Three forces are acting on a column and are concurrent at point A. The magnitudes of the forces are F1 = 300 N, F2= 200 N and F3 = 100 N. • The line of action of F1 runs from point A to B expressed in Cartesian coordinates. · F2 has an elevation angle of 30° from the x-y plane. The projection of F2 on the x-y plane has a 50° transverse angle from the (-) y-axis. F3 is expressed in coordinate direction angles of a3 = 45°, ß3 = 60°, with y3 > 90°. F2 B(-5, 3,2)mM 30°
Three forces are acting on a column and are concurrent at point A. The magnitudes of the forces are F1 = 300 N, F2= 200 N and F3 = 100 N. • The line of action of F1 runs from point A to B expressed in Cartesian coordinates. · F2 has an elevation angle of 30° from the x-y plane. The projection of F2 on the x-y plane has a 50° transverse angle from the (-) y-axis. F3 is expressed in coordinate direction angles of a3 = 45°, ß3 = 60°, with y3 > 90°. F2 B(-5, 3,2)mM 30°
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter2: Basic Operations With Force Systems
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.104RP: The three forces of magnitude P can be replaced by a single, equivalent force R acting at point A....
Related questions
Question
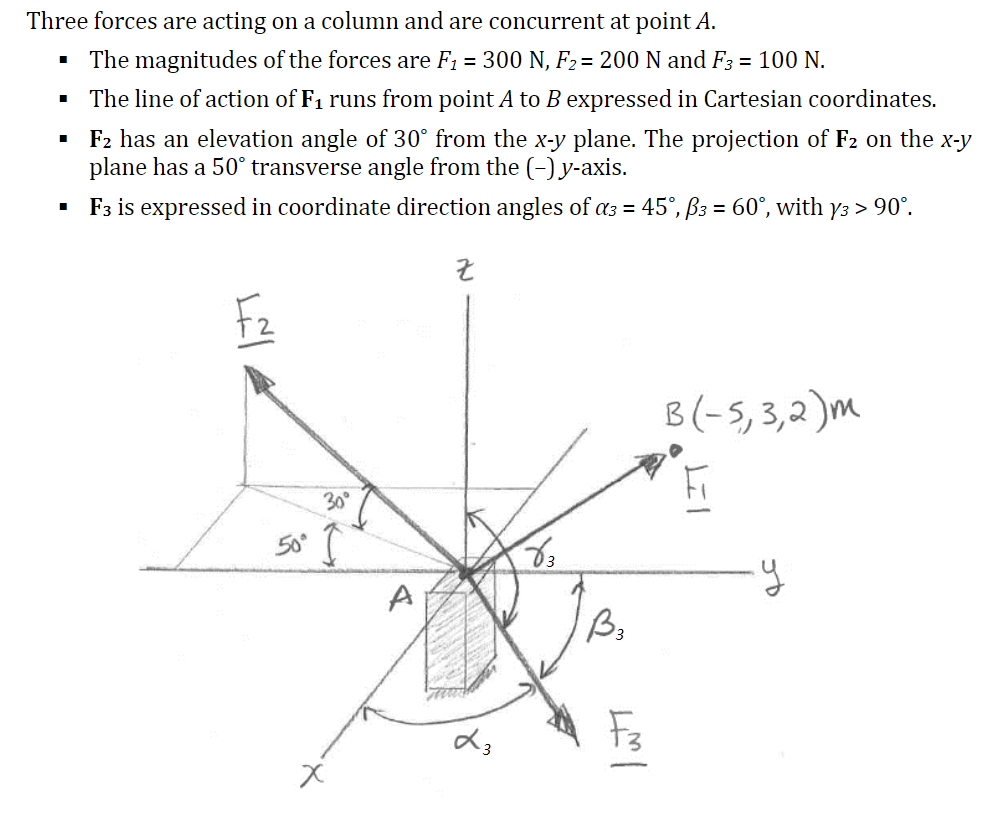
Transcribed Image Text:Three forces are acting on a column and are concurrent at point A.
• The magnitudes of the forces are F1 = 300 N, F2= 200N and F3 = 100 N.
• The line of action of F1 runs from point A to B expressed in Cartesian coordinates.
· F2 has an elevation angle of 30° from the x-y plane. The projection of F2 on the x-y
plane has a 50° transverse angle from the (-)y-axis.
F3 is expressed in coordinate direction angles of a3 = 45°, ß3 = 60°, with
Y3 > 90°.
Fz
B(-5,3,2)m
30°
A
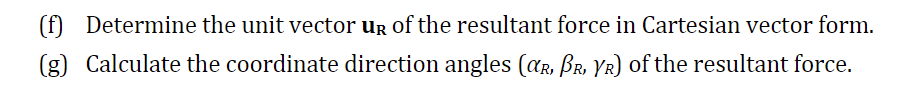
Transcribed Image Text:(f) Determine the unit vector uR of the resultant force in Cartesian vector form.
(g) Calculate the coordinate direction angles (ar, Br, YR) of the resultant force.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L