and that energy is conserved.
initial
final
1.00 kg
deeleee
spring
2.00 m/s
3.00 m/s
30.00
Vị = ?
40.0°
1.00 kg
v2 = ?
kll
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps
