This work aims to investigate the equilibria, local stability, global attractivity and the exact solutions of the following difference equations Bun-1un-5 Un+1 = aun-1+ n = 0,1, ..., (1) YUn-3 - dun-5 Bun-1un-5 Un+1 = QUn-1 n = 0,1, ..., (2) %3D YUn-3 + dun-5 where the coefficients a, B, y, and & are positive real numbers and the initial con- ditions u; for all i = -5, -4, .., 0, are arbitrary non-zero real numbers. We also present the numerical solutions via some 2D graphs. 2. ON THE EQUATION Un+1 = aUn-1+ Bun-1un-5 yun-3-dun-5 This section is devoted to study the qualitative behaviors of Eq. (1). The equilibrium point of Eq. (1) is given by
This work aims to investigate the equilibria, local stability, global attractivity and the exact solutions of the following difference equations Bun-1un-5 Un+1 = aun-1+ n = 0,1, ..., (1) YUn-3 - dun-5 Bun-1un-5 Un+1 = QUn-1 n = 0,1, ..., (2) %3D YUn-3 + dun-5 where the coefficients a, B, y, and & are positive real numbers and the initial con- ditions u; for all i = -5, -4, .., 0, are arbitrary non-zero real numbers. We also present the numerical solutions via some 2D graphs. 2. ON THE EQUATION Un+1 = aUn-1+ Bun-1un-5 yun-3-dun-5 This section is devoted to study the qualitative behaviors of Eq. (1). The equilibrium point of Eq. (1) is given by
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter9: Systems Of Equations And Inequalities
Section9.1: Systems Of Equations
Problem 6E
Related questions
Question
Show me the steps of determine blue and all information is here

Transcribed Image Text:This work aims to investigate the equilibria, local stability, global attractivity
and the exact solutions of the following difference equations
Bun-1un-5
Un+1 = aUn-1+
n = 0,1, ..,
(1)
YUn-3 - dun-5'
Bun-1un-5
Un+1 = aUn-1-
n = 0,1, ..,
(2)
YUn-3 + dun-5'
where the coefficients a, B, y, and & are positive real numbers and the initial con-
ditions ui for all i = -5, -4, .., 0, are arbitrary non-zero real numbers. We also
present the numerical solutions via some 2D graphs.
2. ON THE EQUATION Un+1 = aUn-1 +
Bun-1un-5
Yun-3-dun-5
(1). The
This section is devoted to study the qualitative behaviors of Eq.
equilibrium point of Eq. (1) is given by
6. EXACT SOLUTION OF EQ. (1) WHEN a =
B=y= 8 = 1
In this section, we investigate the exact solutions of the following rational differ-
ence equation
Un-1un-5
Иn+1 — ит-1 +
n = 0, 1, ...,
(10)
Un-3 - Un-5
where the initial conditions are positive real numbers.
Theorem 5 Let {un}n=-5
be a solution to Eq. (10) and suppose that u-5 =
d, u-1 = e, uo = f. Then, for n = 0, 1,2, .., the
а, и-4 — б, и_з — с, и-2 —
solutions of Eq. (10) are given by the following formulas:
e2n c"
U8n-5 =
(c- e)"(a – c)n'
f2n d"
bn-1(d - f)"(b– d)n'
cn+le2n
n-1
U8n-4 =
U8n-3 =
a" (a – c)" (c – e)"'
dn+1 f2n
b" (b – d)" (d- f)"'
e2n+1cn
U8n-2 =
U8n-1 =
a" (a – c)"(c – e)* '
f2n+1gn
br (b – d)"(d – f)"'
cn+1 e2n+1
U8n
U8n+1
a" (c - e)" (a – c)n+1>
dn+1 f2n+1
b" (d – f)"(b – d)n+1*
U8n+2 =
Proof.
It can be easily observed that the solutions are true for n = 0. We now
assume that n > 0 and that our assumption holds for n – 1. That is,
e2n-2 cn-1
n-2(c – e)n-1(a – c)n-1'
f2n-2 an-1
b2-2 (d – f)n-1(b – d)a-I?
U8n-13 =
U8n-12 =
c"e2n-2
U8n-11
n-1(a - c)a-1(c – e)n–1'
an-1
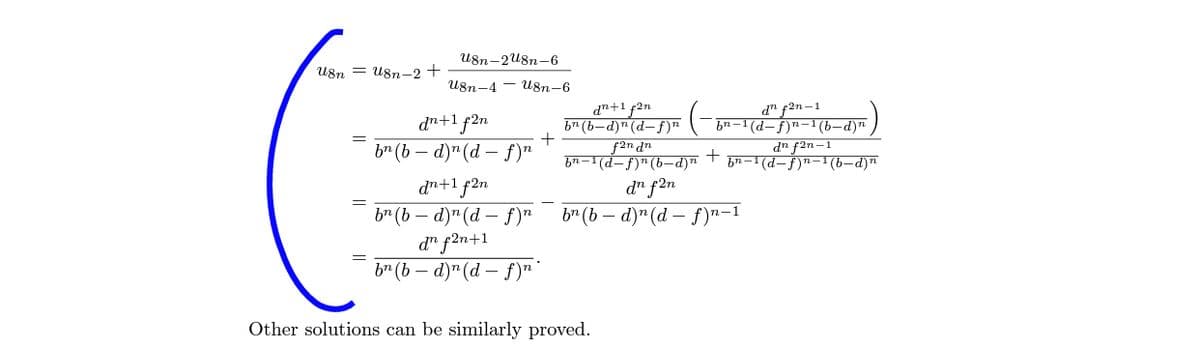
Transcribed Image Text:U8n-2u8n-6
U8n = U8n-2 +
U8n-4 - Ug8n-6
d" f2n-1
bn–1(d-f)n-1 (b-d)n
dn+1 f2n
dn+1 f2n
b" (b – d)" (d – f)"
b" (b-d)"(d- f)"
+
f2n dn
F)" (b-d)"
d" f2n
dn f2n-1
bn-1 (d-f)n-1 (b-d)"
bn-1(d
+
dn+1 f2n
b" (b – d)" (d – f)"
d" f2n+1
br (b – d)" (d – f)"*
br (b – d)"(d – f)n-1
Other solutions can be similarly proved.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage