The uniform lamina L, shown shaded in Figure 2, is formed by removing the square PORV, of side 2a, and the square RSTU, of side 4a, from a uniform square lamina ABCD, of side 8a. The lines QRU and VRS are straight. The side AD is parallel to PV and the side AB is parallel to PQ. The distance between AD and PV is a and the distance between AB and PQ is a. The centre of mass of L is at the point G. 42 (a) Show that the distance of G from the side AD is a 11 (5) The mass of L is M. A particle of mass kM is attached to L at C. The lamina, with the attached particle, is freely suspended from B and hangs in equilibrium with BC making an angle of 45° with the horizontal. (b) Find the value of k.
The uniform lamina L, shown shaded in Figure 2, is formed by removing the square PORV, of side 2a, and the square RSTU, of side 4a, from a uniform square lamina ABCD, of side 8a. The lines QRU and VRS are straight. The side AD is parallel to PV and the side AB is parallel to PQ. The distance between AD and PV is a and the distance between AB and PQ is a. The centre of mass of L is at the point G. 42 (a) Show that the distance of G from the side AD is a 11 (5) The mass of L is M. A particle of mass kM is attached to L at C. The lamina, with the attached particle, is freely suspended from B and hangs in equilibrium with BC making an angle of 45° with the horizontal. (b) Find the value of k.
Related questions
Question
b please
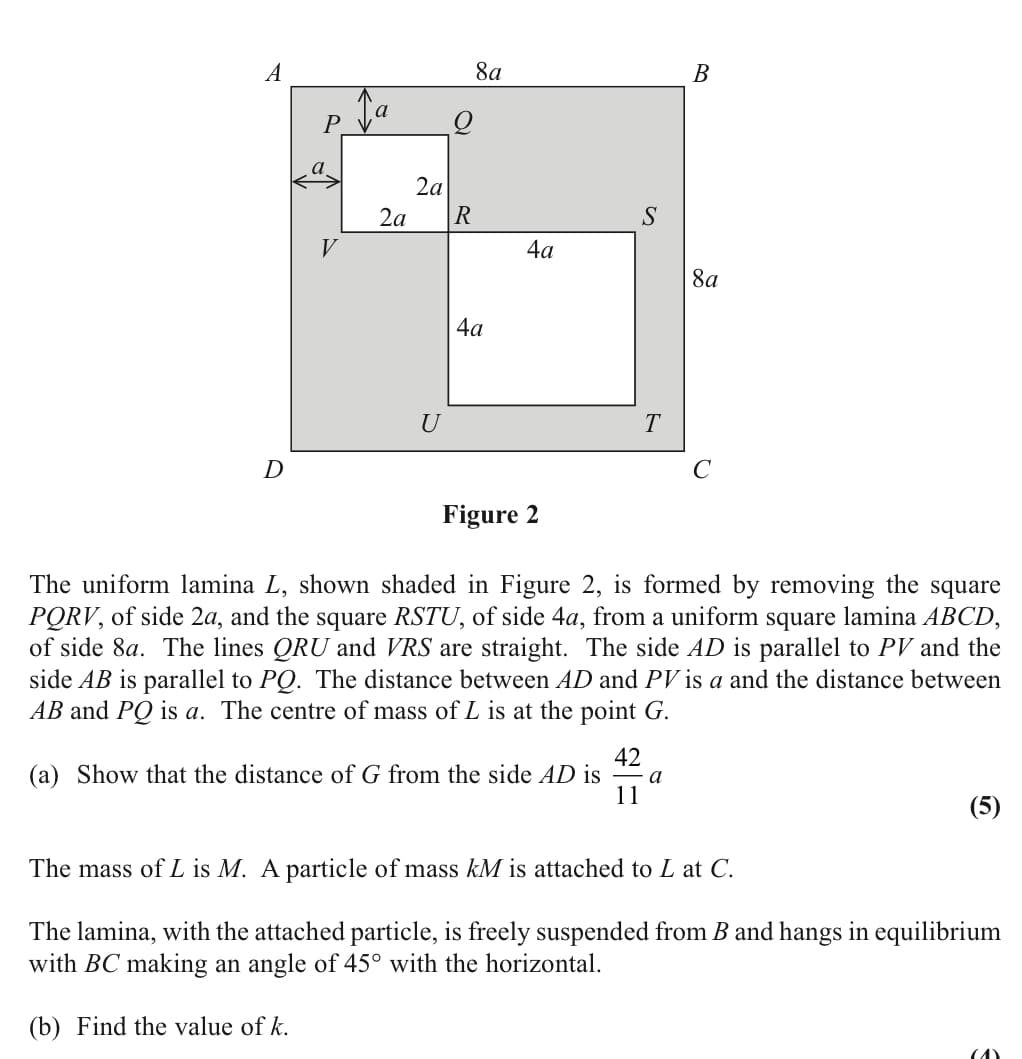
Transcribed Image Text:A
P
V
2a
2a
U
R
8a
4a
4a
S
B
8a
T
D
Figure 2
The uniform lamina L, shown shaded in Figure 2, is formed by removing the square
PORV, of side 2a, and the square RSTU, of side 4a, from a uniform square lamina ABCD,
of side 8a. The lines QRU and VRS are straight. The side AD is parallel to PV and the
side AB is parallel to PQ. The distance between AD and PV is a and the distance between
AB and PQ is a. The centre of mass of L is at the point G.
(a) Show that the distance of G from the side AD is a
42
11
(5)
The mass of L is M. A particle of mass kM is attached to L at C.
The lamina, with the attached particle, is freely suspended from B and hangs in equilibrium
with BC making an angle of 45° with the horizontal.
(b) Find the value of k.
(A)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images
