us at the +x 5 ble at the The functions in Exercises 21-26 are defined for all x except for one value of x. If possible, define f(x) at the exceptional point in a way that makes f(x) continuous for all .x. x²7x+10 21. f(x) = x-5 x²+x-12 x+4 x3 - 5x2 +4 x² x² +25 X-5+X5 (6 + x)² - 36 X √9+x-√9 26. f(x) = x 0 X 27. Computing Income Tax The tax that you pay to the federal government is a percentage of your taxable income, which is what remains of your gross income after you subtract your 22. f(x) = 23. f(x) = 24. f(x) = x5 25. f(x)= x = -4 **0 **0
us at the +x 5 ble at the The functions in Exercises 21-26 are defined for all x except for one value of x. If possible, define f(x) at the exceptional point in a way that makes f(x) continuous for all .x. x²7x+10 21. f(x) = x-5 x²+x-12 x+4 x3 - 5x2 +4 x² x² +25 X-5+X5 (6 + x)² - 36 X √9+x-√9 26. f(x) = x 0 X 27. Computing Income Tax The tax that you pay to the federal government is a percentage of your taxable income, which is what remains of your gross income after you subtract your 22. f(x) = 23. f(x) = 24. f(x) = x5 25. f(x)= x = -4 **0 **0
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter3: Functions And Graphs
Section3.4: Definition Of Function
Problem 16E
Related questions
Question
21,23 and 29 please

Transcribed Image Text:EXERCISES 1.5
Is the function, whose graph is drawn in Fig. 7, continuous at the
following values of x?
-5 -4 -3 -2
Figure 7
1. x = 0
4. x = .001
15. f(x) =
16. f(x) =
[x³
18. f(x) =
^
Is the function, whose graph is drawn in Fig. 7, differentiable at the
following values of x?
7. x = 0
10. x = .001
17. f(x) = {1
ƒ(x) = { 2
(x+2 for-1 ≤x≤1
(3x
for 1 < x≤ 5
Determine whether each of the following functions is continuous
and/or differentiable at x = 1.
13. f(x) = x²
19. f(x)=x
2. x=-3
5. x = -2
[2x-1 for 0≤x≤1
for 1 < x
20. f(x) = 1
8. x = -3
11. x = -2
for 0≤x<1
for 1 ≤ x ≤ 2
x-1
for x 1
for x = 1
(2x-2
1
2
14. f(x)=
=
for x
1
for x = 1
for 0 ≤ x < 1
for x = 1
for x>1
3 4
3. x = 3
6. x = 2
9. x = 3
12. x = 2
+x
5
X
The functions in Exercises 21-26 are defined for all x except for
one value of x. If possible, define f(x) at the exceptional point in a
way that makes f(x) continuous for all x.
21. f(x)=
=
22. f(x)=
23. f(x)
24. f(x)=
-
25. f(x) =
x²7x+10
x-5
x5
x²+x-12
x +4
x3 - 5x2 +4
x²
x² +25
X-5x5
-,x-4
(6 + x)² - 36
x0
x0
X
26. f(x) =
√9+x-√9
x0
X
27. Computing Income Tax The tax that you pay to the federal
government is a percentage of your taxable income, which is
what remains of your gross income after you subtract your
allowed deductions. In a recent year, there were five rates or
brackets for a single taxpayer, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Single Taxpayer Rates
But Not Over
Amount Over
SO
$27,050
$27,050
$65,550
$65,550
$136,750
$136,750
$297,350
$297,350
Tax Rate
15%
27.5%
30.5%
35.5%
39.1%
So, if you are single and your taxable income was less
than $27,050, your tax is your taxable income times 15%
(.15). The maximum amount of tax that you will pay on
your income in this first bracket is 15% of $27,050, or
(15) X 27,050 4057.50 dollars. If your taxable income
is more than $27,050 but less than $65,550, your tax is
$4057.50 plus 27.5% of the amount in excess of $27,050. So,
for example, if your taxable income is $50,000, your tax is
4057.5+275(50,000 -27,050) = 4057.5+275 x 22,950 =
$10,368.75. Let x denote your taxable income and 7(x)
your tax.
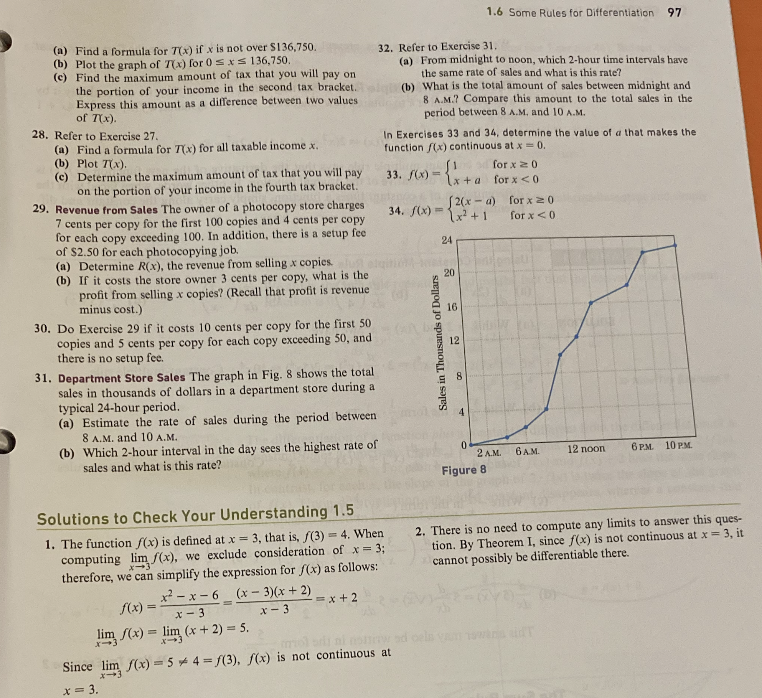
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Find a formula for 7(x) if x is not over $136,750.
(b) Plot the graph of 7(x) for 0≤x≤ 136,750.
(c) Find the maximum amount of tax that you will pay on
the portion of your income in the second tax bracket..
Express this amount as a difference between two values
of 7(x).
28. Refer to Exercise 27.
(a) Find a formula for 7(x) for all taxable income x.
(b) Plot 7(x).
(c) Determine the maximum amount of tax that you will pay
on the portion of your income in the fourth tax bracket.
29. Revenue from Sales The owner of a photocopy store charges
7 cents per copy for the first 100 copies and 4 cents per copy
for each copy exceeding 100. In addition, there is a setup fee
of $2.50 for each photocopying job.
(a) Determine R(x), the revenue from selling x copies.
(b) If it costs the store owner 3 cents per copy, what is the
profit from selling x copies? (Recall that profit is revenue
minus cost.)
30. Do Exercise 29 if it costs 10 cents per copy for the first 50
copies and 5 cents per copy for each copy exceeding 50, and
there is no setup fee.
31. Department Store Sales The graph in Fig. 8 shows the total
sales in thousands of dollars in a department store during a
typical 24-hour period.
(a) Estimate the rate of sales during the period between
8 A.M. and 10 A.
(b) Which 2-hour interval in the day sees the highest rate of
sales and what is this rate?
Solutions to Check Your Understanding 1.5
1. The function f(x) is defined at x = 3, that is, f(3) = 4. When
computing lim f(x), we exclude consideration of x = 3;
therefore, we can simplify the expression for f(x) as follows:
x-3
(x-3)(x + 2)
x-3
x²-x-6
f(x)
x-3
lim /(x) = lim (x + 2) = 5.
=
32. Refer to Exercise 31.
(a) From midnight to noon, which 2-hour time intervals have
the same rate of sales and what is this rate?
=x+2
(b) What is the total amount of sales between midnight and
8 A.M.? Compare this amount to the total sales in the
period between 8 A.M. and 10 A.M.
In Exercises 33 and 34, determine the value of a that makes the
function f(x) continuous at x = 0.
[1 for x ≥ 0
33. f(x)=x+a for x < 0
Since lim f(x) = 5*4=f(3), f(x) is not continuous at
x-
x = 3.
[2(x-a)
34. f(x)=x²+1
Sales in Thousands of Dollars
24
20
16
1.6 Some Rules for Differentiation 97
12
8
4
0
2 A.M.
Figure 8
for x 20
for x < 0
6 A.M.
12 noon
6 PM. 10 PM.
2. There is no need to compute any limits to answer this ques-
tion. By Theorem I, since f(x) is not continuous at x = 3, it
cannot possibly be differentiable there.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning