The wheels of a wagon can be approximated as the combination of a thin outer hoop of radius n= 0.156 m and mass 5.65 kg. and two thin crossed rods of mass 8.66 kg each. Imagine replacing the wagon wheels with uniform disks that are fa = 6.51 cm thick, made out of a material with a density of 7370 kg/m'. If the new wheel is to have the same moment of inertia about its center as the old wheel about its center, what should the radius of the disk be? m ra=
The wheels of a wagon can be approximated as the combination of a thin outer hoop of radius n= 0.156 m and mass 5.65 kg. and two thin crossed rods of mass 8.66 kg each. Imagine replacing the wagon wheels with uniform disks that are fa = 6.51 cm thick, made out of a material with a density of 7370 kg/m'. If the new wheel is to have the same moment of inertia about its center as the old wheel about its center, what should the radius of the disk be? m ra=
Related questions
Question
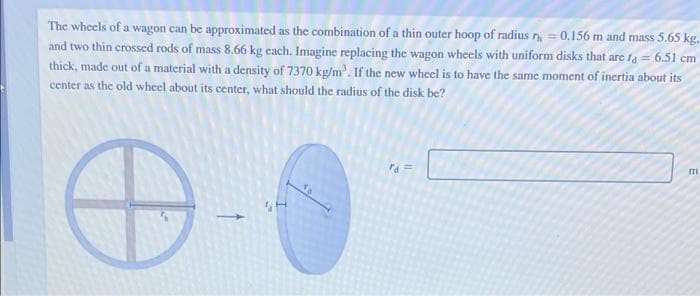
Transcribed Image Text:The wheels of a wagon can be approximated as the combination of a thin outer hoop of radius n = 0.156 m and mass 5.65 kg.
and two thin crossed rods of mass 8.66 kg cach. Imagine replacing the wagon wheels with uniform disks that are fa = 6.51 cm
thick, made out of a material with a density of 7370 kg/m'. If the new wheel is to have the same moment of inertia about its
center as the old wheel about its center, what should the radius of the disk be?
ra =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
