Use the table defining f and g to solve: NOTE: Write Does not exist if the value does not exist. a) (f - g)(4) = b) (f + g)(4) - (g- f)(7) = c) › (4) (4) = [ x f(x) g(x) 3 1 -3 4 -1 -4 5 -5 -2 6 0 1 7 -1 -3
Use the table defining f and g to solve: NOTE: Write Does not exist if the value does not exist. a) (f - g)(4) = b) (f + g)(4) - (g- f)(7) = c) › (4) (4) = [ x f(x) g(x) 3 1 -3 4 -1 -4 5 -5 -2 6 0 1 7 -1 -3
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter5: Inverse, Exponential, And Logarithmic Functions
Section5.3: The Natural Exponential Function
Problem 50E
Related questions
Question
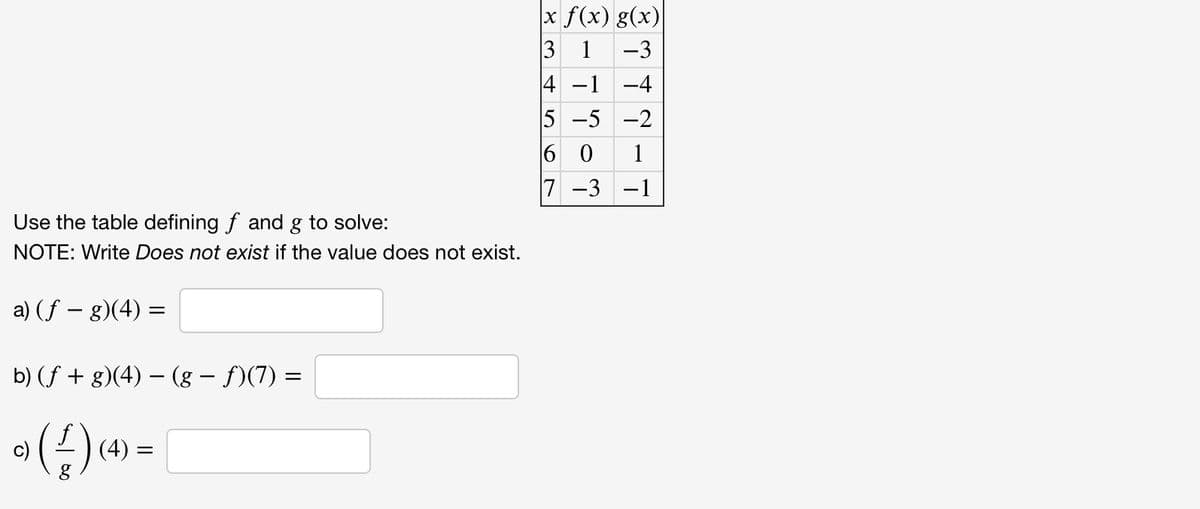
Transcribed Image Text:Use the table defining f and g to solve:
NOTE: Write Does not exist if the value does not exist.
a) (f = g)(4) =
b) (ƒ + g)(4) − (g — ƒ)(7)
°) (¹) (4) =
c)
=
x f(x) g(x)
3 1 -3
4 -1
-4
5
-5
-2
60
7 -3 -1
- T
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage