(u1, u2, u3) and v = (v1, v2, v3) in R such that < u, v >= 2u1v +2uzv2 + 3uzv3. If u = (5, –1,3) and v = (2, k, –2) are orthogonal, then k = %3D %3D %3D A) 2 В) 1 С) -8 D) 4
(u1, u2, u3) and v = (v1, v2, v3) in R such that < u, v >= 2u1v +2uzv2 + 3uzv3. If u = (5, –1,3) and v = (2, k, –2) are orthogonal, then k = %3D %3D %3D A) 2 В) 1 С) -8 D) 4
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter7: Distance And Approximation
Section7.1: Inner Product Spaces
Problem 7EQ
Related questions
Question
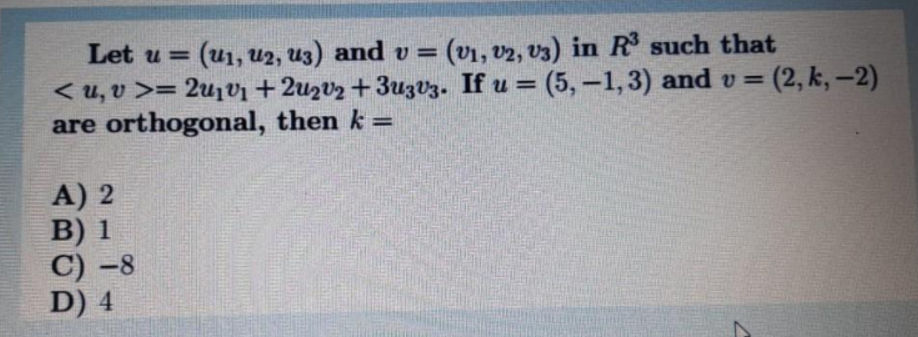
Transcribed Image Text:Let u = (u1, U2, U3) and v = (v1, v2, v3) in R such that
< u, v >= 2u1vi + 2uzvz + 3uzV3. If u = (5,-1,3) and v =
are orthogonal, then k =
%3D
3(2,k,-2)
A) 2
В) 1
С) -8
D) 4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning