Use the "mixed partials" check to see if the following differential equation is exact. If it is exact find a function F(x,y) whose differential, dF(x, y) is the left hand side of the differential equation. That is, level curves F(x, y) = C are solutions to the differential equation: (-4x2 – 3y)dx + (-3x – 4y²)dy = 0 First: M,(x, y) = -3 and N(x, y) = -3 If the equation is not exact, enter not exact, otherwise enter in F(x, y) here
Use the "mixed partials" check to see if the following differential equation is exact. If it is exact find a function F(x,y) whose differential, dF(x, y) is the left hand side of the differential equation. That is, level curves F(x, y) = C are solutions to the differential equation: (-4x2 – 3y)dx + (-3x – 4y²)dy = 0 First: M,(x, y) = -3 and N(x, y) = -3 If the equation is not exact, enter not exact, otherwise enter in F(x, y) here
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter4: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section4.6: Applications And The Perron-frobenius Theorem
Problem 69EQ: Let x=x(t) be a twice-differentiable function and consider the second order differential equation...
Related questions
Question
What is the exact equation
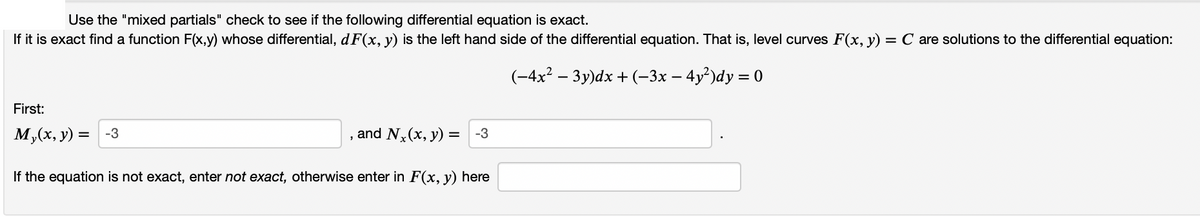
Transcribed Image Text:Use the "mixed partials" check to see if the following differential equation is exact.
If it is exact find a function F(x,y) whose differential, d F(x, y) is the left hand side of the differential equation. That is, level curves F(x, y) = C are solutions to the differential equation:
(-4x² – 3y)dx + (-3x – 4y²)dy = 0
First:
M,(x, y) = -3
and N,(x, y) = -3
If the equation is not exact, enter not exact, otherwise enter in F(x, y) here
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning