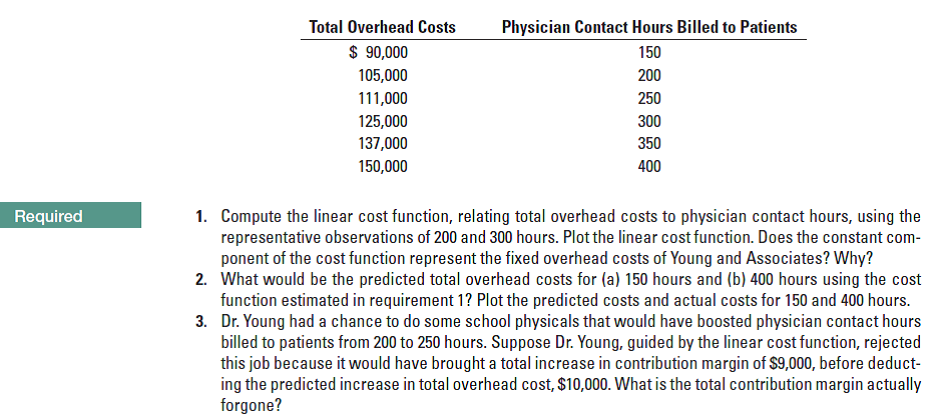
Total Overhead Costs Physician Contact Hours Billed to Patients $ 90,000 150 105,000 200 111,000 250 125,000 300 137,000 350 150,000 400 1. Compute the linear cost function, relating total overhead costs to physician contact hours, using the representative observations of 200 and 300 hours. Plot the linear cost function. Does the constant com- ponent of the cost function represent the fixed overhead costs of Young and Associates? Why? 2. What would be the predicted total overhead costs for (a) 150 hours and (b) 400 hours using the cost function estimated in requirement 1? Plot the predicted costs and actual costs for 150 and 400 hours. 3. Dr. Young had a chance to do some school physicals that would have boosted physician contact hours billed to patients from 200 to 250 hours. Suppose Dr. Young, guided by the linear cost function, rejected this job because it would have brought a total increase in contribution margin of $9,000, before deduct- ing the predicted increase in total overhead cost, $10,000. What is the total contribution margin actually forgone? Required
Total Overhead Costs Physician Contact Hours Billed to Patients $ 90,000 150 105,000 200 111,000 250 125,000 300 137,000 350 150,000 400 1. Compute the linear cost function, relating total overhead costs to physician contact hours, using the representative observations of 200 and 300 hours. Plot the linear cost function. Does the constant com- ponent of the cost function represent the fixed overhead costs of Young and Associates? Why? 2. What would be the predicted total overhead costs for (a) 150 hours and (b) 400 hours using the cost function estimated in requirement 1? Plot the predicted costs and actual costs for 150 and 400 hours. 3. Dr. Young had a chance to do some school physicals that would have boosted physician contact hours billed to patients from 200 to 250 hours. Suppose Dr. Young, guided by the linear cost function, rejected this job because it would have brought a total increase in contribution margin of $9,000, before deduct- ing the predicted increase in total overhead cost, $10,000. What is the total contribution margin actually forgone? Required
Chapter1: Financial Statements And Business Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1Q
Related questions
Question
Linear cost approximation. Dr. Young, of Young and Associates, LLP, is examining how
Transcribed Image Text:Total Overhead Costs
Physician Contact Hours Billed to Patients
$ 90,000
150
105,000
200
111,000
250
125,000
300
137,000
350
150,000
400
1. Compute the linear cost function, relating total overhead costs to physician contact hours, using the
representative observations of 200 and 300 hours. Plot the linear cost function. Does the constant com-
ponent of the cost function represent the fixed overhead costs of Young and Associates? Why?
2. What would be the predicted total overhead costs for (a) 150 hours and (b) 400 hours using the cost
function estimated in requirement 1? Plot the predicted costs and actual costs for 150 and 400 hours.
3. Dr. Young had a chance to do some school physicals that would have boosted physician contact hours
billed to patients from 200 to 250 hours. Suppose Dr. Young, guided by the linear cost function, rejected
this job because it would have brought a total increase in contribution margin of $9,000, before deduct-
ing the predicted increase in total overhead cost, $10,000. What is the total contribution margin actually
forgone?
Required
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 8 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272094
Author:
WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337619202
Author:
Hall, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272094
Author:
WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337619202
Author:
Hall, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis…
Accounting
ISBN:
9780134475585
Author:
Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:
PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781259722660
Author:
J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781259726705
Author:
John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education