Use the figure below to estimate the indicated derivatives, or state that they do not exist. If a derivative does not exist, enter dne in the answer blank. The graph of f(x) is black and has a sharp corner at x = 2. The graph of g(x) is blue. 1.0 4,0 F1 Let h(x) = f(x) · g(x). Find A. h'(1) = B. h' (2) = C. h' (3) = %3D
Use the figure below to estimate the indicated derivatives, or state that they do not exist. If a derivative does not exist, enter dne in the answer blank. The graph of f(x) is black and has a sharp corner at x = 2. The graph of g(x) is blue. 1.0 4,0 F1 Let h(x) = f(x) · g(x). Find A. h'(1) = B. h' (2) = C. h' (3) = %3D
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Chapter1: Functions
Section1.2: Functions Given By Tables
Problem 32SBE: Does a Limiting Value Occur? A rocket ship is flying away from Earth at a constant velocity, and it...
Related questions
Question
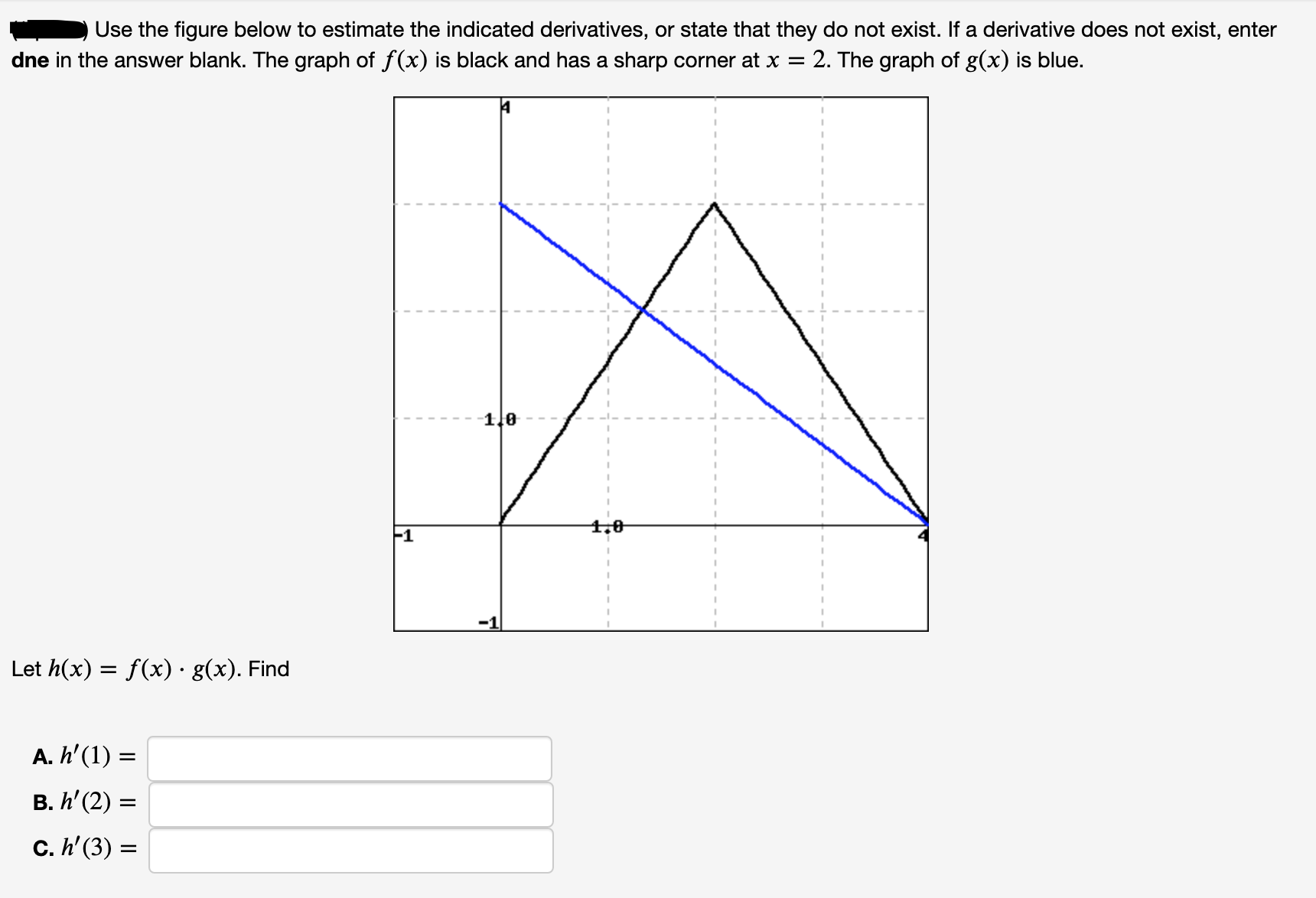
Transcribed Image Text:Use the figure below to estimate the indicated derivatives, or state that they do not exist. If a derivative does not exist, enter
dne in the answer blank. The graph of f(x) is black and has a sharp corner at x =
2. The graph of g(x) is blue.
1.0
4,0
F1
Let h(x) = f(x) · g(x). Find
A. h'(1) =
B. h' (2) =
C. h' (3) =
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning