This problem is related to core exercise 31 (module 5) in the textbook, and reguires you to do some calculations. In this situation the line, l, below does not pass through the origin. Hence, we cannot use vector components to solve for the projection. You can use similar strategies to the ones used in core exercise 31 to find the projection. Let e have vector form = t and let a = -2.0 Then proj,ä 2.0 (Enter your answers in decimal format.)
This problem is related to core exercise 31 (module 5) in the textbook, and reguires you to do some calculations. In this situation the line, l, below does not pass through the origin. Hence, we cannot use vector components to solve for the projection. You can use similar strategies to the ones used in core exercise 31 to find the projection. Let e have vector form = t and let a = -2.0 Then proj,ä 2.0 (Enter your answers in decimal format.)
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305652224
Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Chapter7: Triangles
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RP: We mentioned in Section 7.5 that our algebraic treatment of vectors could be attributed, in part, to...
Related questions
Question
How to solve this question, As stated in the Q "We can not use
I have attached two images, one is the Question itself and second is my attempt on the Question. Please if you could share your working and reasoning behind it, also if you could show an geometric approach.
![vetor form of
a line
m: atab-diretion veutor
paralel to the
line
position vedor
a point on
he line
This is
Projeckion of
ã on line L
x-1-K.
purallel to
the line
"Y=1-X
Realize projection
of a is pavallel to
Ba well.
Approcuh :
1) Gind a restor ů parallel to line
2) ae projection fomula-
We khow that reetor is pavallel to line
projz =
[1]
(-2+C).
+ 1/52](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fc726bc00-9511-42a1-9a4e-883206405958%2Fddbfd676-e37c-4852-9b38-0559e0bd1b42%2F22vyzm_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:vetor form of
a line
m: atab-diretion veutor
paralel to the
line
position vedor
a point on
he line
This is
Projeckion of
ã on line L
x-1-K.
purallel to
the line
"Y=1-X
Realize projection
of a is pavallel to
Ba well.
Approcuh :
1) Gind a restor ů parallel to line
2) ae projection fomula-
We khow that reetor is pavallel to line
projz =
[1]
(-2+C).
+ 1/52
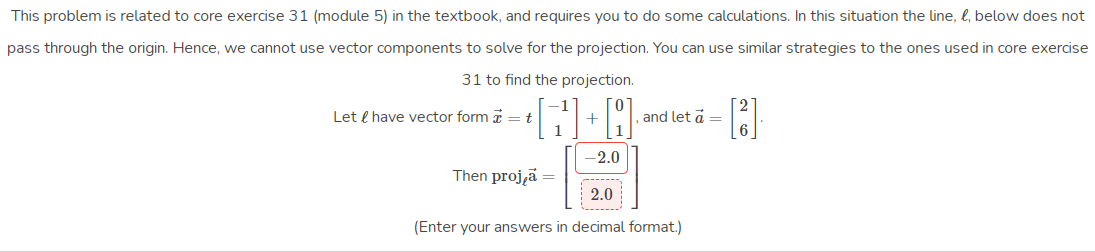
Transcribed Image Text:This problem is related to core exercise 31 (module 5) in the textbook, and reguires you to do some calculations. In this situation the line, l, below does not
pass through the origin. Hence, we cannot use vector components to solve for the projection. You can use similar strategies to the ones used in core exercise
31 to find the projection.
Let e have vector form = t
and let a =
-2.0
Then proj,ä
2.0
(Enter your answers in decimal format.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage