Transfer pricing, perfect and imperfect markets. Letang Company has three divisions (R, S, and T), organized as decentralized profit centers. Division R produces the basic chemical Ranbax, in multiples of 1,000 pounds, and transfers it to divisions S and T. Division S processes Ranbax into the final product Syntex, and division T processes Ranbax into the final product Termix. No material is lost during processing. Division R has no fixed costs. The variable cost per pound of Ranbax is $0.18. Division R has a capacity limit of 10,000 pounds. Divisions S and T have capacity limits of 4,000 and 6,000 pounds, respectively. Divi- sions S and T sell their final product in separate markets. The company keeps no inventories of any kind. The cumulative net revenues (i.e., total revenues – total processing costs) for divisions S and T at vari- ous output levels are summarized below. Division S Pounds of Ranbax processed in S Total net revenues ($) from sale of Syntex 4,000 $1,100 $1,200 1,000 2,000 3,000 $ 500 $ 850 Division T Pounds of Ranbax processed in T Total net revenues ($) from sale of Termix $600 6,000 $2,350 1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 $1,800 $2,100 $2,250 5,000 $1,200
Transfer pricing, perfect and imperfect markets. Letang Company has three divisions (R, S, and T), organized as decentralized profit centers. Division R produces the basic chemical Ranbax, in multiples of 1,000 pounds, and transfers it to divisions S and T. Division S processes Ranbax into the final product Syntex, and division T processes Ranbax into the final product Termix. No material is lost during processing. Division R has no fixed costs. The variable cost per pound of Ranbax is $0.18. Division R has a capacity limit of 10,000 pounds. Divisions S and T have capacity limits of 4,000 and 6,000 pounds, respectively. Divi- sions S and T sell their final product in separate markets. The company keeps no inventories of any kind. The cumulative net revenues (i.e., total revenues – total processing costs) for divisions S and T at vari- ous output levels are summarized below. Division S Pounds of Ranbax processed in S Total net revenues ($) from sale of Syntex 4,000 $1,100 $1,200 1,000 2,000 3,000 $ 500 $ 850 Division T Pounds of Ranbax processed in T Total net revenues ($) from sale of Termix $600 6,000 $2,350 1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 $1,800 $2,100 $2,250 5,000 $1,200
Managerial Accounting
15th Edition
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Chapter10: Evaluating Decentralized Operations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4CMA: Morrisons Plastics Division, a profit center, sells its products to external customers as well as to...
Related questions
Question
What range of transfer prices will motivate divisions S and T to demand the quantities that maximize overall income , as well as motivate division R to produce the sum of those quantities?
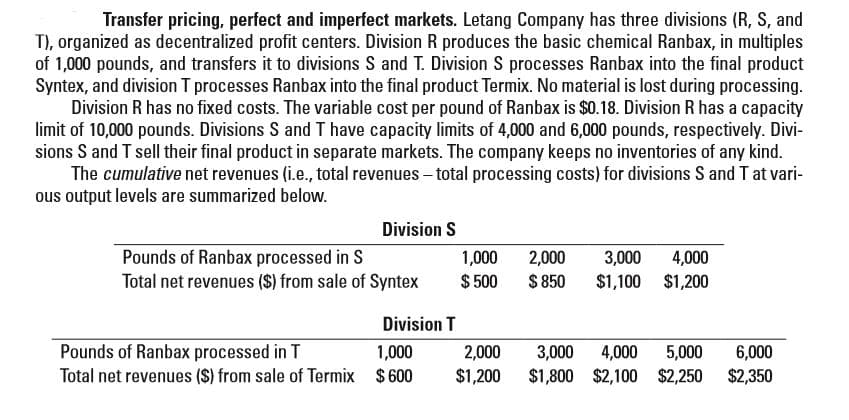
Transcribed Image Text:Transfer pricing, perfect and imperfect markets. Letang Company has three divisions (R, S, and
T), organized as decentralized profit centers. Division R produces the basic chemical Ranbax, in multiples
of 1,000 pounds, and transfers it to divisions S and T. Division S processes Ranbax into the final product
Syntex, and division T processes Ranbax into the final product Termix. No material is lost during processing.
Division R has no fixed costs. The variable cost per pound of Ranbax is $0.18. Division R has a capacity
limit of 10,000 pounds. Divisions S and T have capacity limits of 4,000 and 6,000 pounds, respectively. Divi-
sions S and T sell their final product in separate markets. The company keeps no inventories of any kind.
The cumulative net revenues (i.e., total revenues – total processing costs) for divisions S and T at vari-
ous output levels are summarized below.
Division S
Pounds of Ranbax processed in S
Total net revenues ($) from sale of Syntex
4,000
$1,100 $1,200
1,000
2,000
3,000
$ 500
$ 850
Division T
Pounds of Ranbax processed in T
Total net revenues ($) from sale of Termix $600
6,000
$2,350
1,000
2,000
3,000 4,000
$1,800 $2,100 $2,250
5,000
$1,200
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337912020
Author:
Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,