Use the D’Alembert's principle to determine (Showing the free body diagrams and all steps of your solution): A. The expression of the acceleration of the two masses in terms of M1 and M2. B. The tension in the rope in terms of M1 and M2. C. If M1 = 30 kg, M2 = 10 kg, determine the acceleration of two blocks and the tension in the rope. (Taking in consideration that the gravitational acceleration, g = 9.81 m/s²). D. If M2 is reduced to 5 kg and Mị remains the same (30 kg) what will be the new acceleration. How does the amount of mass M2 affect the acceleration? Repeat the problem if Mı= 15 kg and M2=10 kg. What do you conclude.
Use the D’Alembert's principle to determine (Showing the free body diagrams and all steps of your solution): A. The expression of the acceleration of the two masses in terms of M1 and M2. B. The tension in the rope in terms of M1 and M2. C. If M1 = 30 kg, M2 = 10 kg, determine the acceleration of two blocks and the tension in the rope. (Taking in consideration that the gravitational acceleration, g = 9.81 m/s²). D. If M2 is reduced to 5 kg and Mị remains the same (30 kg) what will be the new acceleration. How does the amount of mass M2 affect the acceleration? Repeat the problem if Mı= 15 kg and M2=10 kg. What do you conclude.
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter7: Dry Friction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.79P: The coefficient of rolling resistance between the 30-kg lawn roller and the ground is r=0.1. (a)...
Related questions
Question
D
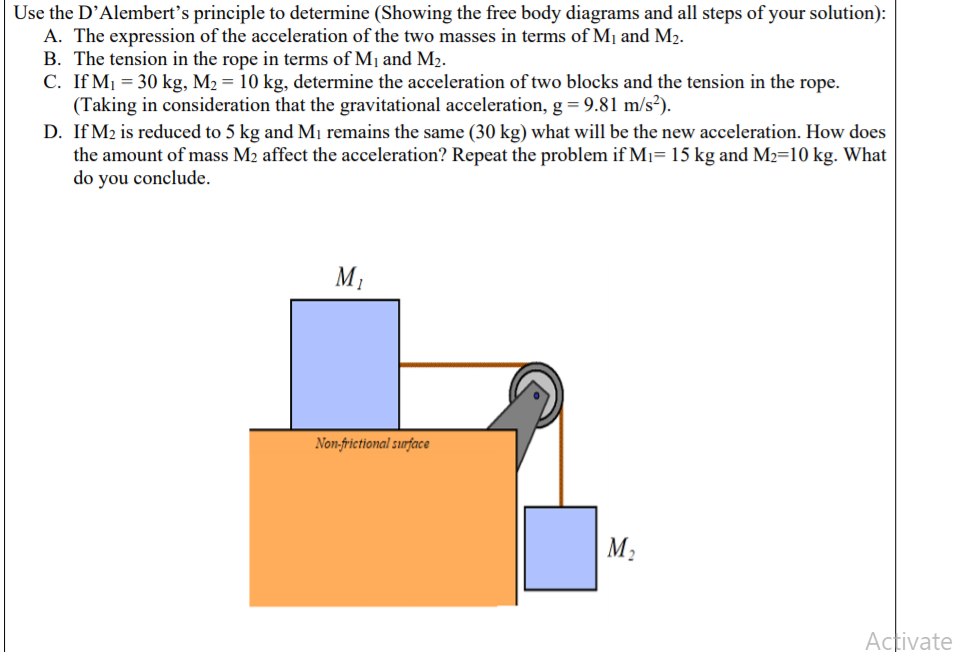
Transcribed Image Text:Use the D'Alembert's principle to determine (Showing the free body diagrams and all steps of your solution):
A. The expression of the acceleration of the two masses in terms of M1 and M2.
B. The tension in the rope in terms of M¡ and M2.
C. If M1 = 30 kg, M2 = 10 kg, determine the acceleration of two blocks and the tension in the rope.
(Taking in consideration that the gravitational acceleration, g = 9.81 m/s²).
D. If M2 is reduced to 5 kg and Mı remains the same (30 kg) what will be the new acceleration. How does
the amount of mass M2 affect the acceleration? Repeat the problem if Mı= 15 kg and M2=10 kg. What
do you conclude.
Non-frictional surface
M2
Activate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L